The largest ocean on earth is the pacific ocean
The Largest Ocean on Earth is the Pacific Ocean
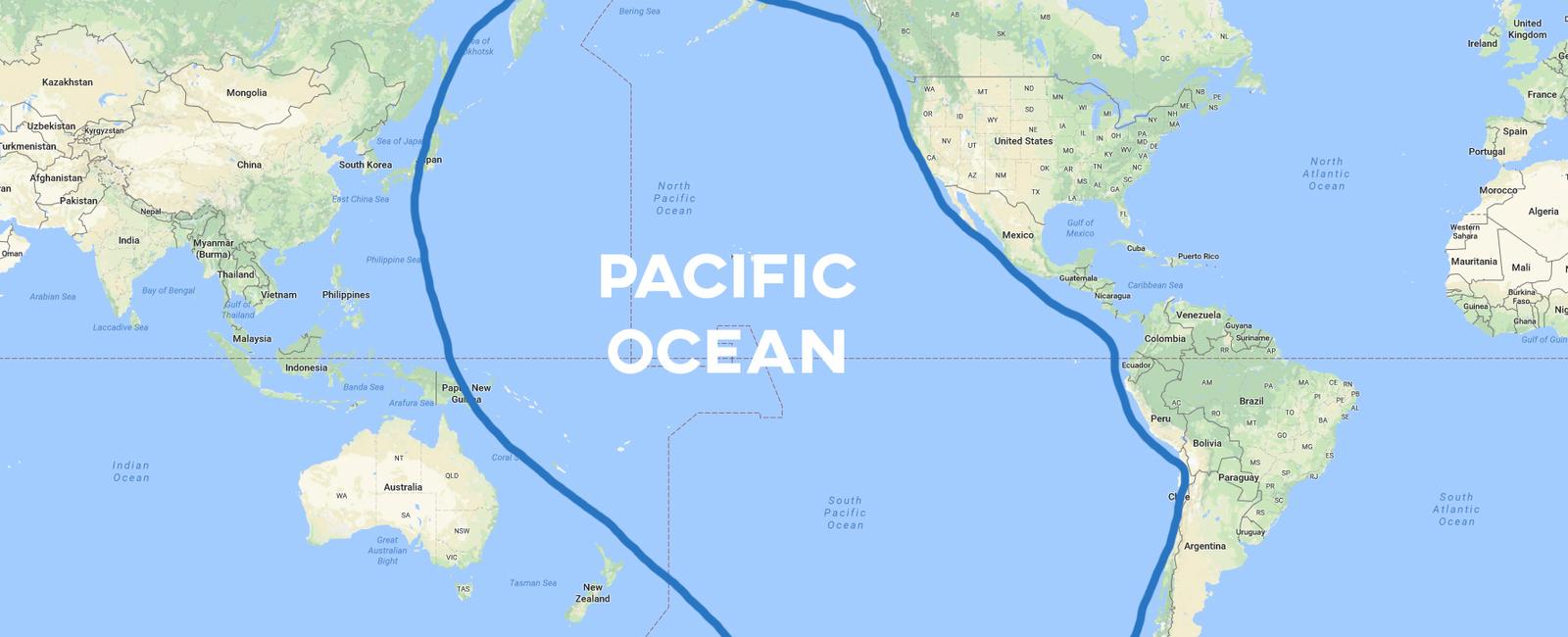
The Pacific Ocean is widely recognized as the largest and deepest ocean on Earth. Stretching across an area of approximately 63 million square miles, the Pacific Ocean covers more than 30% of the planet’s surface. With its vast expanse, this magnificent body of water is home to numerous stunning wonders, diverse marine life, and fascinating geological formations.
This colossal ocean is bordered by the continents of Asia and Australia to the west, and the Americas to the east. Its northern boundary touches the Arctic Ocean, while its southern boundary meets the icy waters of the Southern Ocean. The Pacific Ocean connects various other seas and smaller oceans, such as the Indian Ocean through the Indonesian archipelago, and the Atlantic Ocean through the passage of the Drake Passage.
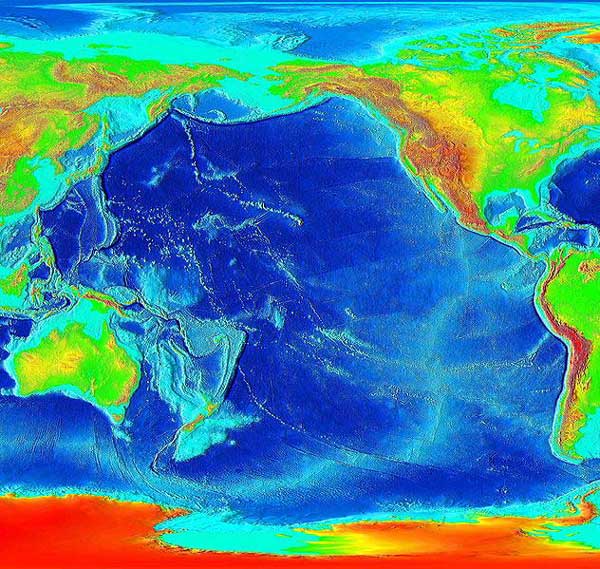
As the largest ocean globally, the Pacific Ocean holds several significant records. The Marianas Trench, located within the western region of the Pacific Ocean, is the deepest point on Earth, plunging down to a staggering depth of around 36,000 feet. This fascinating trench is known for its unique ecosystem and intriguing geological formations, including hydrothermal vents and the Challenger Deep.
Within the Pacific Ocean lies an astonishing array of stunning archipelagos, coral reefs, and atolls. One prominent example is the Great Barrier Reef, the world’s largest coral reef system located off the coast of Australia. This UNESCO World Heritage Site spans over 1,400 miles and is teeming with an astonishing diversity of marine life, including vibrant corals, fish, turtles, and sharks.

The Pacific Ocean’s immense size enables it to influence global climate patterns and weather phenomena. The ocean significantly affects the Pacific Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped band encircling the ocean, renowned for its intense seismic activity and volcanic eruptions. This region is home to approximately 75% of the world’s dormant and active volcanoes and is prone to earthquakes, making it a fascinating area of study for geologists.
The ocean’s significant impact on climate is also highlighted by the presence of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) and El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). These climate patterns influence temperature, rainfall, and weather conditions, not only in the Pacific region but also across the globe. Scientists and researchers closely monitor these oscillations to forecast climate variations and their subsequent effects on agriculture, fisheries, and ecosystems.
In conclusion, the Pacific Ocean’s grandeur and immense scale make it a captivating subject of study and exploration. With its breathtaking landscapes, diverse marine life, and connection to global climate patterns, the Pacific Ocean continues to intrigue scientists and awe enthusiasts with its boundless wonders. Its significance to the Earth’s ecosystem and the countless mysteries it holds within its depths make it an invaluable asset, deserving of our admiration and curiosity.
Source: Science Kids
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

