Male testosterone levels and sperm counts are only a quarter of what they were a century ago
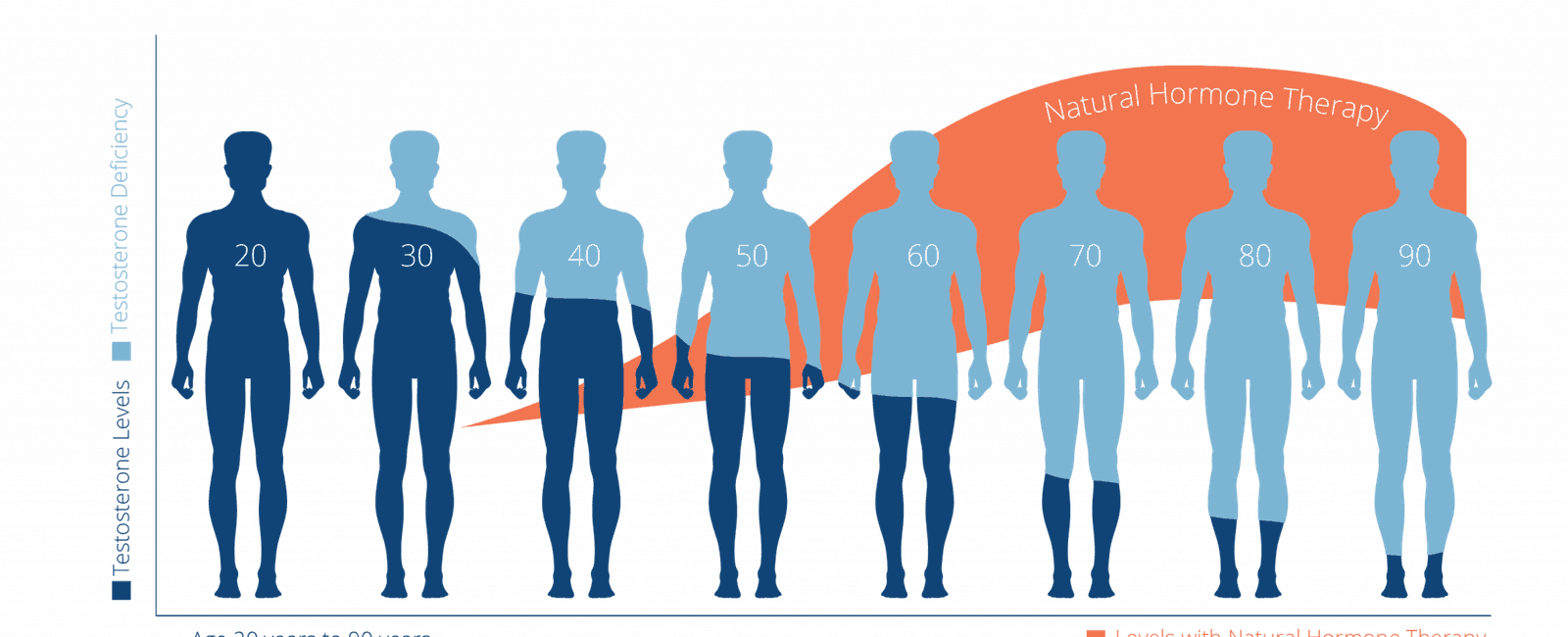

Male Testosterone Levels and Sperm Counts: A Century-Long Decline
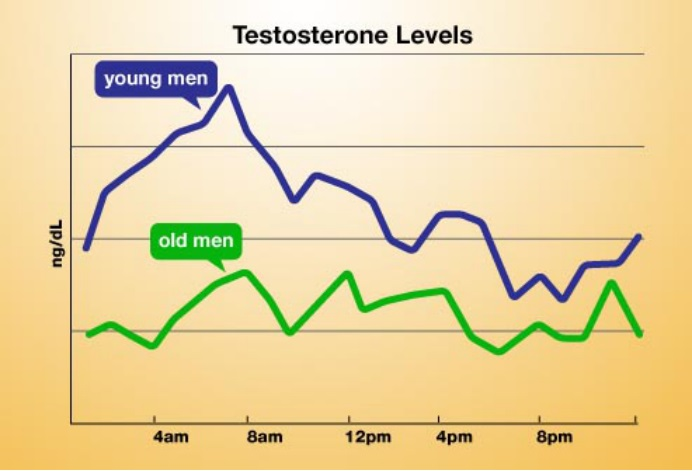
In an era where reproductive health is a pressing concern, scientific research has uncovered a startling fact: male testosterone levels and sperm counts have plummeted by approximately 75% over the past century1^.
A Troubling Discovery
The decrease in male reproductive health has become a global concern, raising questions about the potential consequences for future generations. Research conducted on nearly 43,000 men between 1973 and 2011 revealed a significant decrease in sperm concentration, sperm count, and seminal fluid volume1^. The implications of such a decline in fertility rates are deeply concerning.
Challenging Factors
Numerous factors contribute to the decline in male testosterone levels and sperm counts, making it a complex issue to tackle. Researchers have identified several potential causes, including exposure to environmental pollutants, sedentary lifestyles, obesity, stress, and even certain medications1^. Additionally, unhealthy eating habits and nutritional deficiencies have been linked to the decline in male reproductive health.
