The first man made object sent into space was in 1957 when the russian satellite named sputnik was launched
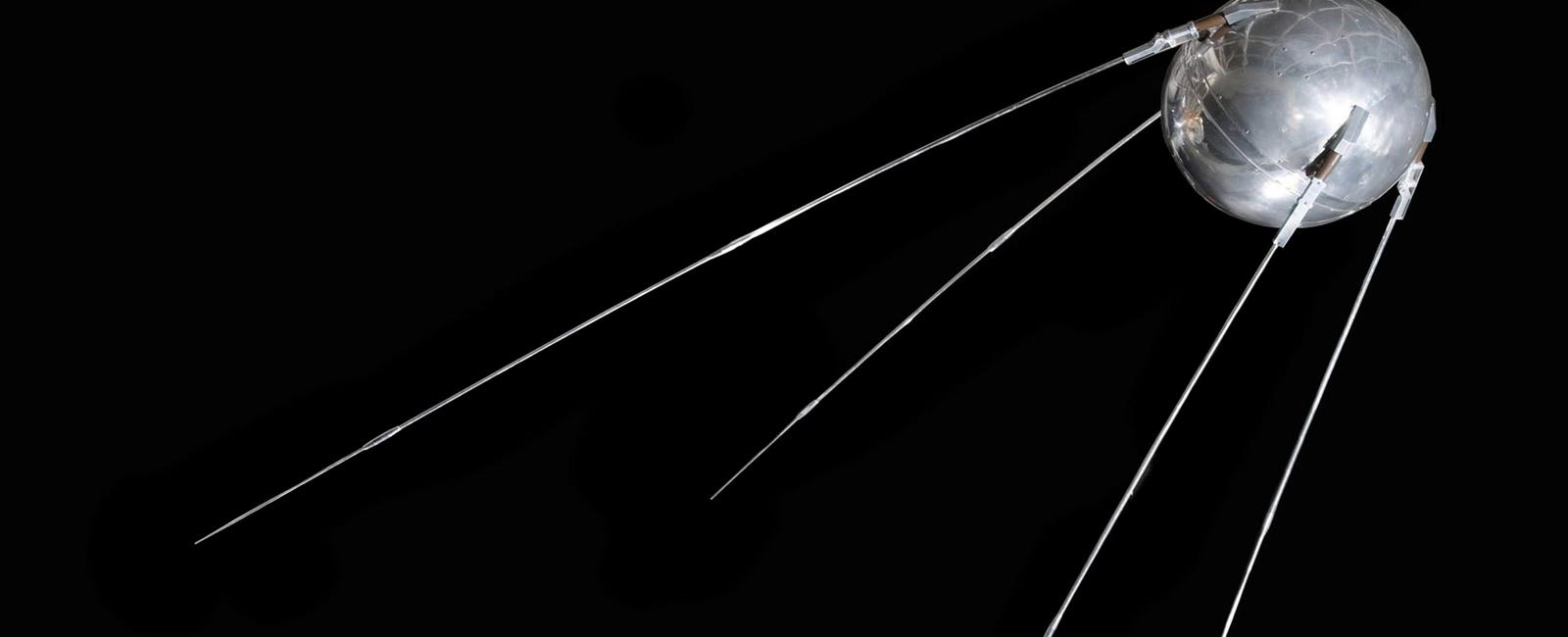

The First Satellite in Space: Sputnik (1957)
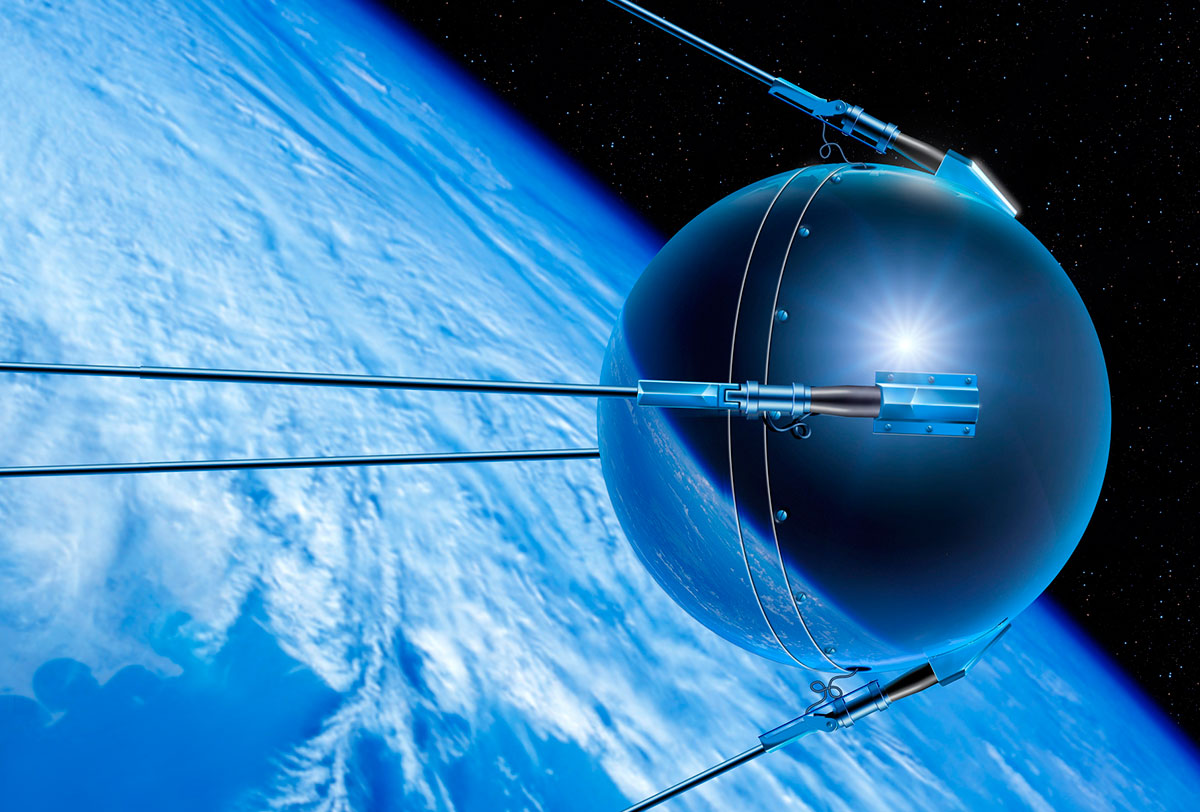
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, a small metal sphere made history on October 4, 1957. Named Sputnik, this humble Russian satellite became the first man-made object to venture into space, forever changing the course of human exploration beyond Earth’s boundaries.
The launch of Sputnik marked a remarkable triumph for the Soviet Union in the midst of the Cold War. It not only astonished the world but also triggered a new era of scientific and technological advancements. This groundbreaking achievement symbolized the dawn of the Space Age and ignited a fierce competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, known as the Space Race.

Measuring just 58 centimeters in diameter and weighing approximately 83 kilograms, Sputnik was a true testament to human ingenuity. Its metallic shell was adorned with four long antennas, which were crucial for transmitting signals back to Earth. Powered by silver-zinc batteries, Sputnik circled the Earth once every 96 minutes, orbiting at an altitude of about 230 kilometers.
The launch of Sputnik not only marked the first human-made object in space but also paved the way for future space exploration endeavors. This seminal event spurred an explosion of scientific exploration, leading to the establishment of numerous space agencies and ambitious space missions.
The successful launch of Sputnik inspired awe and disbelief among people worldwide, sparking intense media coverage and public fascination. It served as a reminder of the limitless potential of human achievement and the awe-inspiring mysteries that lie beyond our home planet. Sputnik became a symbol of scientific progress, capturing the world’s attention and fostering a newfound enthusiasm for space exploration.
Today, Sputnik is regarded as a monument to humanity’s appetite for discovery and technological innovation. Its legacy can still be seen in the countless satellites that now populate Earth’s orbit, improving communication, weather forecasting, and navigation systems. As we continue to push the boundaries of knowledge and explore the vastness of space, we owe a debt of gratitude to Sputnik and the brave minds that made it possible.
In conclusion, the launch of Sputnik in 1957 stands as a momentous leap in the history of human accomplishments. This small, metallic sphere proved that the confines of Earth were no longer limitations, but instead, gateways to the universe waiting to be explored. Sputnik paved the way for future space missions, inspiring generations of scientists, engineers, and explorers to push the boundaries of what is possible in space.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

