Your death microbiome could catch your killer
Your Death Microbiome Could Catch Your Killer
In recent years, the concept of the human microbiome has gained immense attention in the scientific community. The microbiome refers to the trillions of microorganisms that reside in and on our bodies, playing a crucial role in maintaining our health. These tiny organisms influence various aspects of our well-being, from our immune system to our digestion.
But did you know that even after death, the microbiome can continue to provide valuable information? Recent studies have suggested that analyzing the microbial communities present in a deceased person’s body can potentially help solve crimes and catch killers. This fascinating field of research is known as “thanatomicrobiology.”
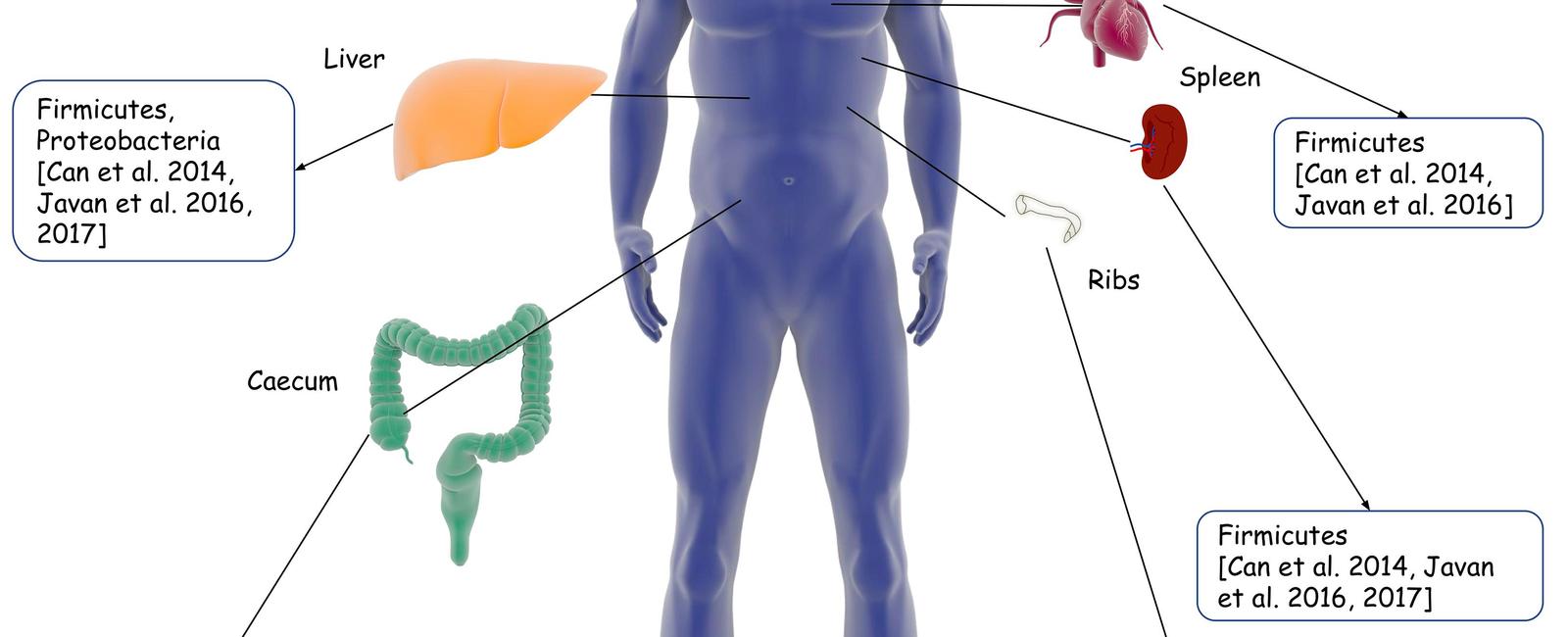
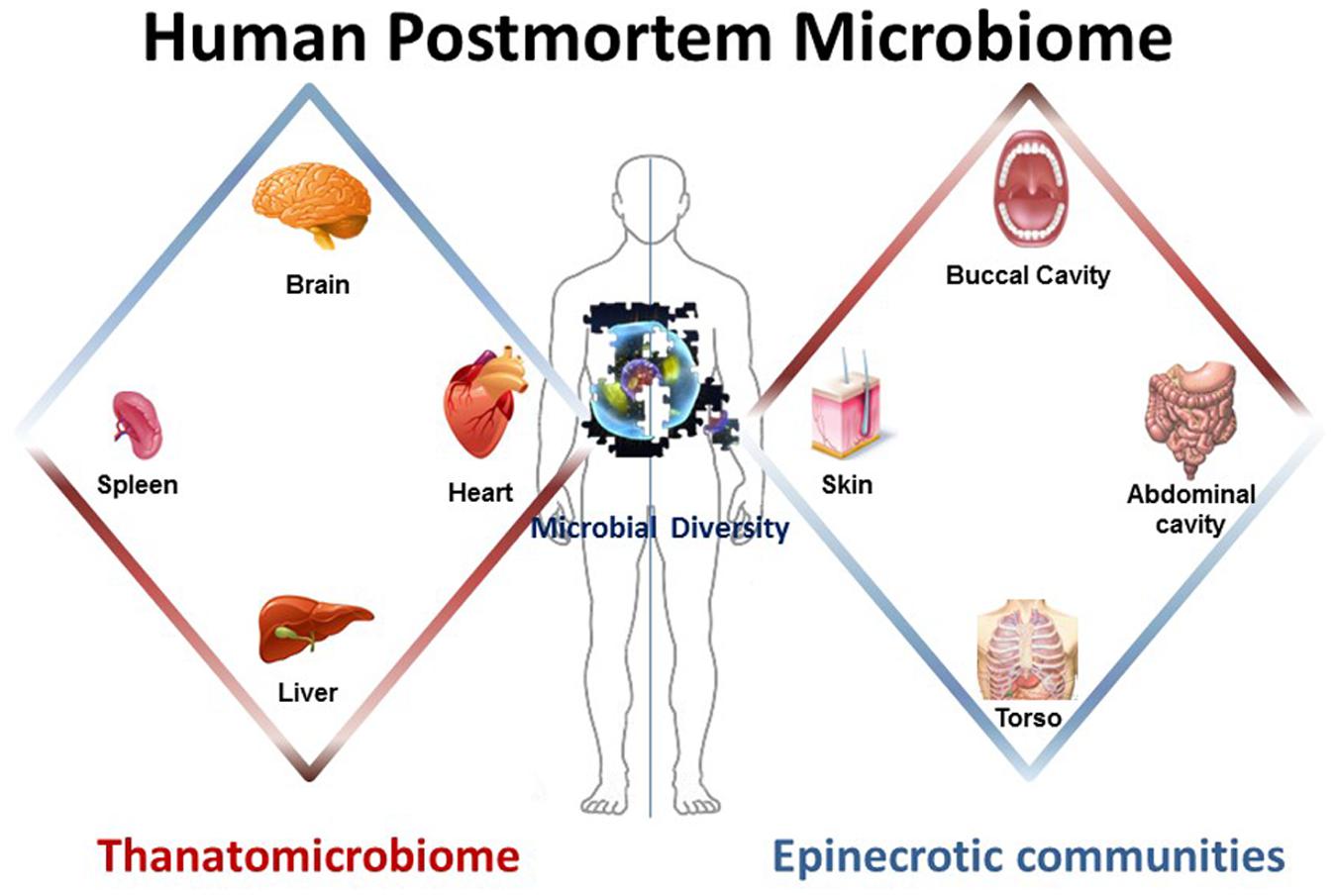
When a person dies, the body undergoes various changes due to decomposition. These changes are mediated by the microbes present in and around the body. By studying the types and abundance of these microorganisms, forensic investigators can gain insights into the postmortem interval (PMI), which refers to the time that has elapsed since death.
The composition of the human microbiome is highly specific to each individual. The same applies to the death microbiome, which is influenced by the individual’s lifestyle, diet, and surrounding environment. By analyzing the microbial signatures left behind during decomposition, scientists can potentially determine the unique microbial profile of an individual and use it to identify their remains.
Additionally, analyzing the death microbiome can help in estimating the location where death occurred. Microbial populations differ between various environments, such as soil, water, and indoor settings. By comparing the microbial communities found on a body with those present in nearby surroundings, forensic investigators can narrow down the search area and potentially uncover crucial evidence.
Forensic microbiology has shown promising results in several real-life cases. In one such case, a woman disappeared under mysterious circumstances and was found dead months later. By analyzing the microbial communities on her remains, researchers were able to determine the approximate time since death, which helped establish a timeline of events and narrow down the list of suspects.
This emerging field of research, however, is not without its challenges. The death microbiome is highly dynamic, and various factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of scavengers can influence the microbial composition. Developing standardized protocols and reference databases for analyzing death-associated microbial communities is essential to ensure accurate and reliable results.
As the field of thanatomicrobiology continues to advance, it holds great potential in revolutionizing forensic investigations. By harnessing the power of the death microbiome, investigators can improve their ability to solve crimes and bring justice to the families of victims. However, more research is needed to fully understand the complexities of the death microbiome and its potential applications in forensic science.
In conclusion, the analysis of the death microbiome has emerged as a new frontier in forensic science. By studying the microbial communities present in and around a deceased person’s body, forensic investigators can gather valuable information about the postmortem interval and potentially identify the remains. While challenges exist, the prospects of using the death microbiome to catch killers are both exciting and promising.
Source: Frontiers
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

