When referring to a medical imaging technique what does mri stand for magnetic resonance imaging
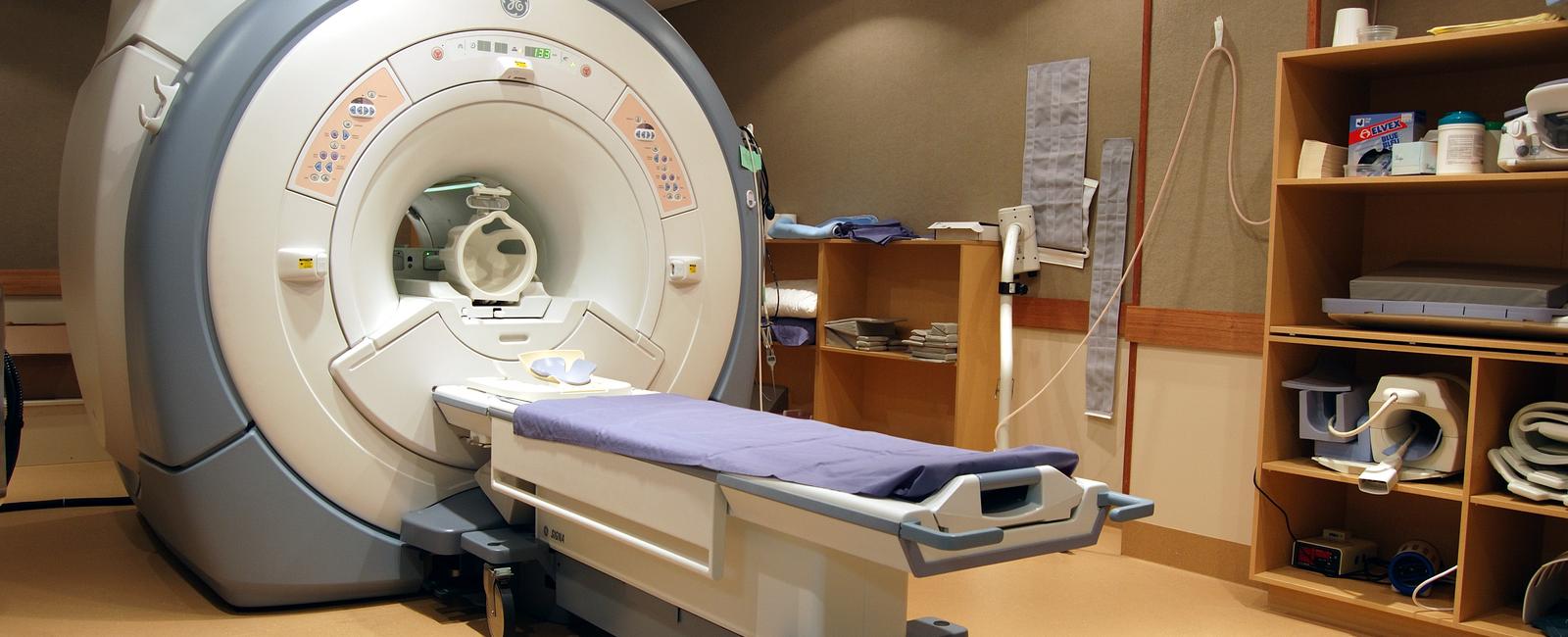
What Does MRI Stand For? Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
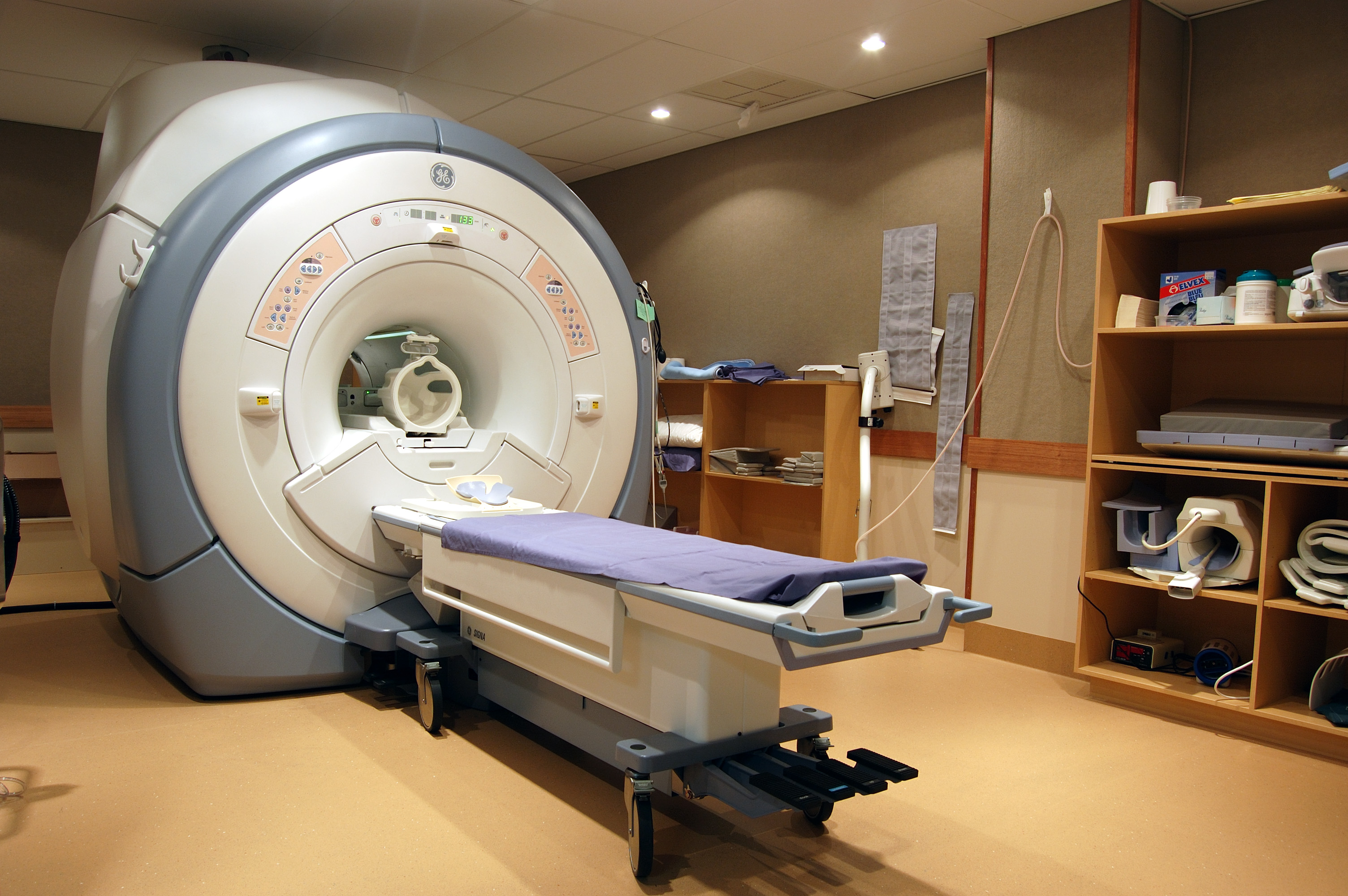
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a widely used medical imaging technique that provides detailed images of the internal structures of the body. It plays a crucial role in helping physicians diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, including cancer, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal injuries.
MRI utilizes a combination of powerful magnets and radio waves to generate highly detailed images of the body’s organs, tissues, and bones. Unlike other imaging techniques such as X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for patients, particularly for those who may require multiple scans over time.
The acronym “MRI” stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. The term “magnetic resonance” refers to the phenomenon of atomic nuclei aligning themselves when exposed to a strong magnetic field. By manipulating these aligned nuclei using radio waves, a magnet in the MRI machine generates a series of signals that are then processed by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body.
