We can sense and are attracted to a person with a different immune system
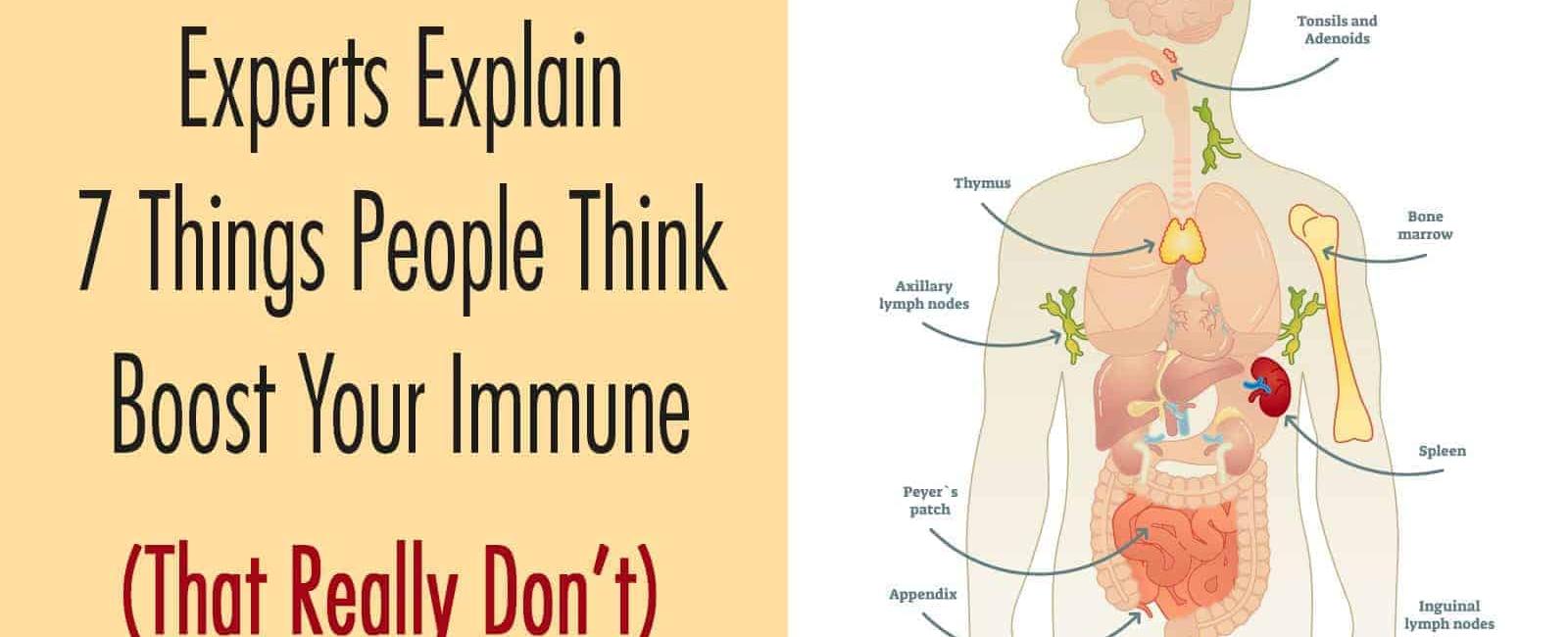
We Can Sense and Are Attracted to a Person with a Different Immune System
Have you ever wondered why you may be drawn to someone who has a different scent or seems to have a different vibe than others? It turns out that our immune systems might be playing a larger role in our attractions than we realize. Studies have shown that we can sense and are attracted to a person with a different immune system, and this phenomenon has fascinated scientists for years.
The bond of true love might go beyond just emotional connections and shared interests. It appears that our bodies have a way of detecting and being drawn to potential partners with a different set of immune genes. This concept is known as “biological compatibility” or “olfactory genes hypothesis.”
Research suggests that our noses play a significant role in this process. The major histocompatibility complex (MHC), which is linked to our immune system, influences body odor. The theory is that people with different MHC genes produce distinct scents. And, it seems that this scent is an indicator of genetic diversity that can result in healthier offspring.
An article published in The Guardian mentioned a study conducted by the University of Liverpool, where female participants were asked to smell a set of t-shirts worn by men. Surprisingly, the majority of women were more attracted to the scent of men whose MHC genes differed from their own. This indicates that our sense of smell may be tuned to select partners with complementary immune systems.

But how does this process work exactly? Scientists believe that our bodies’ ability to detect genetic diversity goes beyond just the sense of smell. It is thought that our immune systems might communicate with each other, allowing us to sense compatibility on a deeper level. This mechanism may involve pheromones, chemical signals that trigger social responses within members of the same species.
The olfactory genes hypothesis raises intriguing questions about the evolution of human attraction. It suggests that our desire for genetic diversity in potential partners could be an adaptive strategy to maximize the chances of producing healthy offspring. By choosing mates with different immune systems, we may enhance the strength and effectiveness of our offspring’s immune response, giving them a greater chance of survival and reproductive success.
While these findings are fascinating, it’s important to note that many factors contribute to attraction and mate selection. Genetic compatibility might be just one piece of the puzzle, and it certainly doesn’t guarantee a successful relationship. Humans are complex beings, driven by a multitude of factors in choosing romantic partners.
In conclusion, our ability to sense and be attracted to individuals with different immune systems is a fascinating aspect of human biology. Our olfactory genes hypothesis suggests that genetic diversity may be a strong driver of attraction, potentially leading to healthier offspring. However, it’s crucial to remember that there’s more to attraction than just biology, and the complexity of human relationships cannot be entirely reduced to genetic compatibility.
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

