Arabic numerals are not really arabic they were created in india
Arabic numerals are not really Arabic; they were created in India.
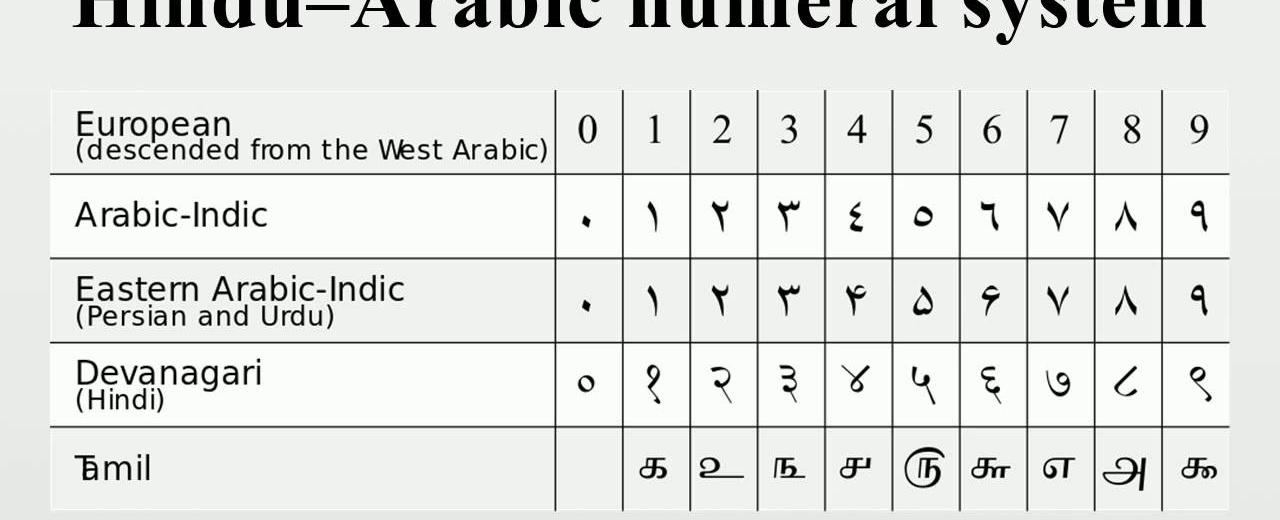
Arabic numerals are widely used today as a decimal numeric system. However, despite their name, they are not actually of Arabic origin. These numerals were developed in ancient India and later introduced to the West by Arab merchants.

The Hindu-Arabic or Indo-Arabic numeral system, as it is often referred to, was invented by mathematicians in India. It is believed that these numerals evolved from the Brahmi numerals used in ancient India. The earliest evidence of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system can be found in ancient Indian texts dated as early as the 6th century.
This numeral system was further refined and expanded upon by Persian and Arab mathematicians, who encountered it during their interactions with Indian traders and scholars. Arab mathematicians recognized the value and efficiency of the system and brought it back to their own societies.

Arab merchants played a significant role in spreading these numerals to the West. As they traveled and traded with various cultures, they introduced the Hindu-Arabic numeral system to regions such as Persia, North Africa, and eventually Europe.
The introduction of Arabic numerals revolutionized mathematics and commerce. These numerals provided a more efficient and intuitive way to represent numbers, as opposed to the Roman numeral system that was prevalent in the West at the time. The use of zero as a placeholder was also a significant breakthrough that enabled more complex calculations.
The wide acceptance and adoption of Arabic numerals in Europe can be attributed to the efforts of influential mathematicians like Fibonacci. His book, “Liber Abaci,” which was published in 1202, introduced the Hindu-Arabic numerals to European mathematicians, leading to their eventual widespread use.
In conclusion, while Arabic numerals are called so, their origin lies in ancient India. The Hindu-Arabic numeral system was developed by Indian mathematicians and later spread to the Arab world through trade and intellectual exchanges. From there, it found its way to Europe, where it revolutionized mathematics and became the standard numerical system we use today.
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

