We only use 1 of the available water on earth while our planet is 71 water only 1 of it is safe for humans to drink
We Only Use 1% of the Available Water on Earth: A Freshwater Crisis

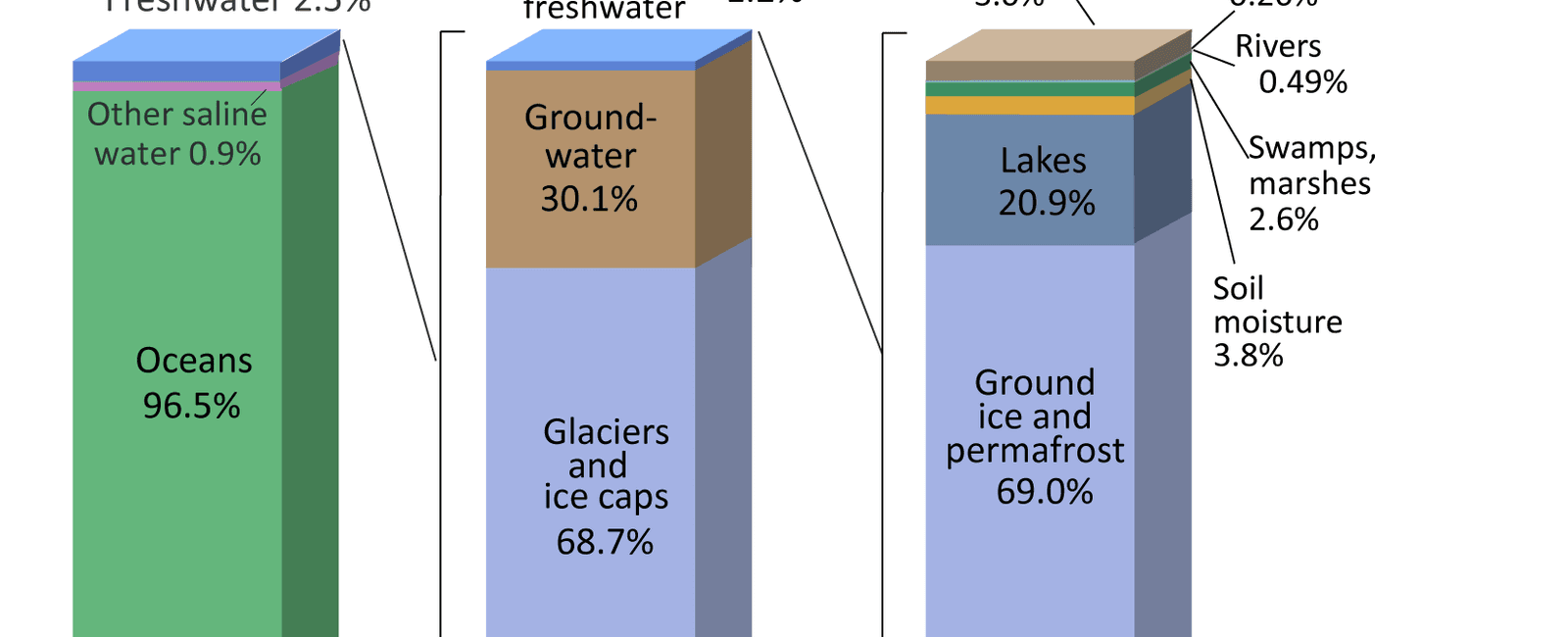
Water covers approximately 71% of the Earth’s surface, making it an abundant resource that seems to be available to us in abundance. However, the reality is quite different. Despite the wide expanse of water, only a mere 1% of it is safe and suitable for human consumption. This startling fact highlights a pressing issue that our planet faces - a freshwater crisis.
Water is essential for all forms of life, and access to clean drinking water is a basic human right. Unfortunately, the scarcity of safe drinking water puts the lives and well-being of countless individuals at risk. To better understand this crisis, let’s delve deeper into the reasons behind this alarming fact.
The available water on Earth can be broadly classified into two categories: saltwater and freshwater. Saltwater, which accounts for about 97% of the Earth’s water, is found in oceans and seas, making it undrinkable for humans without desalination processes that are expensive and energy-intensive. On the other hand, freshwater, which constitutes only 3% of the total water resources, is what we primarily rely on for our daily needs.

Freshwater can be found in various forms, including surface water such as lakes, rivers, and streams, as well as groundwater stored beneath the Earth’s surface. While it might seem like freshwater is abundant, the major challenge lies in the fact that most of it remains inaccessible or unsuitable for immediate use.
Contamination is a significant issue that affects the quality of freshwater sources. Industrial pollutants, agricultural run-off, and untreated sewage find their way into water bodies, contaminating the limited freshwater reserves. This pollution poses significant health risks, particularly in developing countries where access to clean water is already limited.
The global freshwater crisis is further exacerbated by climate change. Rising global temperatures lead to increased evaporation rates, resulting in reduced water availability. This, combined with changing precipitation patterns, creates periods of droughts in some regions and intense rainfall events in others, leading to water scarcity and waterlogging, respectively.
To mitigate the freshwater crisis, it is crucial to adopt sustainable water management practices. Conservation efforts, such as reducing water wastage and implementing efficient irrigation techniques, can contribute to preserving the available freshwater resources. Additionally, investing in wastewater treatment facilities is vital to preventing further contamination of freshwater sources.
Education and awareness also play a significant role in addressing the freshwater crisis. By raising awareness about the importance of water conservation and promoting responsible water use, individuals can actively contribute to the preservation of this scarce resource.
In conclusion, despite Earth’s extensive water coverage, only a mere 1% is safe for human consumption. This alarming fact highlights the freshwater crisis the planet faces. Through sustainable water management practices and increased awareness, we can work towards safeguarding this precious resource for generations to come.
Source: National Geographic - Freshwater Crisis
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

