The so called southern accent in the united states today only began to form after the civil war
The Evolution of the Southern Accent after the Civil War
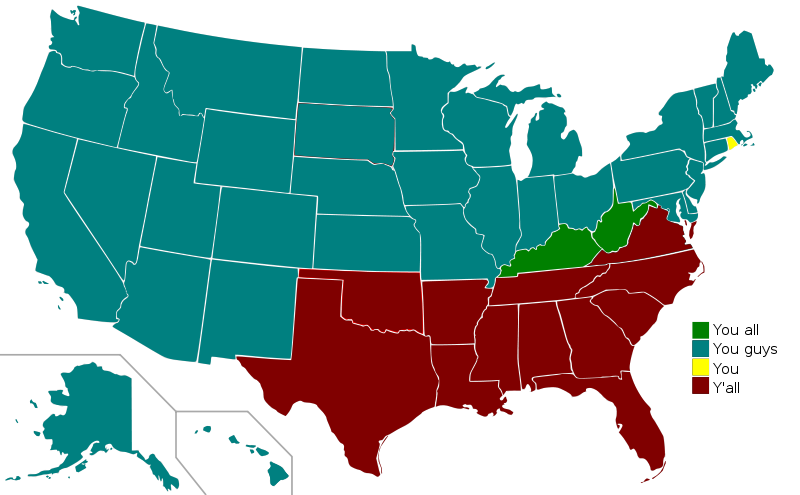
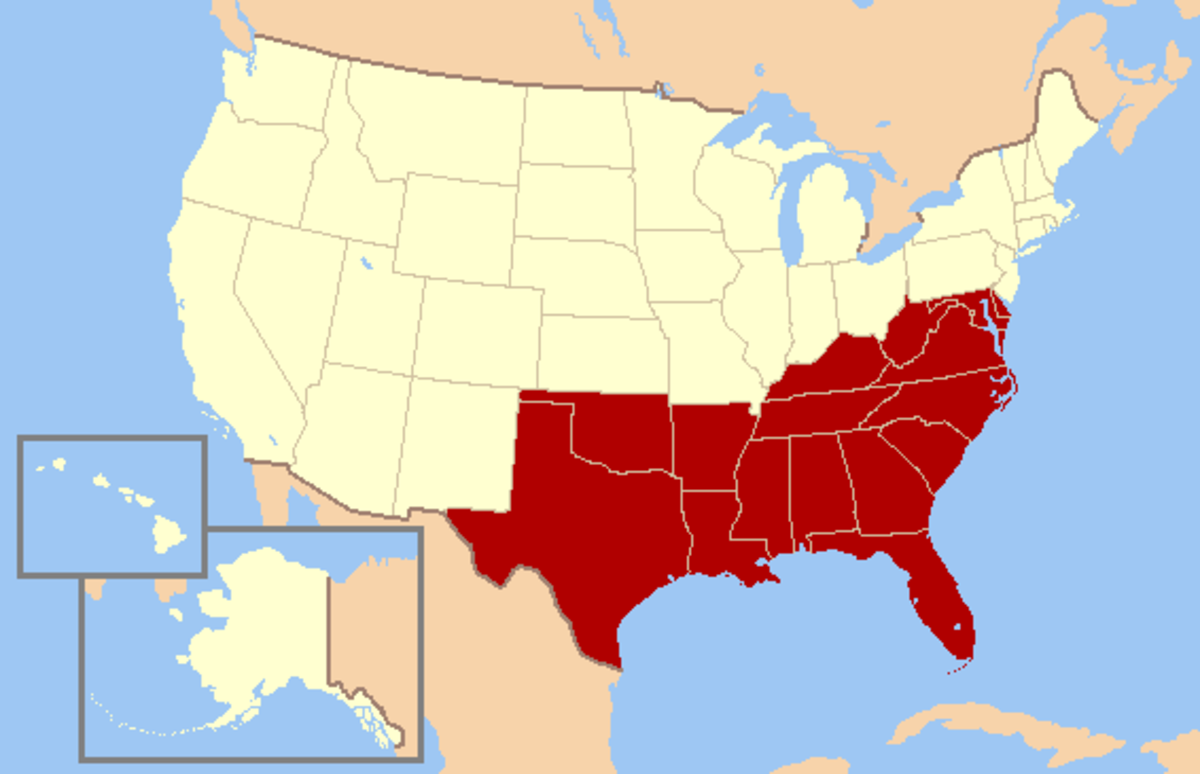
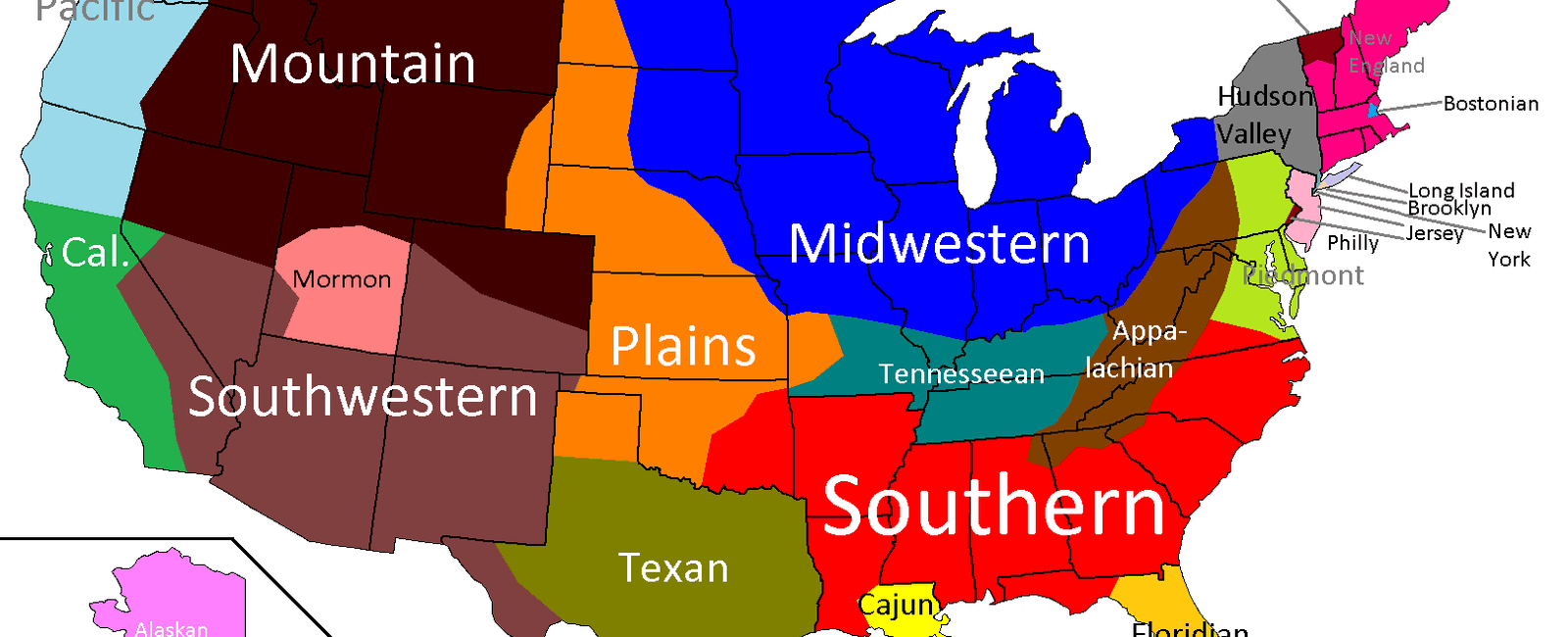
The United States is a vast melting pot of cultures, languages, and accents. One of the most distinct and recognizable accents is the Southern accent. However, the so-called “Southern accent” that we commonly associate with states such as Georgia, Louisiana, and Mississippi today did not exist in its current form until after the Civil War.
Before the Civil War, the accents in the Southern states were varied and differed greatly from region to region. The primary influences on the linguistic patterns in the South were English, Scottish, Irish, and African languages. These influences, mixed with local dialects and accents, created a diverse linguistic landscape.
However, the Civil War had a significant impact on the linguistic development in the Southern states. The war and its aftermath marked the beginning of a shift in the Southern accent.
The influx of people from different parts of the country during the post-war reconstruction period brought new influences and dialects to the South. Many individuals from the Northern states moved to the South to assist in rebuilding the war-torn region. This migration led to a blending of accents and language patterns.
Furthermore, the increased interaction between different cultural groups, including African Americans, also contributed to the evolution of the Southern accent. African Americans, who had their own distinct linguistic patterns rooted in the languages of their African ancestors, influenced the speech patterns of the Southern white population as well.
Over time, this blending of accents and language patterns resulted in the emergence of what we now recognize as the Southern accent. It is characterized by elongated vowels, a drawl, and distinct pronunciation features such as the use of “y’all” as a second-person plural pronoun.
It’s important to note that while the “Southern accent” has become associated with a certain region in the United States, there are still variations within the accent itself. The Southern accent can differ between states, cities, and even rural and urban areas.
In conclusion, the so-called “Southern accent” in the United States today only began to form after the Civil War. The blending of various linguistic influences, migration patterns, and increased interaction between different cultural groups all played a role in its development. The Southern accent is a testament to the rich and complex history of the region, and continues to be a distinct feature of Southern culture.
Sources:
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

