You have taste receptors in the stomach intestines pancreas lungs anus testicles and the brain
Taste Receptors: Not Just in the Mouth, but Also in Unexpected Places
Did you know that taste receptors are not limited to your mouth? In fact, they can be found in various parts of your body such as the stomach, intestines, pancreas, lungs, anus, testicles, and even in the brain! Yes, you read it right. Your taste buds are not the only ones responsible for experiencing flavors and sensations. This fascinating fact opens up a whole new world of possibilities and understanding about how our bodies perceive and interact with the world.

Expanding Our Concept of Taste
Traditionally, taste has been associated with the sensation we experience when consuming food or drinks. However, recent scientific research has challenged this notion, revealing that taste receptors can be found in unexpected places throughout our body.
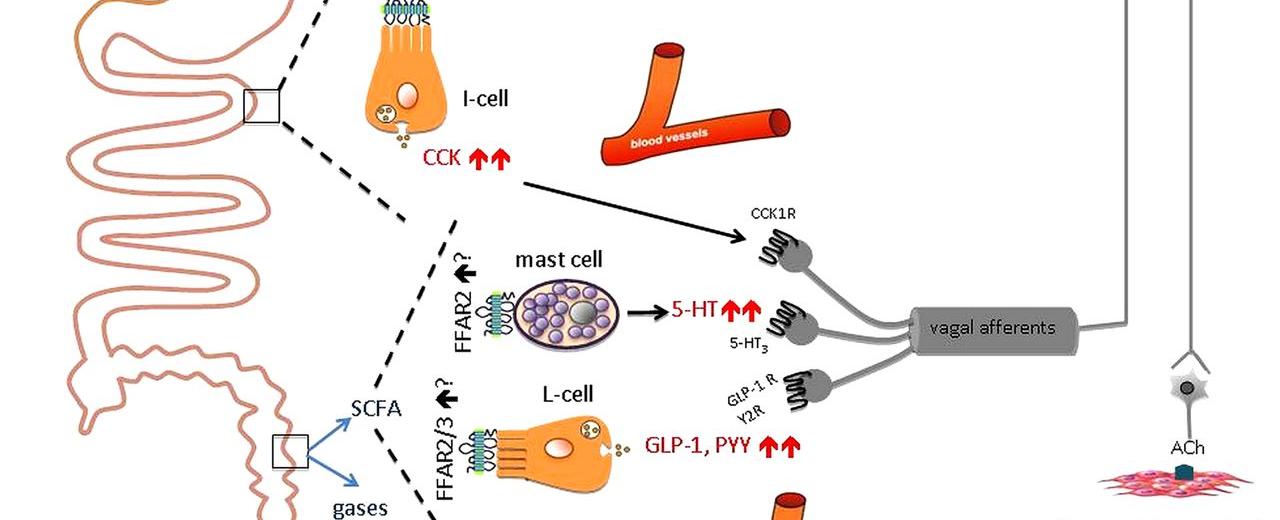
For instance, studies have shown that taste receptor cells are present in the stomach and intestines. These receptors act as chemical sensors, allowing these organs to detect and respond to different nutrients and compounds present in the food we consume. This suggests that our gut can actually taste and identify various flavors, providing a deeper understanding of how our digestive system works.
But the surprises don’t end there. Taste receptors have also been found in the lungs, testicles, anus, pancreas, and even the brain. While the functionality of these taste receptors in these organs is still being explored, it opens up a whole new realm of possibilities when it comes to understanding our body’s complex relationship with taste and flavor.
Taste Receptors and Unexpected Connections
The discovery of taste receptors in unexpected places has led scientists to explore potential connections and implications for various health conditions and behaviors.
For example, researchers have found taste receptors in the testicles, which are involved in the detection of sweet flavors. This finding raises interesting questions about the link between taste perception and fertility. It has been suggested that these sweet taste receptors in the testicles could play a role in sperm development and function. This connection opens up new avenues for further investigation and understanding of male fertility issues.
The Brain’s Role in Taste
The presence of taste receptors in the brain further emphasizes the brain-gut connection. Alongside the receptors in the mouth and gastrointestinal tract, taste receptors in the brain contribute to our overall experience of taste and flavor perception. This complex network of taste receptors helps our brain process and interpret the signals it receives, allowing us to discern and appreciate different tastes.
Furthermore, the discovery of taste receptors in the brain highlights the intricate relationship between taste, emotions, and memory. The sensory experience of taste can evoke powerful emotional responses and trigger memories associated with certain flavors. Understanding the mechanics behind these processes can provide valuable insights into conditions like food addiction, eating disorders, and even neurodegenerative diseases.
Conclusion
The presence of taste receptors in unexpected parts of our body unveils a fascinating aspect of human biology. This remarkable discovery challenges our traditional understanding of taste and opens up new avenues of research. By expanding our knowledge of taste perception, scientists are gaining a deeper understanding of how our body interacts with the world around us. From the gut to the brain, taste receptors play a crucial role in our daily experiences, connecting various organs and emotions, and impacting our overall well-being.
Source: businessinsider.com
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff


