Unlike planets and moons which evolve over time asteroids and comets remain unchanged and are considered the fossils that record planetary history and evolution
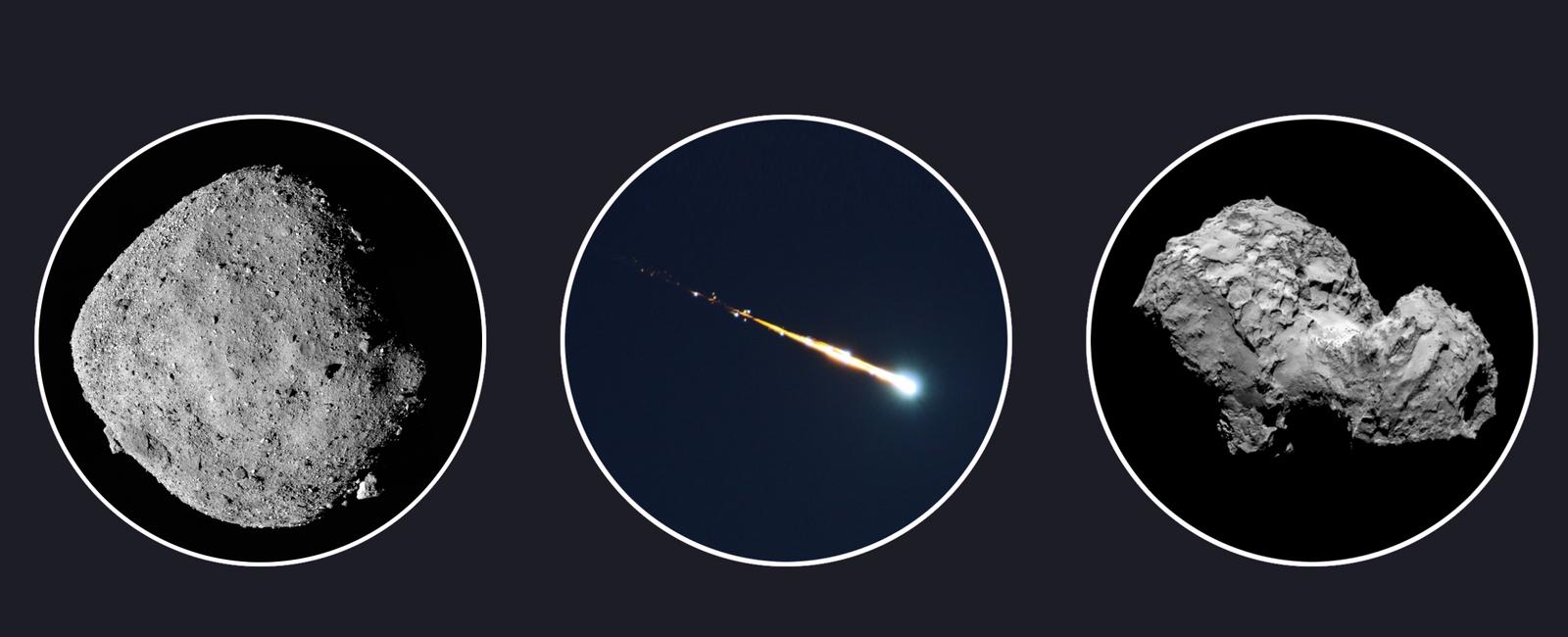
Asteroids and Comets: Fossils of Planetary History and Evolution

Asteroids and comets, unlike planets and moons, are celestial bodies that have remained relatively unchanged over time. They are often referred to as the “fossils” that record the rich history and evolution of our solar system. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of asteroids and comets, exploring their significance as the remnants of ancient planets and the key to understanding our planetary past.
Unveiling the Nature of Asteroids and Comets

Asteroids, also known as minor planets, are rocky objects that orbit the Sun. They are primarily composed of metals and silicate rocks, and their sizes can range from small boulders to objects several hundred kilometers in diameter. Comets, on the other hand, are composed of ice, dust, and rocky material, and they originate from regions of the solar system beyond Neptune called the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud.
These celestial bodies offer unique insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system. Unlike planets and moons, which have undergone significant changes over time due to geological activity and other processes, asteroids and comets provide a glimpse into the conditions that existed during the early stages of the solar system’s development.
Windows to the Past: Tracing Planetary History
By studying asteroids and comets, scientists can unlock valuable information about the composition, structure, and dynamics of the early solar system. These ancient fragments retain the pristine characteristics of the materials from which they originated, allowing scientists to decipher the chemical makeup of the protoplanetary disk from which the planets formed.
It is believed that asteroids and comets formed from the same building blocks that gave rise to the planets. As remnants of the early solar system, they provide critical clues about the processes that led to the formation of planets and the subsequent evolution of our cosmic neighborhood.
Additionally, the craters present on the surfaces of asteroids and comets bear witness to countless collisions with other objects over billions of years. By analyzing these impact sites, scientists can reconstruct the history of our solar system, including the frequency and intensity of these events, and how they have shaped the celestial bodies we observe today.
Significance for Planetary Research and Space Exploration
The study of asteroids and comets not only provides insights into the past, but it is also crucial for our future explorations of space. These celestial bodies offer numerous opportunities for scientific research and resource extraction. For example, asteroids may contain valuable metals, such as platinum and gold, which could potentially be mined for future space missions or utilized for economic purposes.
Moreover, comets hold vast amounts of water ice, which can be converted into breathable air and rocket propellant. Access to these resources on comets could revolutionize long-duration space travel and enable the sustained presence of humans beyond Earth.
Understanding the nature and origins of asteroids and comets is, therefore, essential for advancing our knowledge of the solar system and unlocking the potential of space exploration.
Source: NASA Solar System Exploration - Asteroids, Comets, and Meteors
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

