Peeing after having sex prevents you from catching urinary tract infections

Does Peeing After Sex Prevent Urinary Tract Infections?

Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be unpleasant and sometimes painful. They occur when bacteria enter the urethra and multiply in the urinary tract. While anyone can develop a UTI, women tend to be more prone to them due to their anatomical structure.
One widely spread fact that many have heard is that peeing after sex can help prevent UTIs. But is this statement based on scientific evidence or just a mere myth? Let’s dive deeper into the topic and explore the relationship between peeing after sex and UTI prevention.
The Link Between Sex and UTIs
Before we understand the connection between peeing and UTIs, let’s briefly discuss how sex can lead to these infections. During sexual activity, the urethra—the tube connecting the bladder to the external genitalia—can come into contact with bacteria from the genital area. These bacteria can then migrate up the urethra and cause infection.
The Theory Behind Peeing After Sex
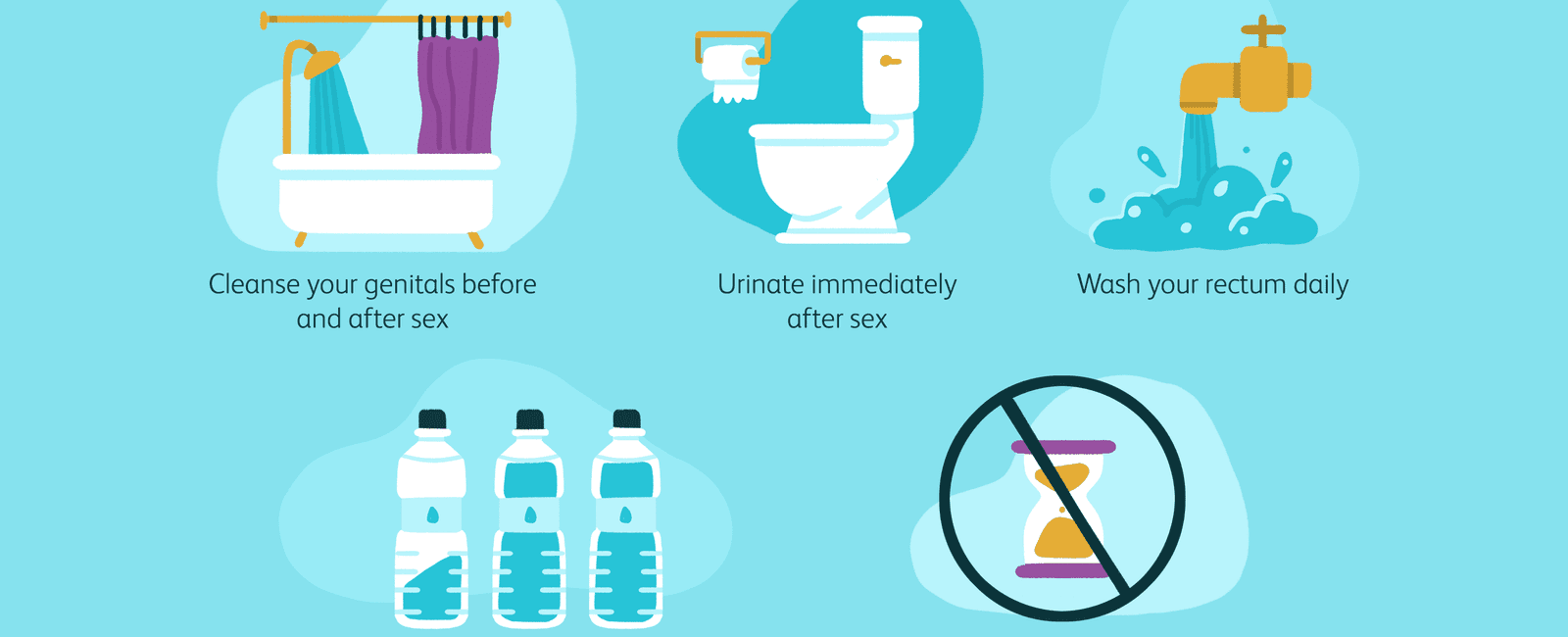
The notion that peeing after sex can reduce the risk of UTIs is based on the idea that urinating helps flush out any potentially harmful bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity. By voiding the bladder, it is believed that one can effectively clear away any bacteria lingering in the urinary tract.
Scientific Evidence and Expert Opinions
While anecdotal evidence often supports the claim that peeing after sex can prevent UTIs, what does the scientific community say about it?
A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine shed light on this matter. The research investigated the impact of postcoital voiding on UTI prevention. It concluded that women who urinated within an hour after having sex experienced a reduced risk of developing a UTI compared to those who didn’t.
Experts explain that peeing helps eliminate any bacteria that may have entered the urethra during intercourse. The action of urinating essentially flushes out these bacteria, preventing them from colonizing and causing an infection. However, it’s worth noting that peeing alone may not entirely eliminate the risk. Other preventive measures, such as proper genital hygiene and avoiding irritating substances, also play a significant role.
Additional Tips for Preventing UTIs
Besides peeing after sex, adopting certain lifestyle habits can further reduce the risk of UTIs:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Urinate regularly: Don’t hold in urine for an extended period as it allows bacteria to multiply in the bladder.
- Wipe correctly: After using the toilet, always wipe front to back to prevent spreading bacteria from the anus to the urethra.
- Wear breathable clothing: Choose underwear made of natural fabrics like cotton and avoid tight-fitting pants to keep the genital area dry and bacteria-free.
Conclusion
Peeing after sex is a widely recommended practice to decrease the risk of urinary tract infections in women. Scientific evidence suggests that this simple act helps flush out bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity. However, it’s essential to note that additional preventive measures, such as proper genital hygiene and staying hydrated, also contribute to UTI prevention.
Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice regarding your individual circumstances. By being proactive and implementing these preventive measures, you can potentially minimize your chances of developing a UTI and maintain optimal urinary tract health.
Source: MedicalNewsToday
Tags
Share
Table Of Contents
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

