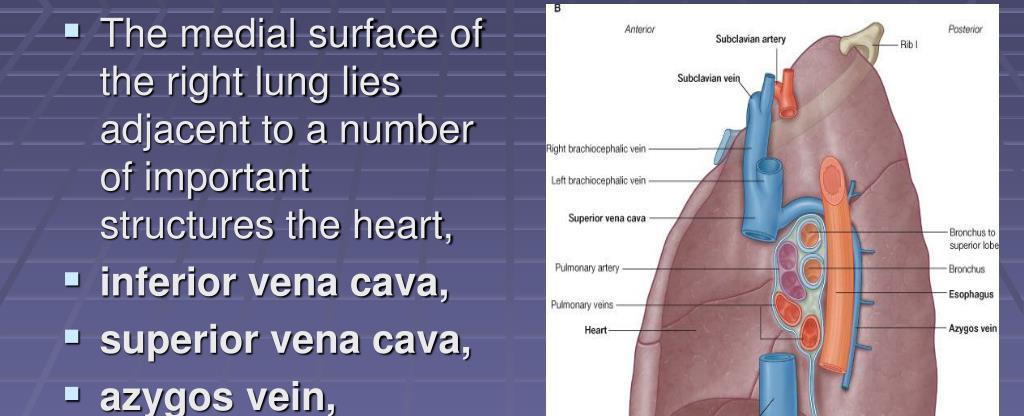
The right lung of a human is larger than the left one this is due to the placement of the heart
The Right Lung of a Human is Larger Than the Left One
The human respiratory system is a complex and intricate network of organs that work together to ensure the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide. One of the intriguing facts about our lungs is that the right lung is larger than the left one. This size difference is primarily due to the placement of the heart in our chest cavity.

The human heart is positioned slightly towards the left side of the chest, which naturally pushes against the left lung. This pressure exerted by the heart causes the left lung to be smaller and to have a slightly different shape compared to its counterpart.
To better understand this anatomical discrepancy, let’s delve into the details. The respiratory system consists of various components, including the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. The trachea divides into two bronchi, and each bronchus connects with a lung. The right bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the left bronchus. This difference is a direct result of the right lung’s larger size.
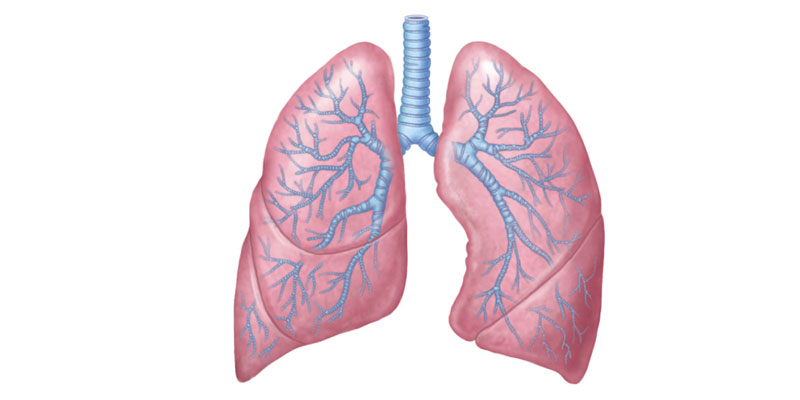
The right lung is divided into three lobes: the superior, middle, and inferior lobes. In contrast, the left lung is slightly smaller and is divided into two lobes: the superior and inferior lobes. Despite the size difference, both lungs have a similar function, which is to facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of respiration.
Interestingly, the right lung not only compensates for its larger size but also performs additional functions. It has a wider diameter, allowing it to supply oxygen to a larger volume of lung tissue. The larger right lung can accommodate the heart, which sits slightly to its left, while still ensuring the necessary space for efficient function.
While the size difference between the right and left lungs may seem peculiar, it is an example of the human body’s remarkable adaptability and efficiency. The asymmetrical structure allows for the optimal functioning of both the respiratory and circulatory systems within our body.
In conclusion, the larger size of the right lung in comparison to the left lung is a result of the heart’s placement within the chest cavity. This anatomical characteristic enables the lungs and the heart to work together harmoniously, ensuring the proper exchange of gases and maintaining our respiratory health.
Source: Still Unfold
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

