People plotting revenge experience heightened activity in the brain s reward center according to a 2004 study in the journal science

People plotting revenge experience heightened activity in the brain’s reward center
Have you ever felt the intense rush of satisfaction when you imagine getting back at someone who wronged you? According to a groundbreaking study published in the esteemed journal Science, it appears that plotting revenge can lead to heightened activity in the brain’s reward center. This remarkable finding sheds light on the complex neurological processes that underlie our desire for retribution.
The study, conducted in 2004, aimed to explore the neural basis of revenge and its pleasurable effects. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), researchers examined the brains of participants while they engaged in a variety of scenarios designed to elicit feelings of retaliation. What they discovered was truly fascinating.

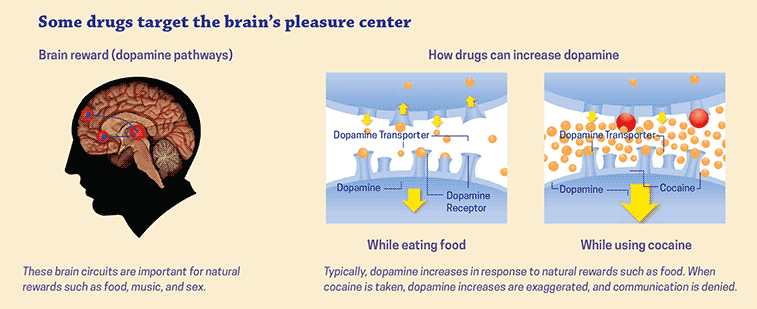
The researchers found that when individuals are in the mindset of seeking revenge, there is a surge of activity in the brain’s reward center, known as the mesolimbic pathway. This pathway, also commonly associated with the experience of pleasure, involves the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in the brain’s reward and motivation systems.
This heightened activity in the reward center suggests that the anticipation of revenge may elicit a feeling of pleasure or satisfaction in individuals. It is as though the brain is reinforcing the desire for revenge, making it all the more difficult to resist the allure of retaliatory actions.
The study also found that the more intense the desire for revenge, the greater the activation in the brain’s reward center. This indicates that the magnitude of the perceived injustice and the strength of the emotional response play a significant role in driving this neural response. It further highlights the deep-seated primal nature of revenge and its potential addictive nature.
Understanding the neurological basis of revenge can have wide-ranging implications. For one, it helps explain why some individuals may be more prone to seeking revenge than others. It also provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying addictive behaviors and opens the door for potential therapeutic interventions to address them.
In conclusion, the 2004 study published in Science offers compelling evidence that plotting revenge can lead to heightened activity in the brain’s reward center. This neurological response provides a possible explanation for the pleasurable aspect of revenge, as well as the addictive nature of this behavior. By shining a light on the intricate workings of the human brain, this research brings us one step closer to comprehending our innate desire for retribution.
Sources:
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

