More than 8 7 billion machines are currently connected to the internet
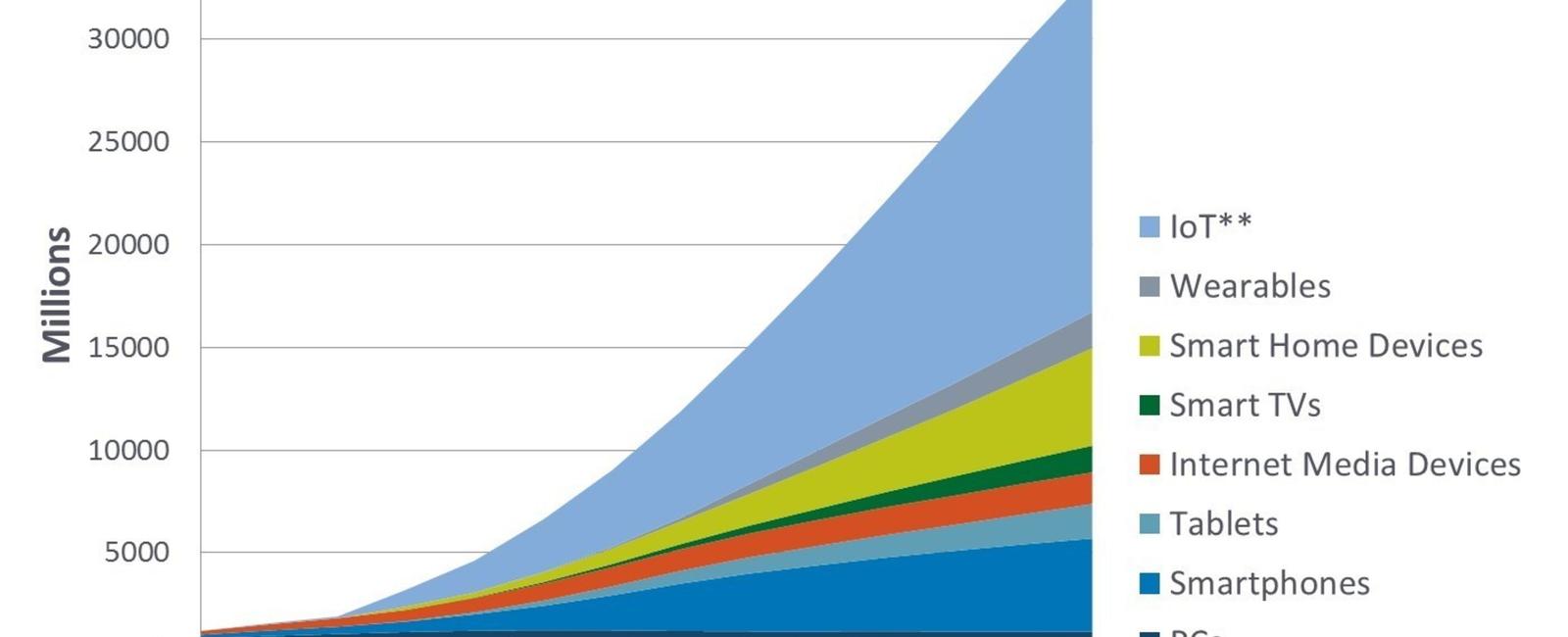
More than 8.7 billion machines are currently connected to the internet

In today’s digital age, the presence of technology is ubiquitous. We are surrounded by an immense number of devices that are interconnected through the internet, forming what is commonly referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT has revolutionized the way we live, work, and interact with technology, making our lives more convenient and efficient than ever before.
According to Forbes1, there are currently more than 8.7 billion machines that are connected to the internet. This staggering number showcases the widespread adoption of IoT devices across various industries and sectors. From smartphones and laptops to smart home appliances and wearable devices, the IoT has permeated every aspect of our lives.

The IoT has transformed our homes into smart spaces equipped with intelligent devices that can be controlled remotely. We can now adjust our thermostats, lock our doors, and even monitor our energy consumption using our smartphones or voice assistants. This interconnectedness has not only enhanced our convenience and comfort but also improved energy efficiency, leading to a greener and more sustainable future.
In the healthcare industry, the IoT has paved the way for telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. Patients can now receive medical consultations and monitor their health conditions from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for physical visits to healthcare facilities. This advancement has been particularly crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic, where remote healthcare services have played a vital role in ensuring the continuity of healthcare delivery.
Moreover, the industrial sector has embraced the IoT to optimize operations and increase productivity. Through IoT-enabled sensors and automation, manufacturing processes have become more efficient and cost-effective. Machines can now communicate with each other, analyzing data in real-time to identify potential issues and prevent downtime. This predictive maintenance approach has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, minimizing disruptions and maximizing output.
However, with the increasing number of connected devices comes the concern for data security and privacy. As more personal and sensitive information flows through these interconnected machines, protecting data becomes paramount. Manufacturers and service providers must prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard user data and prevent unauthorized access.
In conclusion, the Internet of Things has ushered in a new era of connectivity, with more than 8.7 billion machines currently connected to the internet. This interconnectedness has transformed our daily lives, making them more convenient, efficient, and productive. However, it is crucial to address the security and privacy challenges associated with the IoT to ensure a safe and reliable digital ecosystem.
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

