What hormone allows the cells in your body to absorb sugar from your blood insulin
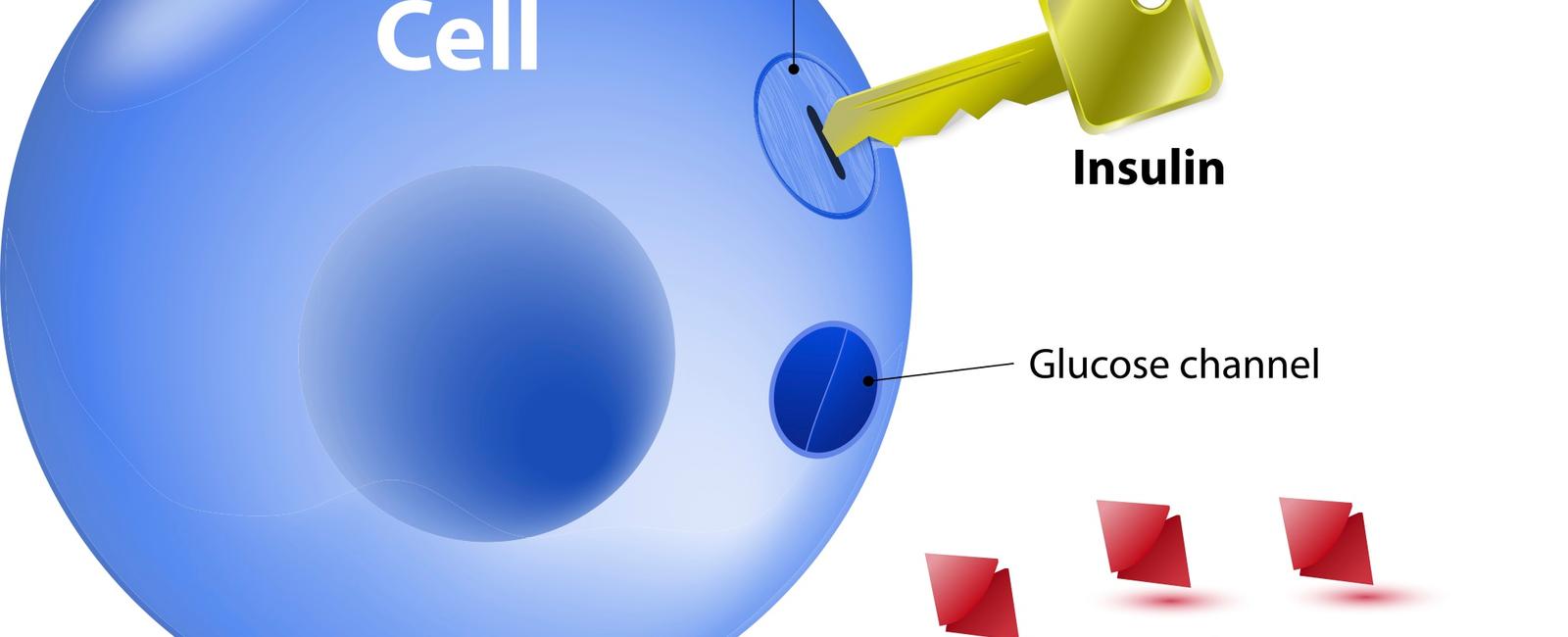
What hormone allows the cells in your body to absorb sugar from your blood? Insulin.
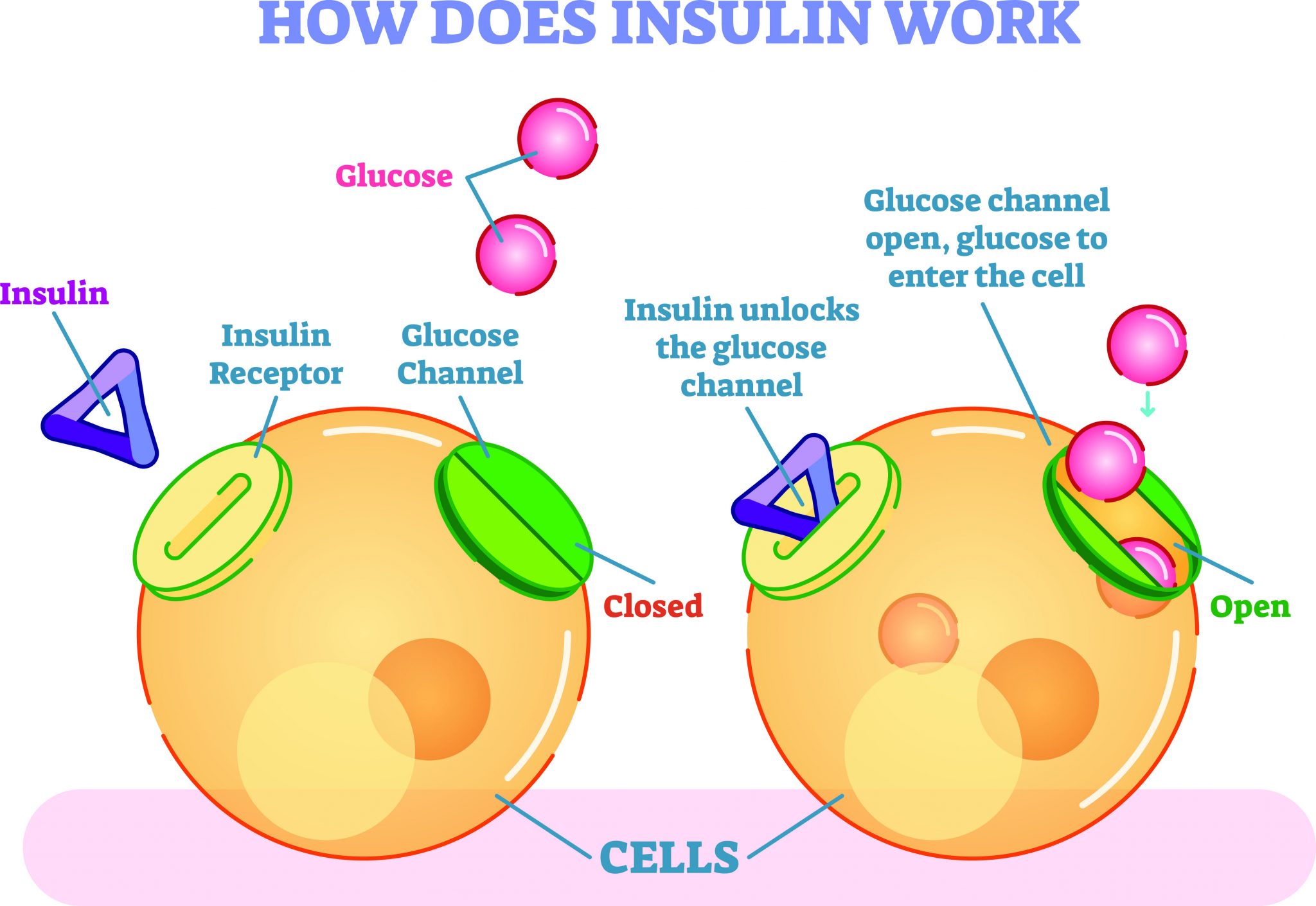
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating the amount of sugar in your blood. It allows the cells in your body to absorb glucose from your bloodstream, providing them with the energy they need to function effectively.
When you eat a meal, especially one high in carbohydrates, the sugar levels in your blood rise. In response to this rise, the pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin acts as a key that unlocks the cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy production.
Without sufficient insulin or if your body’s cells become resistant to insulin, glucose cannot efficiently enter the cells. As a result, the sugar remains in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels, also known as hyperglycemia. This can eventually result in the development of diabetes.
Insulin also plays a vital role in preventing the breakdown of stored glucose in the liver. It inhibits the liver from releasing excess glucose into the bloodstream, ensuring a balanced blood sugar level.
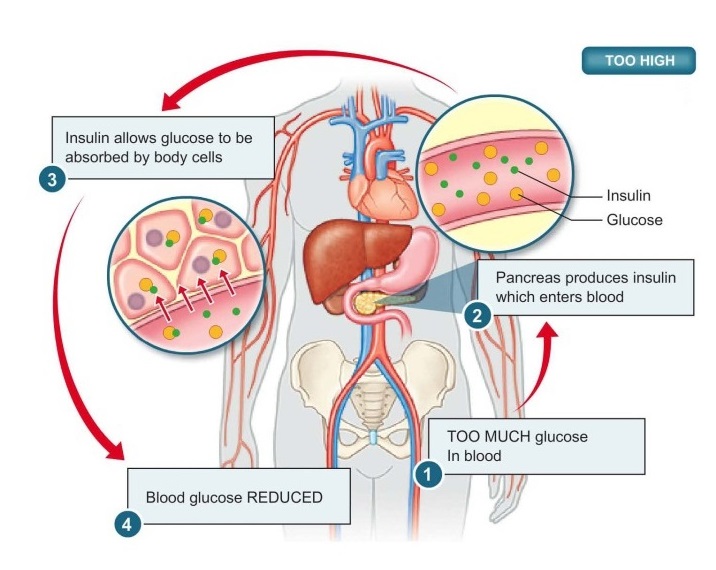
The production and release of insulin are tightly regulated in a process that involves multiple factors. After eating, particularly when consuming carbohydrates, the pancreas releases an appropriate amount of insulin to maintain blood sugar levels within a normal range.
In individuals with diabetes, this regulation is disrupted, leading to either insufficient insulin production or inadequate response of the body’s cells to insulin. This can result in high blood sugar levels, which can have detrimental effects on various organs and systems in the body.
The importance of insulin in maintaining proper blood sugar levels cannot be understated. It allows cells to efficiently use the glucose present in the bloodstream, preventing the harmful effects of high blood sugar. While medications can help manage blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes, insulin therapy is often required for those with type 1 diabetes and sometimes for those with type 2 diabetes as well.
In conclusion, insulin is the hormone that allows the cells in your body to absorb sugar from your blood. It plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels and providing the body’s cells with the energy they need to function.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

