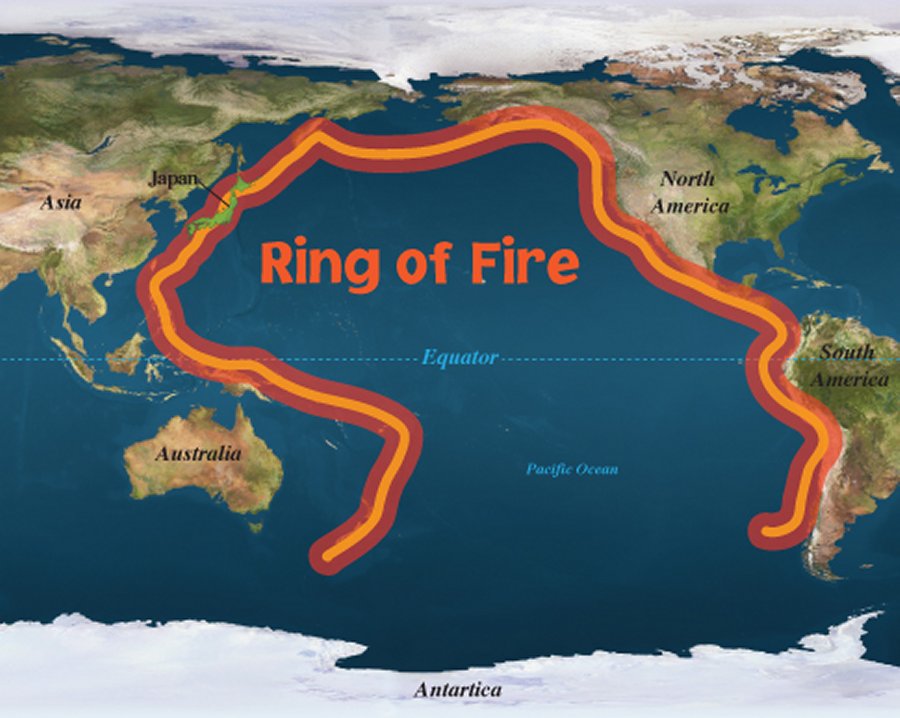
Around 75 of the volcanoes on earth are found in the pacific ring of fire an area around the pacific ocean where tectonic plates meet
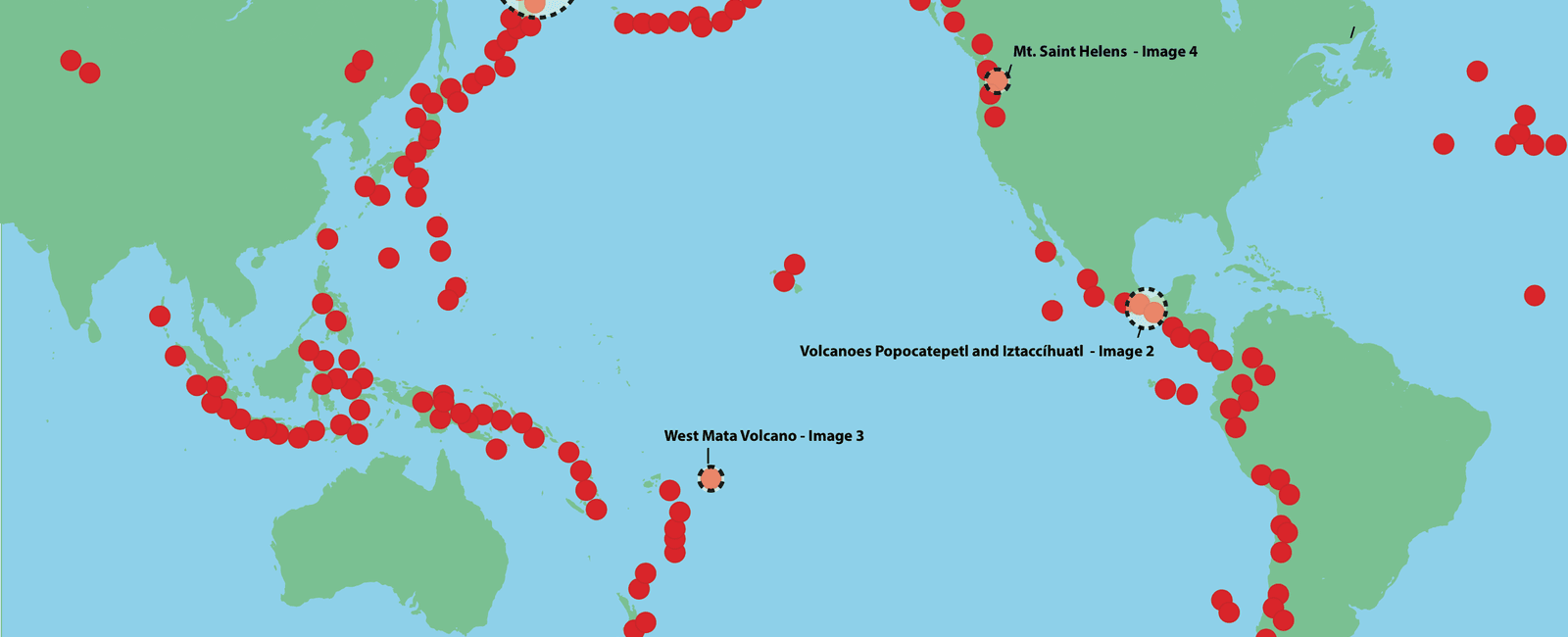
Around 75% of the volcanoes on Earth are found in the Pacific Ring of Fire

Volcanoes have always fascinated both scientists and the general public alike. These majestic natural formations can be found in various parts of the world, but a significant number are concentrated in a unique region known as the Pacific Ring of Fire. This region, encompassing the area around the Pacific Ocean where tectonic plates meet, is home to approximately 75% of the Earth’s volcanoes. The Pacific Ring of Fire is a constantly active and dynamic zone, resulting in numerous volcanic eruptions and seismic activities.
As the name suggests, the Pacific Ring of Fire forms a ring-like structure, extending for approximately 40,000 kilometers. It stretches from the coasts of eastern Asia, down the western coast of North America, and up through the western coast of South America. This expansive area encompasses iconic locations such as the Aleutian Islands in Alaska, the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, the Philippines, Japan, Indonesia, and numerous volcanic chains along the western coast of the Americas.
The Pacific Ring of Fire is shaped by the movement and collision of several tectonic plates, including the Pacific Plate, North American Plate, Eurasian Plate, Philippine Sea Plate, and many others. These plates are enormous slabs of Earth’s crust that float on the semi-fluid mantle layer beneath them. As these plates interact, they can either converge, where one plate slides beneath another, or diverge, where two plates move away from each other.
