Language is thought to have originated circa 100 000 bc
Language is thought to have originated circa 100,000 BC.

Language, an essential means of communication, has been a fundamental part of human existence for thousands of years. It is widely believed that language originated around 100,000 BC, marking a significant milestone in the development of our species. This fact is supported by various historical and archaeological evidence that sheds light on the evolution of human language.
The Dawn of Language: The emergence of language can be traced back to the Upper Paleolithic period, when Homo sapiens began to exhibit signs of complex communication skills. Although the exact date of its origin remains uncertain, researchers estimate that language first appeared between 50,000 and 100,000 years ago. This breakthrough contributed to the advancement of human culture and paved the way for civilization as we know it today.
Evidence from Artifacts: Archaeological discoveries have played a crucial role in unravelling the mystery of language origins. Cave paintings and rock art have provided valuable insights into early human communication. For example, the ancient cave paintings in Lascaux, France, believed to be over 17,000 years old, depict various animals and symbols, suggesting a form of primitive language and storytelling. Such artifacts provide tangible evidence of our ancestors’ desire to communicate through visual representations.
The Evolution of Vocalization: One prominent theory regarding the origin of language centers around the development of vocalization skills. It is believed that early humans began using vocal sounds to communicate emotions, intentions, and needs. Over time, these basic sounds evolved into more sophisticated language systems, enabling individuals to convey abstract ideas and complex thoughts. This evolution was a vital step in human cognitive development, allowing for the exchange of knowledge and the formation of stronger social bonds.

The Social Aspect: Language is not only a tool for communication but also a means to connect with others. It fosters social cohesion and facilitates cooperation within communities. As humans began to form groups and societies, language became crucial for sharing knowledge, passing on cultural traditions, and maintaining social order. The development of language laid the foundation for collective learning and enabled the transmission of accumulated knowledge across generations.
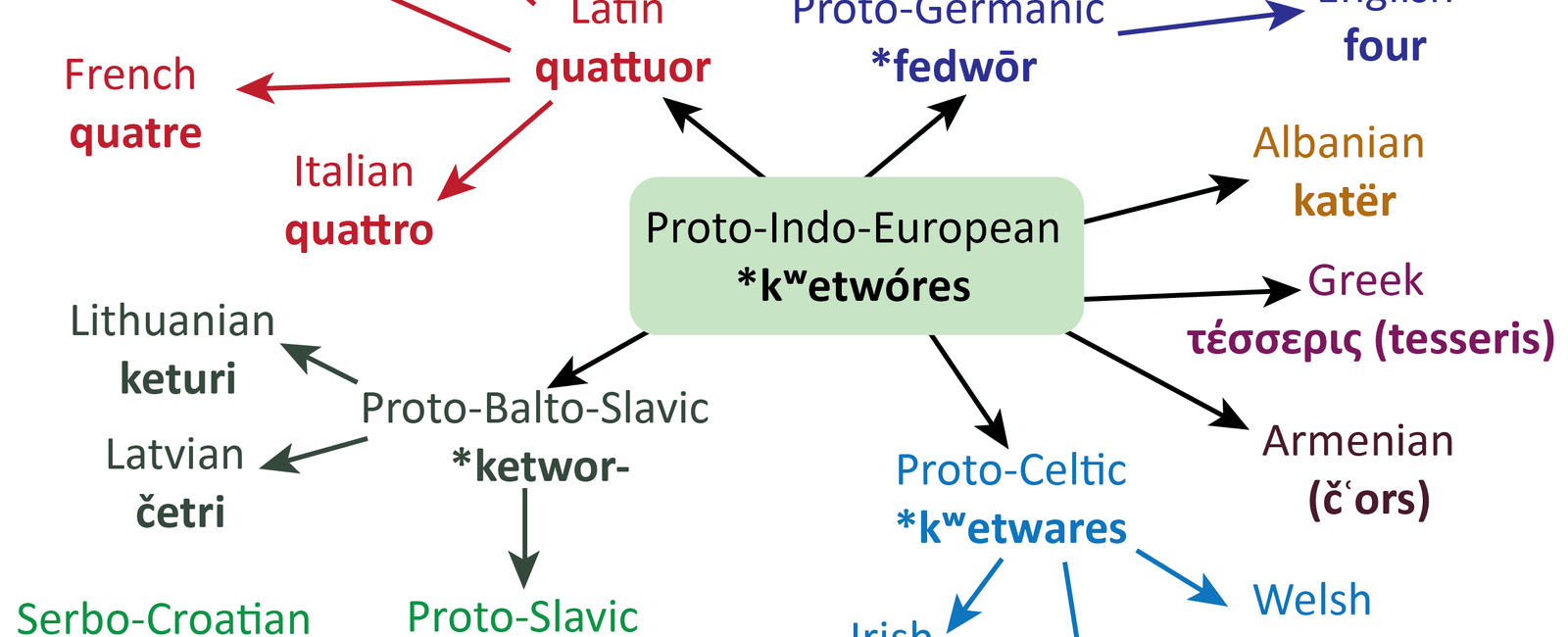
Language Diversification: As populations expanded and groups migrated to different regions, language diversified. This diversification resulted in the formation of numerous language families and the development of distinct languages. Today, there are estimated to be over 7,000 languages spoken worldwide. Each language carries its unique cultural identity and reflects the diverse histories and experiences of its speakers.
The Conquest of Words: Language has proven to be a powerful tool that has shaped the course of human history. It has been instrumental in scientific, cultural, and technological advancements, allowing humans to explore new frontiers and transcend boundaries. From literature and art to science and diplomacy, language serves as the medium through which ideas are exchanged and knowledge is shared.
In conclusion, the origin of language around 100,000 BC marked a significant turning point in human development. It allowed us to express our thoughts, emotions, and experiences, leading to the formation of complex societies and the growth of civilization. Language remains an ever-evolving aspect of our lives, enabling us to connect, learn, and thrive in a diverse and interconnected world.
Sources: LinguaLinx
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