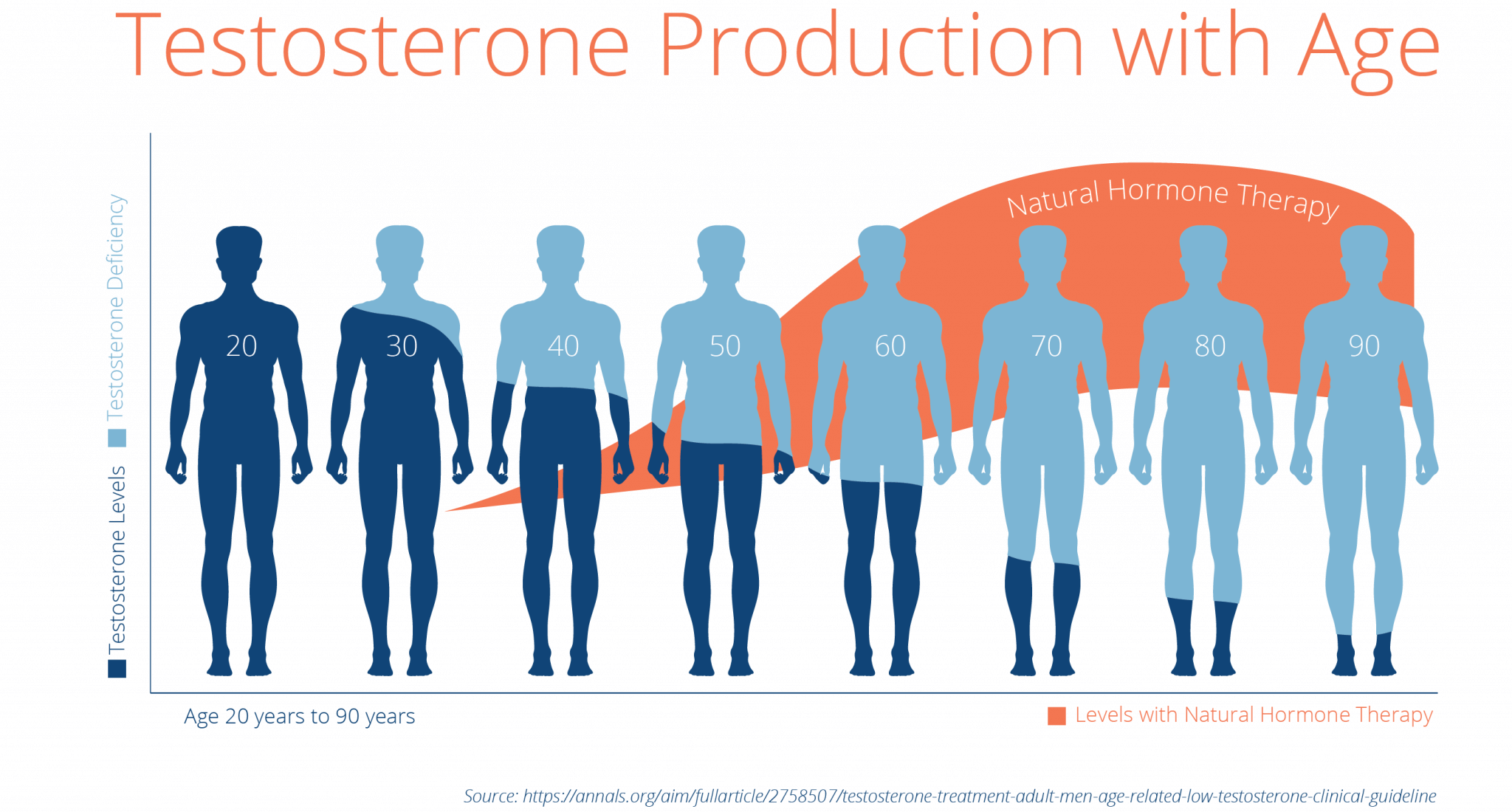
Environmental Threats
Environmental pollutants, such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA), have been identified as potential contributors to decreasing testosterone levels and sperm counts. These chemicals are prevalent in everyday products like plastics, food containers, and personal care items. Studies have shown that exposure to these endocrine-disrupting chemicals can interfere with hormone production and impair fertility1^.
Sedentary Lifestyles and Obesity
Modern lifestyles, characterized by a lack of physical activity and the prevalence of desk jobs, play a significant role in the decline of male reproductive health. Sedentary lifestyles contribute to obesity, which further exacerbates the problem. Obesity can disrupt hormone production, leading to decreased testosterone levels and impaired sperm production1^.
Stress and Medications
High levels of stress have been linked to decreased testosterone levels. The demanding nature of modern life, coupled with increased work pressure, may have a profound impact on male reproductive health. In addition, certain medications, such as those used to treat depression, blood pressure, and ulcers, have been associated with reduced testosterone levels and sperm counts1^.
Looking Towards the Future
The decline in male testosterone levels and sperm counts is an issue that demands attention and action. While further research is needed to fully understand the extent of the problem, it is crucial to take proactive steps to counteract the factors contributing to this decline. Lifestyle modifications focused on regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and avoiding environmental pollutants can support male reproductive health.
As a society, we must prioritize education, awareness, and research to reverse this disconcerting trend. By engaging in meaningful discussions, promoting healthier lifestyles, and advocating for stricter regulation of environmental toxins, we can work towards a more fertile future for all.
Sources:
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

