Which atmospheric gas is the most common nitrogen
Which atmospheric gas is the most common? Nitrogen.

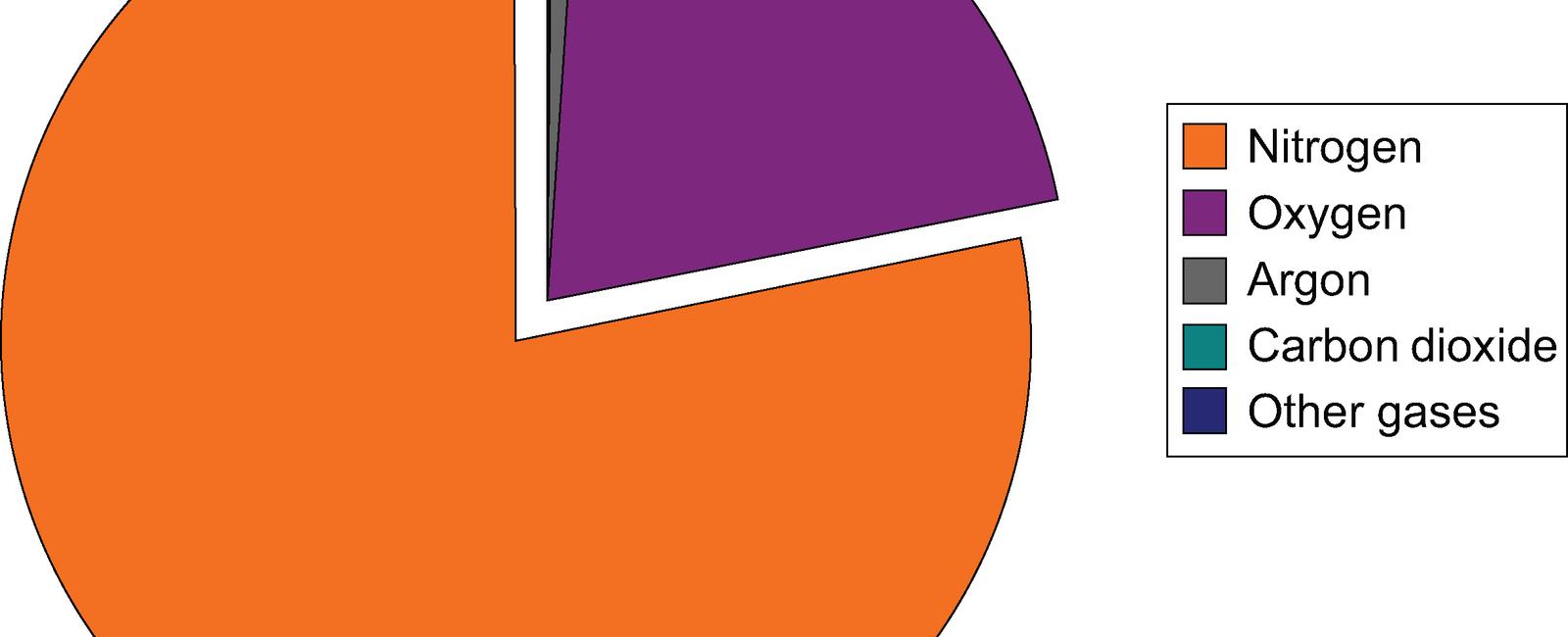
Nitrogen, the most abundant atmospheric gas on our planet, plays a vital role in shaping the Earth’s atmosphere and maintaining various ecosystems. Comprising around 78% of the air we breathe, this odorless and colorless gas is essential for supporting life as we know it.
The Dominant Player in Earth’s Atmosphere
According to NASA, nearly four-fifths of the Earth’s atmosphere is composed of nitrogen gas (N₂). Its abundance surpasses all other gases present in the atmosphere, including oxygen, which makes up approximately 21%. The remaining 1% is made up of trace gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, neon, helium, methane, krypton, hydrogen, and ozone.
Nitrogen’s Sources and Cycles
The nitrogen gas that surrounds us primarily originates from natural processes such as volcanic emissions, oceanic activities, and microbial activity in soils. Additionally, human activities contribute to the release of nitrogen into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels and agricultural activities.
Nitrogen goes through various cycling processes in the atmosphere. Nitrogen fixation is the process in which nitrogen is converted into a usable form by certain bacteria in the soil or legume plants. This fixed nitrogen then enters the food chain and is eventually released back into the atmosphere through a process called denitrification, which is facilitated by other soil bacteria.
Impact on Life and Ecosystems

The abundance of nitrogen gas has significant implications for the planet’s ecosystems and life forms. It is a critical nutrient for plants, playing a key role in their growth and development. Nitrogen is a primary component of amino acids, proteins, and DNA, making it necessary for the production of agricultural crops and sustaining diverse plant life.
Beyond the plant kingdom, nitrogen plays a pivotal role in the animal kingdom. Herbivores obtain nitrogen by consuming plants, while carnivores obtain it indirectly by consuming herbivores. Nitrogen is thus incorporated into the bodies of animals and contributes to their growth and survival.
Nitrogen’s Environmental Impact
While nitrogen is essential for life, excessive amounts can have negative consequences. Human activities, such as the use of synthetic fertilizers and the burning of fossil fuels, have substantially increased the amount of nitrogen released into the environment. This excess nitrogen can lead to environmental issues such as eutrophication, smog formation, and water pollution.
Eutrophication occurs when an excessive amount of nitrogen enters bodies of water, causing rapid algae growth. As these algae die, their decomposition depletes the oxygen content in the water, leading to oxygen-starved zones and harming aquatic life.
Furthermore, nitrogen compounds released into the atmosphere contribute to the formation of smog, negatively impacting air quality and human health in urban areas. Nitrogen pollution in groundwater can also contaminate drinking water supplies, posing risks to both humans and animals.
The Fragile Balance of Atmospheric Gases
Nitrogen, as the most common atmospheric gas, plays an indispensable role in Earth’s systems. Its abundance sustains life and enables vital processes, such as plant growth and nutrient cycling. However, the human-induced excess release of nitrogen can lead to environmental problems.
As stewards of the planet, it is essential to strike a balance and develop sustainable practices to minimize the negative impacts of nitrogen on our environment. By understanding the significance of nitrogen and its intricate interactions within the atmosphere, we can work towards a healthier and more harmonious coexistence with the natural world.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

