What is the name used for the study of earthquakes seismology
The Fascinating Field of Seismology
Earthquakes have captivated the human imagination for centuries. These powerful and unpredictable natural events have the potential to cause widespread devastation and loss of life. Scientists dedicate their lives to understanding and studying earthquakes in the field known as seismology.
Seismology, derived from the Greek word “seismos” (meaning “earthquake”) and “logos” (meaning “study” or “word”), is the scientific discipline that explores the behavior and characteristics of earthquakes. Seismologists analyze various aspects of earthquakes, including their causes, effects, and ways to mitigate their impact on human life and infrastructure.
The Study of Earthquakes
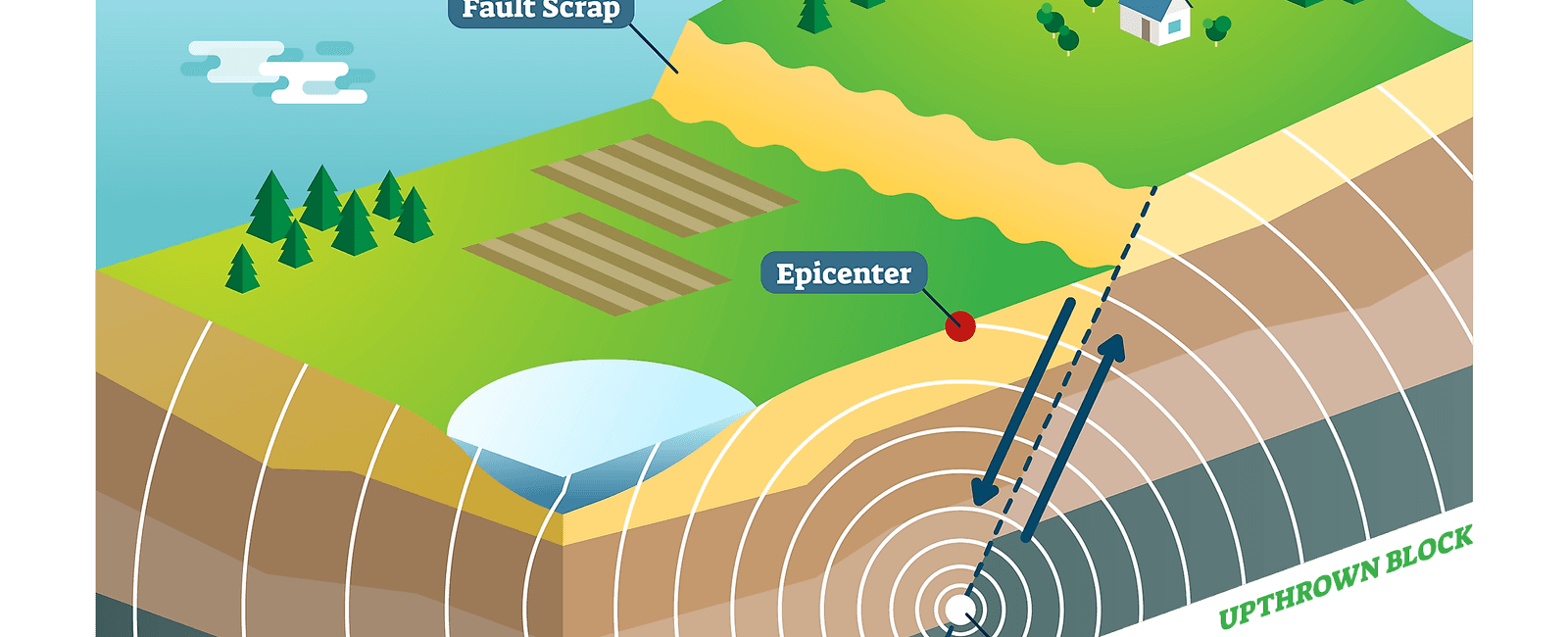
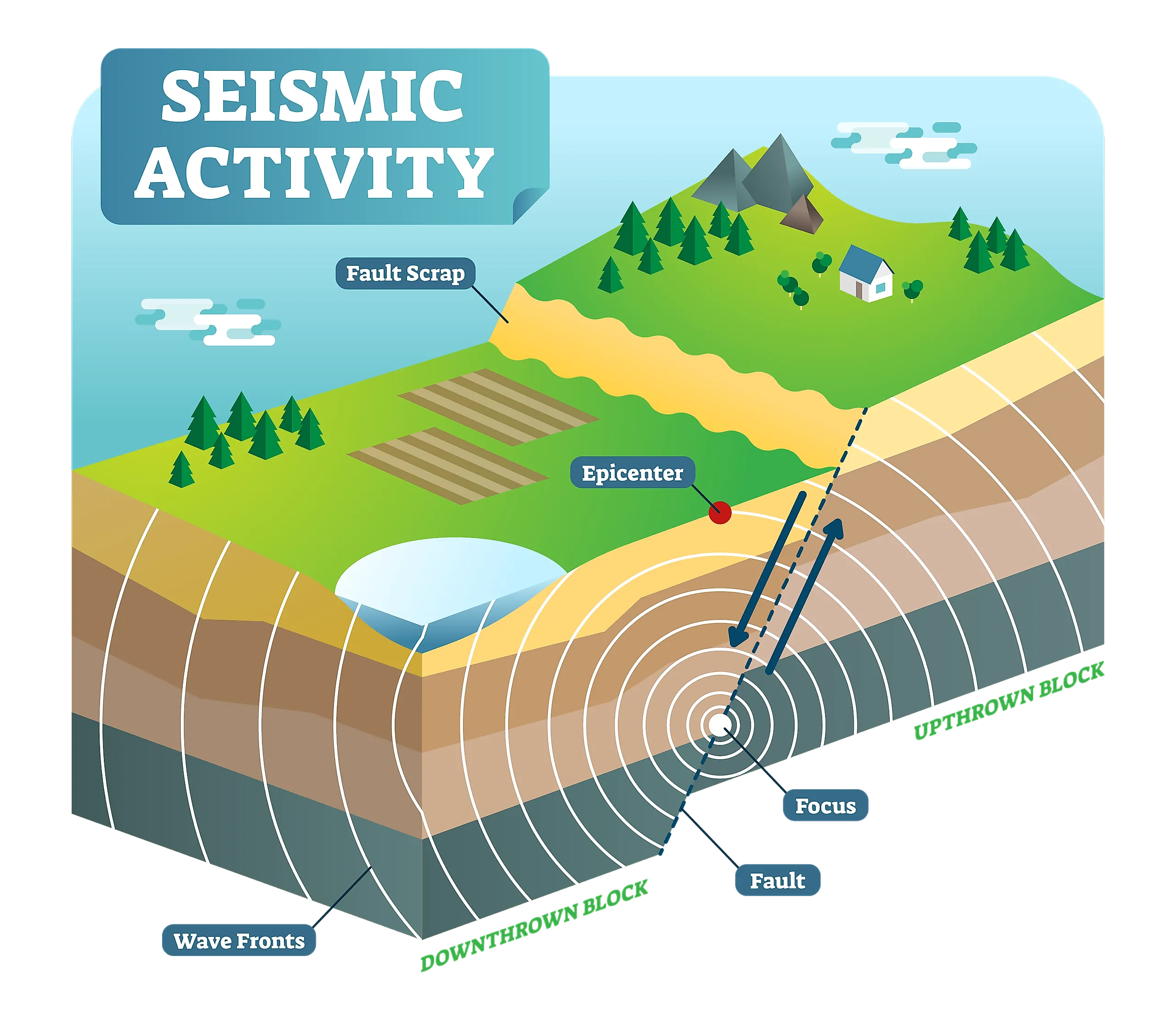
Seismologists employ various tools and techniques to investigate earthquakes. One of the essential instruments used in seismology is the seismograph, which records the ground motion caused by seismic waves. These waves propagate through the Earth’s interior and provide crucial information about the location and magnitude of an earthquake.
By examining and interpreting the data collected by seismographs, scientists can determine the exact location of an earthquake’s epicenter and estimate the amount of energy released during a seismic event. This data aids in mapping earthquake-prone areas and improving our understanding of the Earth’s geology.
The Causes of Earthquakes
Understanding the factors that cause earthquakes is a fundamental aspect of seismology. Most earthquakes occur near tectonic plate boundaries, where massive pieces of the Earth’s crust interact with one another. The movement and interaction of these plates generate immense quantities of energy that can be released as seismic waves.
Tectonic earthquakes, which account for the majority of seismic activity, occur when stress builds up along faults. When the stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, the accumulated energy is released, resulting in an earthquake. However, earthquakes can also be triggered by volcanic activity, human-induced activities such as mining or reservoir-induced seismicity, and even natural factors like landslides.
