Your left lung is about 10 percent smaller than your right one
Your Left Lung is 10% Smaller Than Your Right One
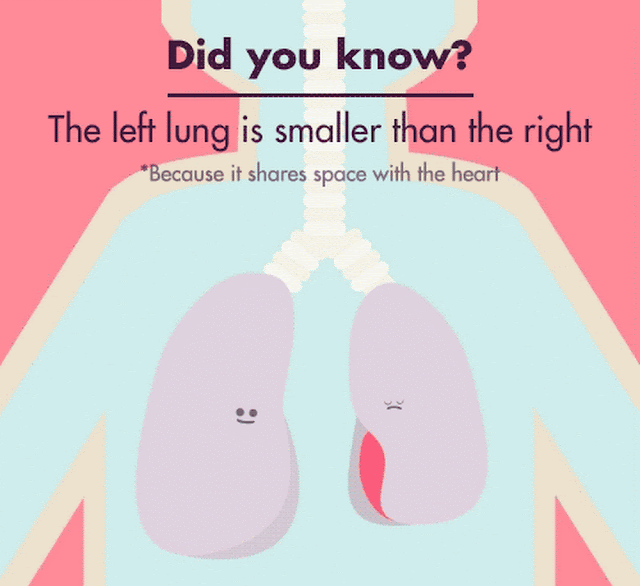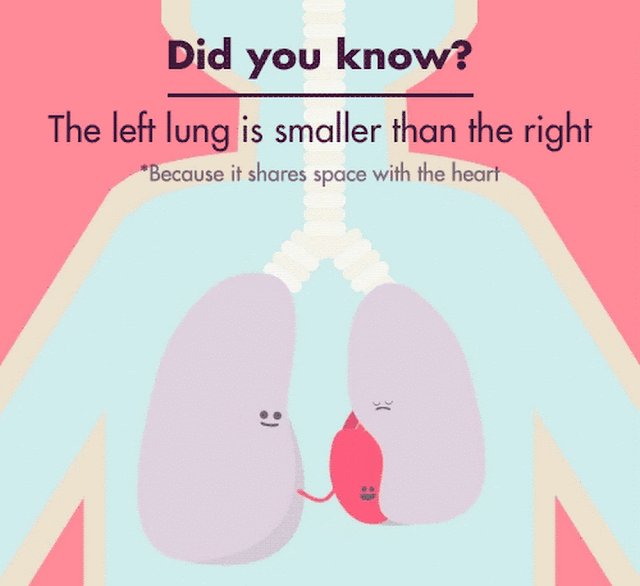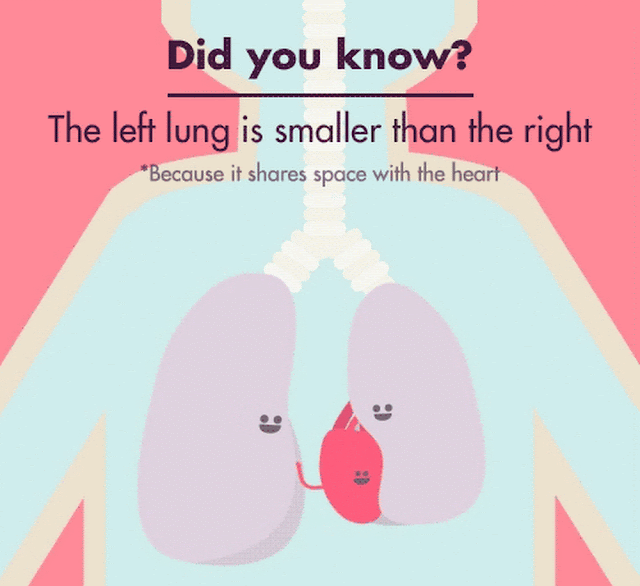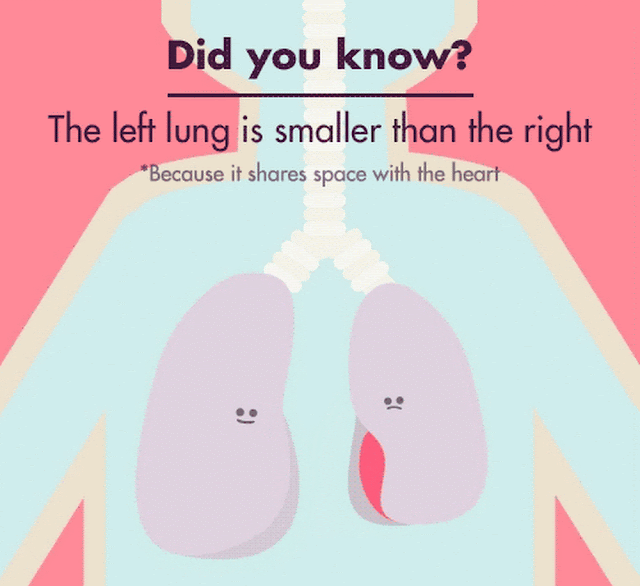
Did you know that your left lung is about 10 percent smaller than your right lung? It may sound surprising, but it’s true. Your lungs, the amazing organs responsible for oxygenating your blood and removing carbon dioxide, are not symmetrical. This anatomical difference between your lungs has intrigued scientists and medical professionals for years, leading to various studies and theories.
