Upon dying some pharaohs were sealed into their tombs alongside their living servants pets and concubines
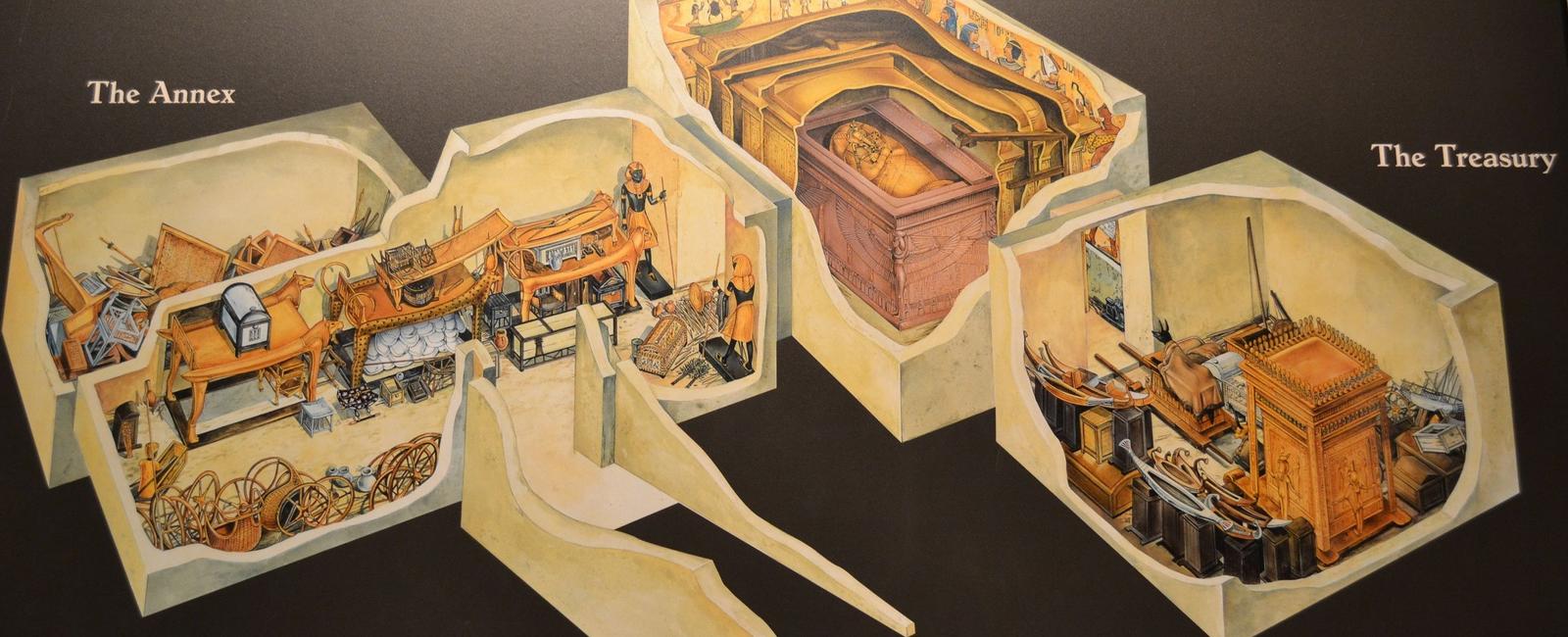
Upon dying, some pharaohs were sealed into their tombs alongside their living servants, pets, and concubines.

Ancient Egypt has always been shrouded in mystery and fascination for its elaborate burial rituals and practices. One intriguing fact that has captivated historians and archeologists alike is the practice of sealing pharaohs in their tombs alongside their living servants, pets, and concubines upon their death.
This ancient tradition reflects the belief in the afterlife held by the ancient Egyptians. They believed that in order for the pharaoh to enjoy an opulent and comfortable existence in the afterlife, he needed to be accompanied by his loyal subjects and possessions. The idea was that these individuals would continue to serve the pharaoh in the afterlife, ensuring his comfort and wellbeing.
This practice was primarily reserved for pharaohs and members of the royal family. The tombs were constructed to be vast and elaborate, showcasing the wealth and power of the deceased. The pharaohs were typically buried with countless treasures, including jewelry, furniture, and other valuable items. These belongings were meant to provide the pharaoh with all the necessities and luxuries he would require in the afterlife.

However, the inclusion of living servants, pets, and concubines in the pharaoh’s tomb raises ethical questions about the treatment of these individuals. It is important to note that these practices were a reflection of the beliefs and norms of the time and should be understood within that context.
Recent studies and archeological excavations have shed light on the lives of those buried alongside the pharaohs. While it is difficult to determine the extent of their social status and position in society, it is believed that they volunteered or were selected for this honor. Being buried alongside the pharaoh was considered a great privilege, as it signified their importance and dedication to the ruler.
The inclusion of pets in the tombs further illustrates the close bond between the pharaoh and his animal companions. Dogs, cats, and even birds were often found buried alongside the pharaohs, indicating the value placed on their companionship and loyalty. It is a testament to the reverence the ancient Egyptians had for their pets, as these animals were believed to be essential guides and protectors in the afterlife.
While the practice of sealing pharaohs in tombs alongside their living servants, pets, and concubines may seem unusual to modern sensibilities, it was an integral part of ancient Egyptian funerary rituals. It served as a means to ensure the pharaoh’s comfort and prosperity in the afterlife, as well as a reflection of the hierarchical structure of their society.
In conclusion, the burial practices of ancient Egypt continue to fascinate and intrigue us today. The inclusion of living servants, pets, and concubines in the tombs of pharaohs exemplifies the complexity and reverence the ancient Egyptians had for the afterlife. By understanding these practices within their historical context, we gain valuable insights into the beliefs and values of this ancient civilization.
Source: History of the Ancient World - Did the Ancient Egyptians Practice Human Sacrifice?
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

