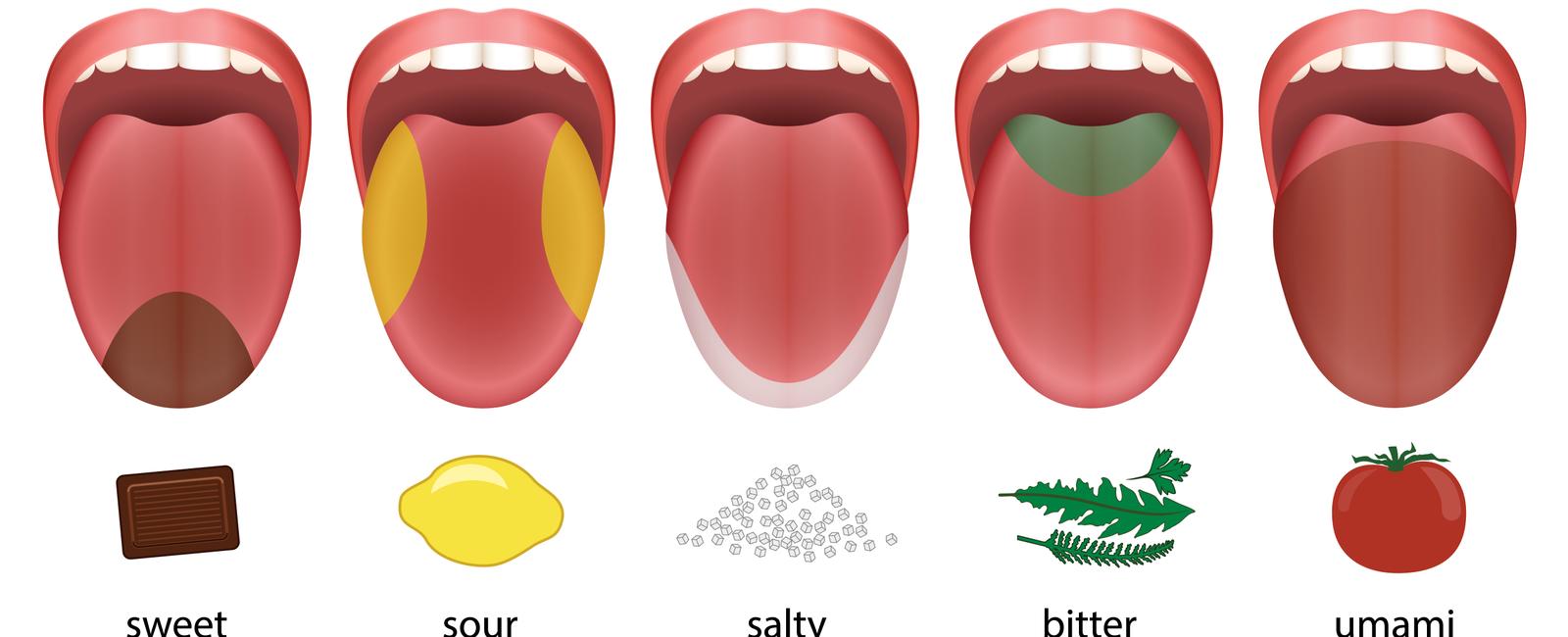
The human tongue tastes bitter things with the taste buds toward the back salty and pungent flavors are tasted in the middle of the tongue sweet flavors at the tip
The Human Tongue and Its Sensory Map
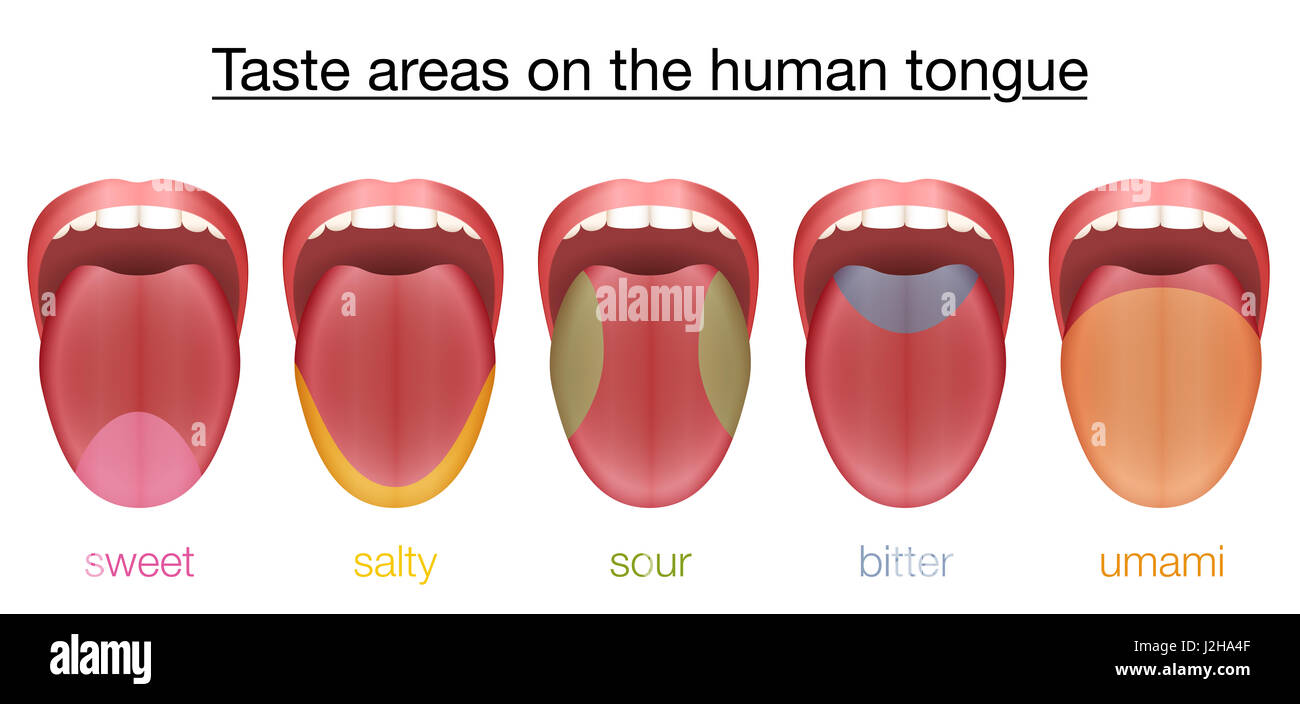
For years, many of us were under the impression that the human tongue could only perceive certain tastes in specific regions. According to this commonly misconstrued notion, bitter flavors were primarily tasted at the back of the tongue, while salty and pungent flavors were more prominent in the middle, and sweet flavors were best sensed at the tip.
However, scientific research has debunked this so-called “tongue map” theory, revealing a more accurate understanding of how we taste various flavors across the entire tongue. Recent studies have shown that taste buds, or groups of cells responsible for perceiving specific tastes, are distributed all over the tongue’s surface.
Contrary to the myth, our taste buds are not confined to specific areas but are spread across the tongue, ready to detect the diverse range of flavors that we encounter daily. In fact, each taste bud contains receptors for all tastes, allowing us to fully experience the sweet, salty, bitter, sour, and umami flavors in every part of our tongue.

The taste buds present on our tongues are designed to detect specific taste molecules in food and beverages. When we consume something, these molecules dissolve in the saliva and come into contact with the taste buds, triggering nerve signals that are sent to our brains for interpretation.
While it is true that certain tastes may be more noticeable in specific regions of the tongue, this is primarily due to the varying concentrations of taste buds found across its surface. For example, bitter tastes may be more prominently detected at the back of the tongue due to the higher concentration of bitter taste receptors in that area. Similarly, sweet flavors might feel more pronounced at the tip of the tongue. However, it is essential to emphasize that all tastes can be perceived regardless of the region.
The debunking of the tongue map theory is significant not only for our understanding of taste perception but also for culinary innovation and the enjoyment of food. It highlights the complexity and versatility of our taste buds and emphasizes that every part of the tongue can experience the full spectrum of flavors.
In conclusion, the human tongue does not have specific regions dedicated to tasting particular flavors. Rather than adhering to the outdated tongue map theory, we now know that our tongue contains taste buds evenly distributed across its entire surface, allowing us to savor the diverse tastes life has to offer.
Source: Live Science
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