The size difference between the left and right lungs is due to the position of the heart within your chest cavity. The heart is positioned more towards the left side of your body, occupying space that would otherwise be taken up by the left lung. As a result, the left lung has to share space with the heart, causing it to be slightly smaller.
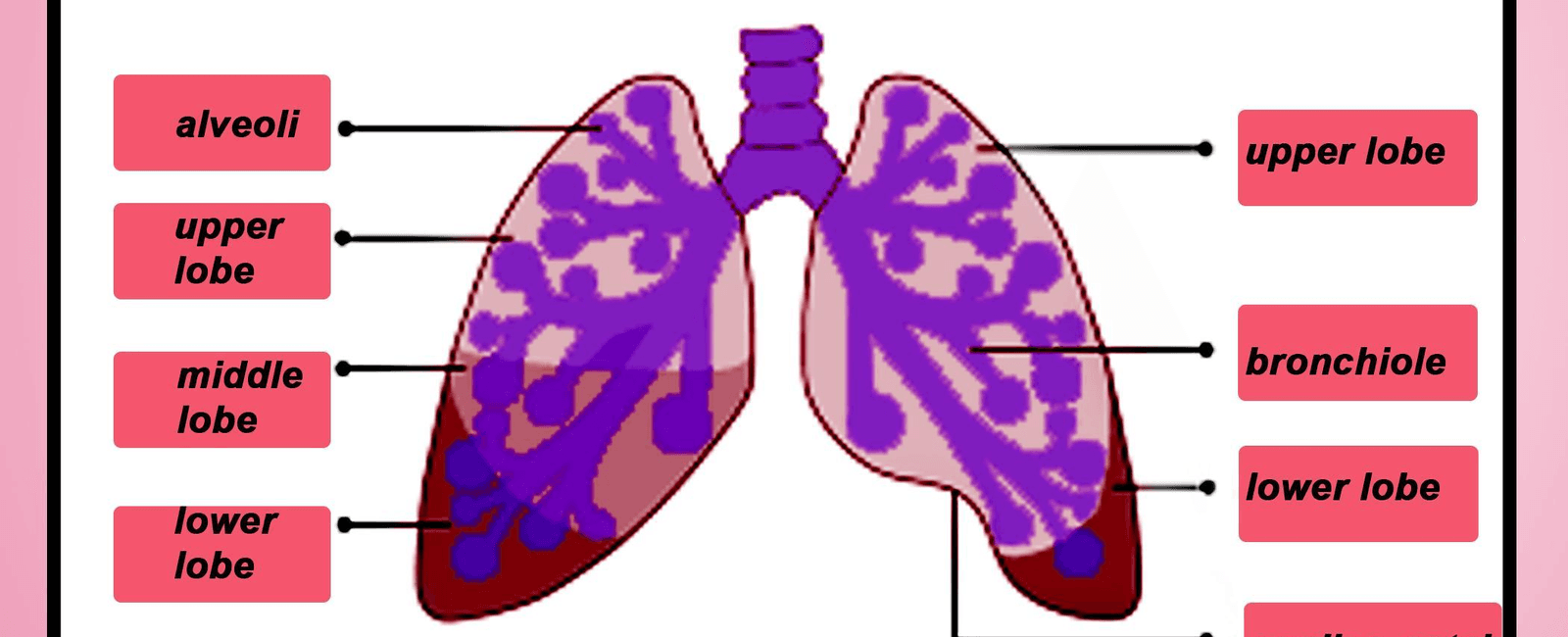
But don’t underestimate the left lung just because it’s smaller. Both lungs play crucial roles in your respiratory system and work together seamlessly to ensure the optimal exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The left lung has two lobes, while the right lung has three lobes, compensating for the size difference.

From an evolutionary perspective, this anatomical difference may have resulted from the need to accommodate the heart’s position and the complex network of blood vessels that connect the heart and lungs. Although the size difference is not significant enough to affect overall lung function in healthy individuals, it does highlight the intricacies of human anatomy.
Understanding the unique features and functions of the human body, such as the size difference between our lungs, helps us appreciate the complex nature of our physiology. These fascinating facts not only pique our curiosity but also provide valuable insight into the inner workings of our bodies.
Sources:
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

