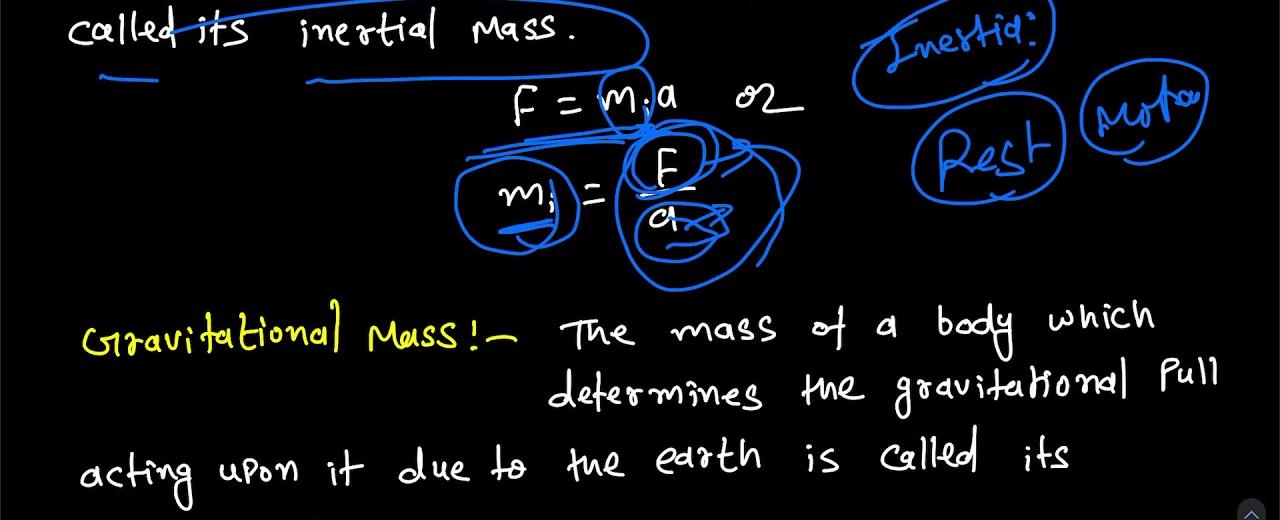
There are two types of mass inertial mass and gravitational mass
Two Types of Mass: Inertial Mass and Gravitational Mass


When it comes to mass, we often think of it as a measure of the amount of matter an object possesses. However, did you know that there are actually two types of mass? These are inertial mass and gravitational mass. Let’s take a closer look at each of them and understand their significance.
Inertial Mass
Inertial mass, as the name suggests, is associated with an object’s resistance to changes in its motion. It determines how much force is required to accelerate or decelerate an object. If two objects of different masses are subjected to the same force, the object with a higher inertial mass will experience a smaller acceleration compared to the one with a lower inertial mass.
Consider a scenario where you’re pushing two identical boxes, one made of cardboard and the other made of solid wood. Although they have the same gravitational mass, you’ll notice that the wooden box requires more force to get it moving. This is because the wooden box has a higher inertial mass, showcasing its resistance to changes in motion.
Gravitational Mass
Gravitational mass, on the other hand, is related to an object’s response to gravitational forces. It determines the strength of the gravitational attraction an object experiences towards another massive object. According to Newton’s law of gravitation, the gravitational force between two objects is directly proportional to their gravitational masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
To understand this concept more clearly, let’s consider a scenario where a small and a large object are held at the same height above the ground. Due to their different gravitational masses, the larger object will experience a stronger gravitational force towards the Earth compared to the smaller object.
The Equivalence Principle
While inertial mass and gravitational mass may seem distinct, they are remarkably equivalent to each other. This fascinating connection is known as the equivalence principle. According to this principle, the ratio of inertial mass to gravitational mass remains constant for all objects, regardless of their composition or size.
The equivalence principle forms a fundamental basis for Einstein’s general theory of relativity. It suggests that gravitational forces are not a result of a mysterious “gravitational pull” but rather the consequence of spacetime curvature caused by massive objects.
In conclusion, understanding the two types of mass, inertial mass and gravitational mass, allows us to comprehend how objects respond to forces and gravitational interactions. While inertial mass determines an object’s resistance to changes in motion, gravitational mass determines the strength of its gravitational attraction. The equivalence principle further highlights the deep connection between these two properties, revealing the profound implications it has on our understanding of gravity.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

