The stomach can break down goat s milk faster than cow s milk

The Stomach Can Break Down Goat’s Milk Faster Than Cow’s Milk
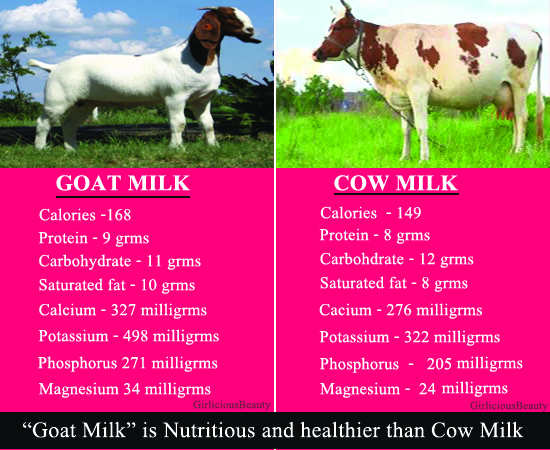
Goat’s milk and cow’s milk have been consumed by humans for centuries, and both have their unique set of qualities. However, when it comes to digestion, the stomach has a different approach to breaking down these two types of milk. Recent studies have revealed that the stomach can break down goat’s milk faster than cow’s milk, making it a more easily digestible option for certain individuals.
Goat’s milk has a composition that closely resembles human breast milk, making it more compatible with our digestive system. This similarity in composition allows the stomach to quickly break down the proteins and fats present in goat’s milk, resulting in easier digestion and reduced discomfort for those with sensitive stomachs.
On the other hand, cow’s milk contains a higher amount of lactose, a natural sugar present in milk. The human body requires an enzyme called lactase to break down lactose into simpler forms for absorption. However, as individuals age, the production of lactase decreases, making it difficult for some individuals to digest lactose properly. This lactose intolerance can cause symptoms like bloating, gas, and diarrhea.

The faster digestion of goat’s milk can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the fat globules in goat’s milk are smaller and more homogenized, which allows them to be broken down more easily in the stomach. This results in a smoother digestion process, reducing the chances of discomfort or indigestion.
Moreover, the proteins present in goat’s milk, such as casein and whey, are structurally different from those found in cow’s milk. Goat’s milk contains a higher proportion of beta-casein A2, which is considered to be easier to digest compared to the beta-casein A1 found in cow’s milk. This structural difference may contribute to the faster breakdown of proteins in goat’s milk.
In addition to its easier digestibility, goat’s milk offers several other benefits. It is a rich source of essential nutrients like calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D. These nutrients are crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth, making goat’s milk an excellent choice for individuals looking to improve their bone health.
Furthermore, goat’s milk also contains higher levels of medium-chain fatty acids, such as caprylic and capric acids. These fatty acids are easily absorbed and utilized by the body, providing a quick source of energy. Additionally, they have antimicrobial properties, which can help support a healthy digestive system.
In conclusion, due to its composition and structural properties, the stomach can break down goat’s milk faster than cow’s milk. This quick digestion makes goat’s milk a favorable option for those with sensitive stomachs or lactose intolerance. Moreover, goat’s milk offers various nutritional benefits, making it an excellent choice for individuals seeking a nutrient-rich and easily digestible alternative to cow’s milk.
Sources:
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

