The hyoid bone in your throat is the only bone in your body not attached to any other
The Unattached Bone: Exploring the Fascinating Hyoid Bone in Your Throat
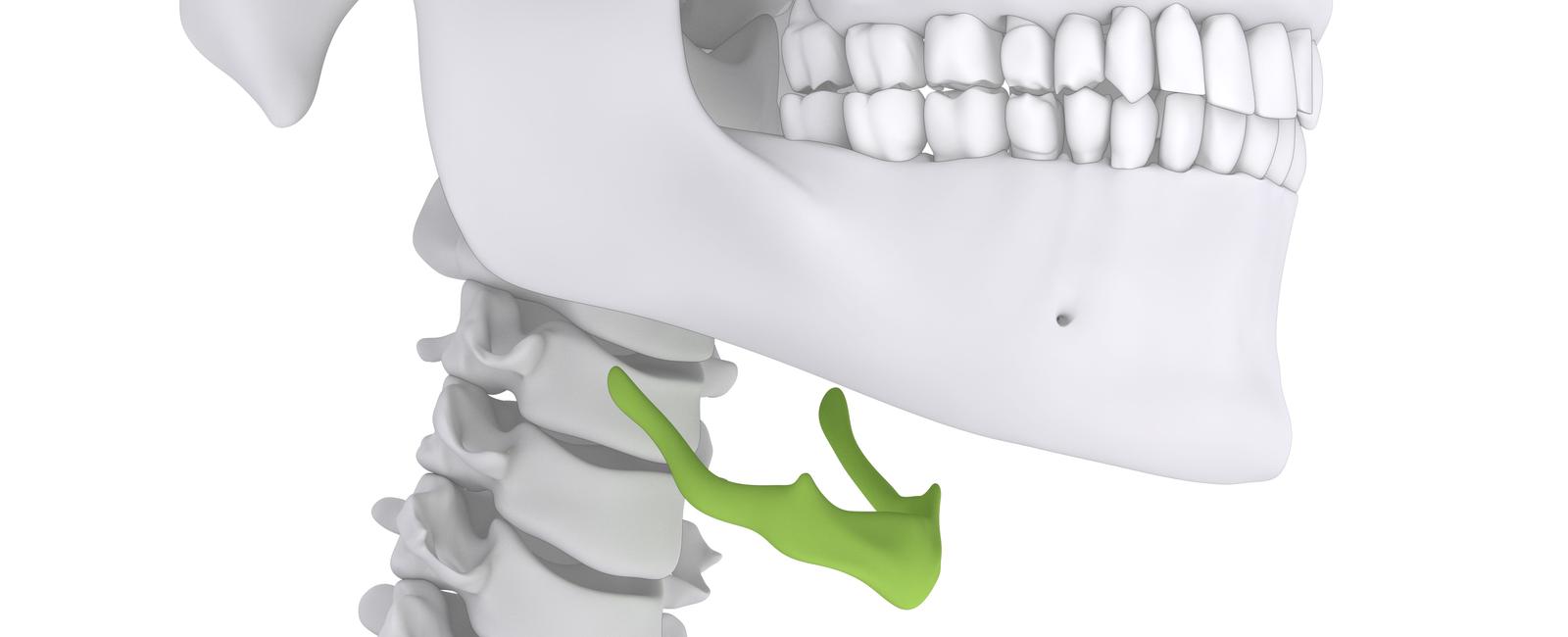
The human body is an intricate marvel, with bones providing the foundation and structure upon which it thrives. Each bone plays a crucial role in maintaining shape, supporting movement, and protecting vital organs. However, amidst this interconnected skeletal system, there exists a solitary bone that stands alone - the hyoid bone. Remarkably, the hyoid bone in your throat is the only bone in your body not attached to any other.