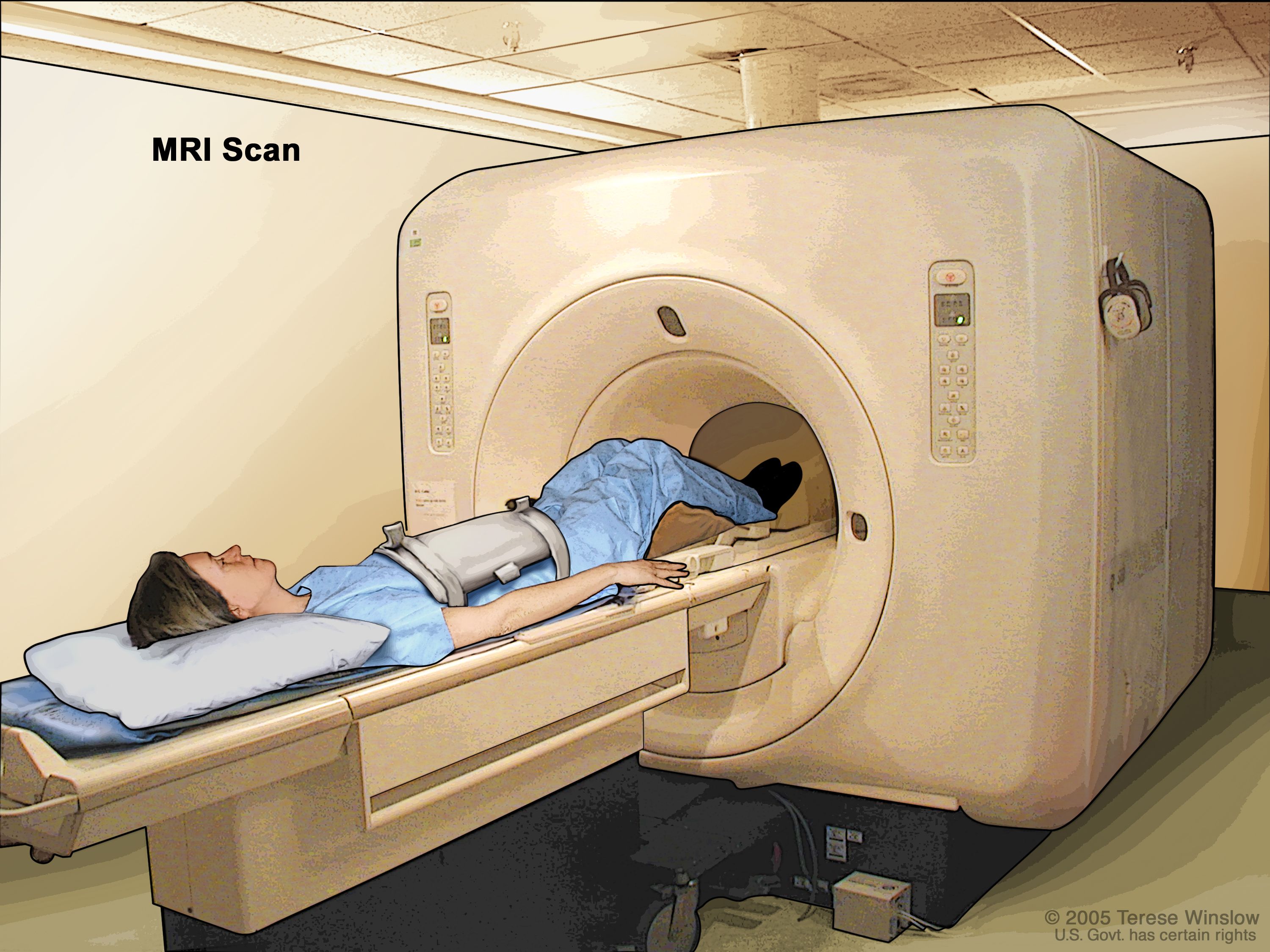
MRI is a versatile imaging technique that can provide valuable diagnostic information. It allows doctors to visualize soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, heart, and internal organs, with excellent contrast and resolution. This level of detail enables them to distinguish between healthy and abnormal tissues, identify tumors, detect abnormalities in blood vessels, and evaluate injuries or diseases affecting the joints, ligaments, and tendons.
The non-invasive nature of MRI makes it a preferred choice for diagnosing conditions in sensitive areas, like the brain or spinal cord. Additionally, MRI is often used in combination with other imaging techniques, such as functional MRI (fMRI), which measures the changes in blood flow to identify brain activity, or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), which focuses on blood vessels’ structure and blood flow.
MRI scans are performed using specialized equipment, including a large cylindrical magnet, radiofrequency coils, and a computer system to generate, process, and store the images. The patient lies on a movable table that slides into the opening of the MRI scanner. During the scan, they need to remain still to prevent blurring of the images.
With its ability to provide detailed information and aid in the diagnosis and treatment planning process, MRI has become an essential tool in modern medicine. It allows physicians to make accurate assessments, monitor the progress of diseases, and determine the effectiveness of treatments.
In conclusion, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) stands for a medical imaging technique that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Its non-invasive nature and high-resolution imaging capabilities make it a valuable diagnostic tool in various medical fields.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