The majority of the volcanoes within the Pacific Ring of Fire are formed as a result of plate convergence. When two plates collide, one may be forced beneath the other in a process known as subduction. This subduction zone acts as a hotspot for volcanic activity, allowing molten rock, or magma, to rise to the surface and erupt as a volcano. This volcanic activity is responsible for the creation of numerous volcanic arcs and island chains seen throughout the region.
The presence of such a high concentration of volcanoes in the Pacific Ring of Fire is not without its risks. The region is known for its frequent volcanic eruptions, some of which have had devastating consequences. Volcanoes like Mount St. Helens in the United States, Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, and Mount Krakatoa in Indonesia have all experienced violent eruptions that caused significant loss of life and property damage.
However, the Pacific Ring of Fire is not just about the dangers and destruction it brings. It also plays a crucial role in the Earth’s geological processes. The volcanoes within this region contribute to the formation and growth of new land, enrich the surrounding soils with essential nutrients, and create unique habitats for various species of plants and animals.
In conclusion, the Pacific Ring of Fire is a fascinating and geologically active region that showcases the incredible forces at work within our planet. With approximately 75% of the world’s volcanoes located in this area, it serves as a constant reminder of Earth’s dynamic nature. Understanding the processes occurring within the Pacific Ring of Fire is crucial for scientists, as it provides valuable insights into Earth’s tectonic activity and helps us prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with volcanic eruptions and seismic events.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