The Impact of Earthquakes
Earthquakes can have catastrophic consequences, causing the destruction of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructures. They can also lead to landslides, tsunamis, and secondary hazards like fires or gas leaks. Seismologists work towards understanding and predicting the impact of these events to develop strategies for disaster preparedness and response.
By studying data from seismographs, seismologists can model the behavior and effects of earthquakes. Such understanding helps in devising building codes, implementing early warning systems, and formulating emergency plans to minimize casualties and damage.
The Ongoing Research in Seismology
Seismology is a constantly evolving field. Scientists continue to explore new technologies and methodologies to enhance earthquake detection and forecasting capabilities. Advanced techniques like tomography and space-based observations contribute to our understanding of the Earth’s interior and the processes that trigger earthquakes.
The information collected from ongoing seismological research allows seismologists to improve our knowledge of earthquake hazards and the chances of future events occurring in particular regions. Ultimately, the aim is to foster safer communities by equipping societies with the necessary tools to mitigate the impact of earthquakes.
The Vital Role of Seismology in Society
Through seismology, society gains a deeper comprehension of earthquakes and their complexities. This knowledge facilitates more effective disaster management strategies, aids in the development of resilient infrastructure, and helps protect vulnerable populations from the devastating consequences of seismic activities.
Seismologists continuously strive to broaden our understanding of earthquakes, in the hope of ultimately generating early warning systems and improved response strategies. The field of seismology plays a key role in ensuring the safety and resilience of communities worldwide in the face of seismic events.

Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

