The pacific ocean has the ability to affect the climate of the entire world
The Impact of the Pacific Ocean on Global Climate

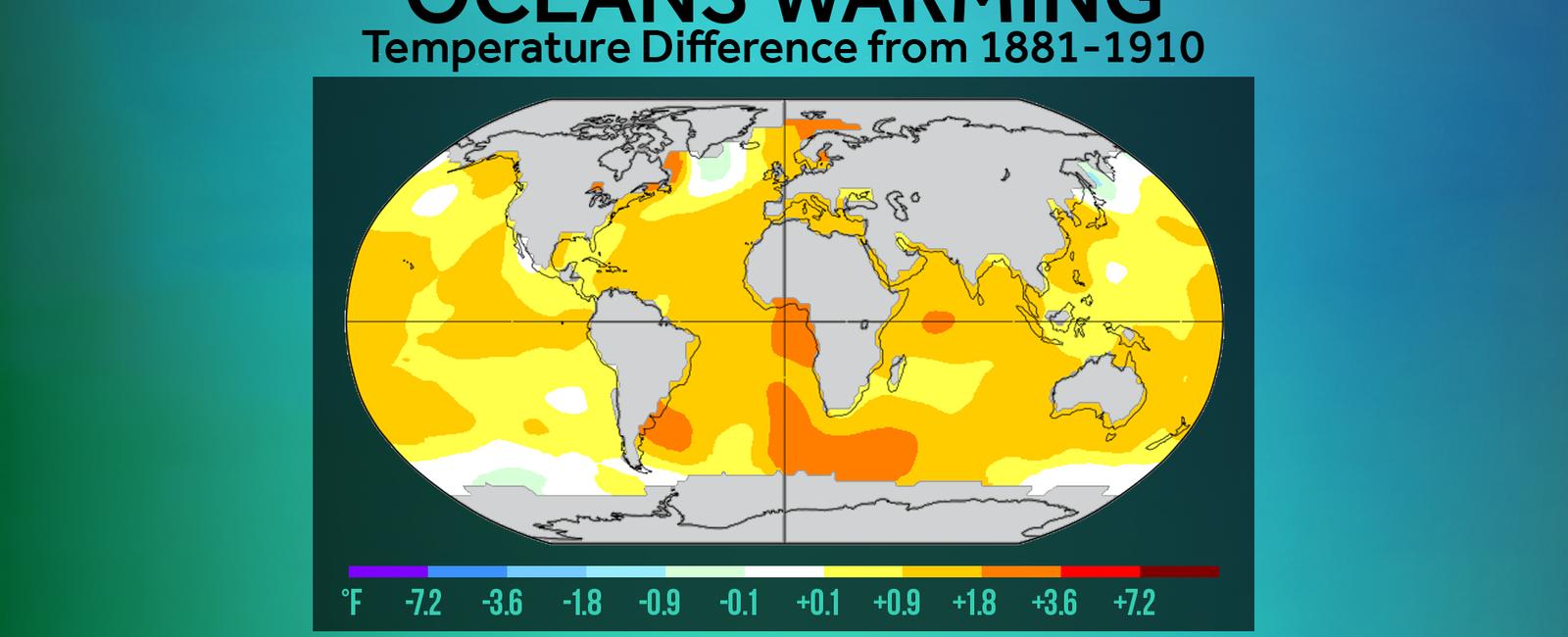
The Pacific Ocean, known as the largest and deepest ocean on Earth, exerts a significant influence on the climate patterns across the globe. Its immense size and dynamic nature make it a critical component in our planet’s climate system. The interactions between the Pacific Ocean and the atmosphere have far-reaching implications for weather patterns, ocean currents, and overall climate conditions worldwide.
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation Phenomenon
One of the most prominent ways in which the Pacific Ocean impacts global climate is through a phenomenon known as El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). ENSO is a recurring climate pattern characterized by the warming and cooling of the tropical Pacific Ocean surface waters. It has a profound effect on weather patterns over vast areas, influencing temperature and precipitation levels across continents.
During El Niño years, warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures prevail in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. This shift in temperature elevates heat and moisture into the atmosphere, altering global weather patterns. Regions that are typically wet may experience droughts, while areas that are usually dry may encounter heavy rainfall. These extreme variations in weather conditions can have significant impacts on agriculture, wildlife, and overall ecosystem health.
Conversely, the La Niña phase of ENSO occurs when the Pacific Ocean surface waters are cooler than average. La Niña often brings about opposite effects to El Niño, resulting in cooler and wetter conditions in some regions, while others experience drier weather and increased wildfire risks. These oscillating climate patterns have implications far beyond the Pacific Ocean basin, influencing weather phenomena, such as monsoons and hurricanes, on a global scale.
Pacific Ocean Currents and Climate Regulation

In addition to ENSO, the Pacific Ocean’s intricate network of currents plays a crucial role in regulating global climate. The ocean currents act as conveyer belts, transporting heat from the equator towards the poles. The Pacific’s most well-known current, the North Pacific Gyre, circulates water in a clockwise direction, influencing climate in both the northern and southern hemisphere.
The warm waters brought by ocean currents have a direct impact on coastal climates. For instance, the west coasts of North and South America experience a marine climate, characterized by cooler summers and milder winters due to the influence of the cold California Current and the Humboldt Current, respectively. Similarly, the Asian monsoon pattern is heavily influenced by Pacific Ocean currents, as warm ocean waters provide the necessary moisture for the monsoon rains.
Feedback Mechanisms and Global Climate Change
The Pacific Ocean also acts as a crucial player in the ongoing climate change crisis. Rising global temperatures directly affect the Pacific Ocean, leading to the melting of polar ice caps and resulting in sea-level rise. The warming waters contribute to the intensification of extreme weather events, such as tropical storms and hurricanes. Additionally, changes in ocean temperature and chemistry alter marine ecosystems, putting stress on coral reefs and marine biodiversity.
Furthermore, the Pacific Ocean plays a vital role in regulating atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. It serves as a vast carbon sink, absorbing significant amounts of CO2 from the atmosphere through biological processes like photosynthesis and physical processes such as mixing and upwelling. This natural absorption helps mitigate climate change to some extent by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
In conclusion, the Pacific Ocean’s impact on global climate cannot be underestimated. Through phenomena like El Niño-Southern Oscillation, intricate ocean currents, and feedback mechanisms, this vast body of water governs weather patterns and influences climate conditions on a global scale. Understanding and monitoring the Pacific Ocean’s dynamics is crucial for predicting and adapting to climate change, ensuring the long-term preservation of the planet’s climate balance.
Source:
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