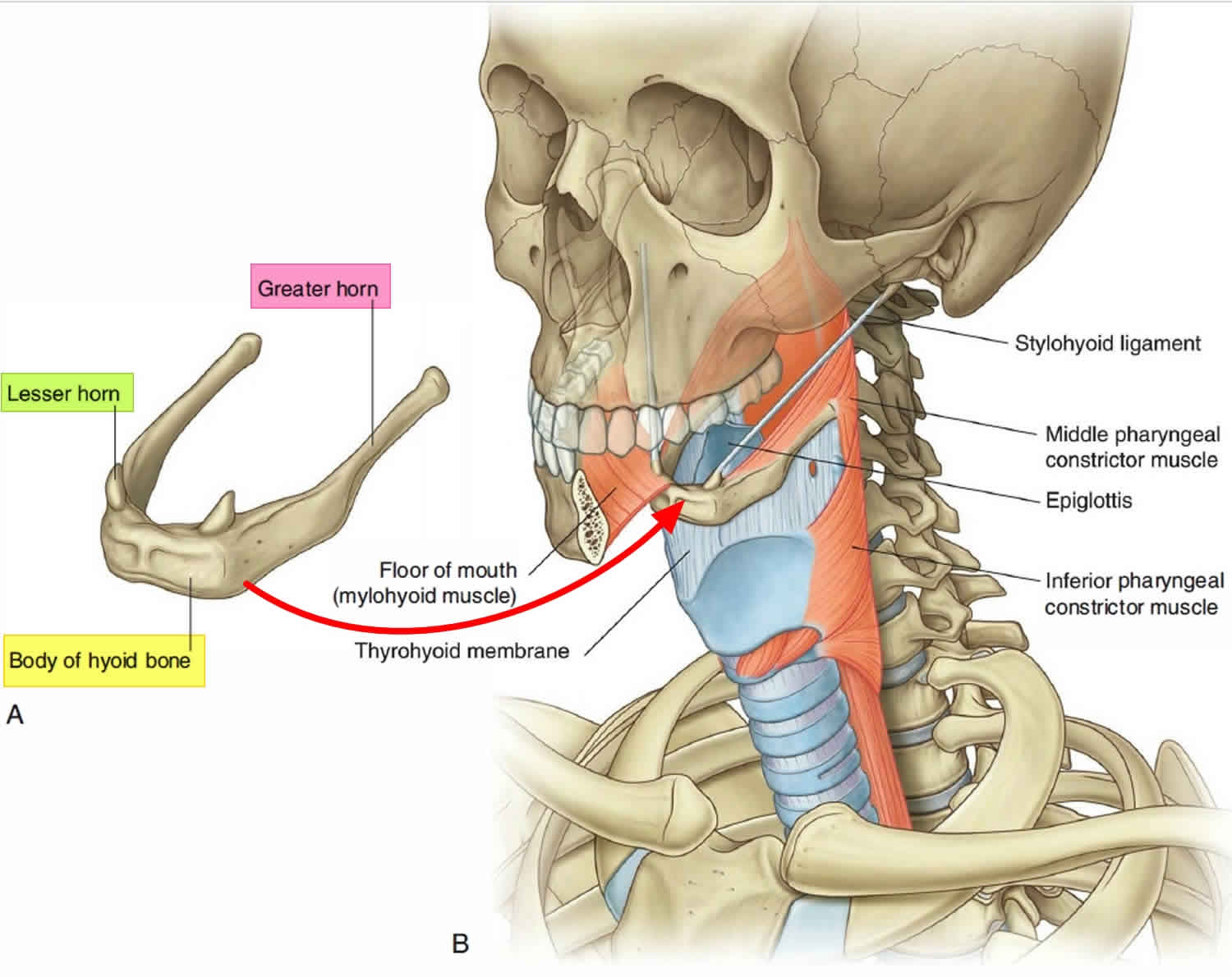
The hyoid bone, often described as a U-shaped bone, is located in the anterior midline of the neck, just above the adam’s apple. Despite its small size and seemingly insignificant presence, the hyoid bone holds significant importance in our lives.
The Role of the Hyoid Bone

The unique positioning and structure of the hyoid bone enable it to support many essential functions. Situated between the lower jaw and the larynx, this bone serves as a crucial attachment point for numerous muscles involved in swallowing, speech, and breathing.
One of the pivotal roles of the hyoid bone is to assist in swallowing. When you swallow, muscles in your throat contract, guiding food and liquid from the mouth to the esophagus and ultimately into the stomach. The hyoid bone acts as a fulcrum, providing a stable base for these muscular movements, ensuring the smooth and efficient passage of food and fluids.
Additionally, the hyoid bone plays a vital role in speaking. It provides anchorage for the muscles involved in the complex movements necessary for speech production. By functioning as a support structure, this bone facilitates the control and modulation of vocalized sounds, enabling clear and articulate communication.
Historic Significance of the Hyoid Bone
Beyond its physiological significance, the hyoid bone has also captivated the interest of researchers and archaeologists due to its link to our ancestors. Recent studies have indicated that the shape and position of the hyoid bone can provide insights into the evolutionary pathways of Homo sapiens.
In a prehistoric sense, the hyoid bone holds great importance in determining the ability of early humans to use verbal language. It is speculated that changes in the hyoid bone’s structure over time coincided with the development of language and communication abilities.
A 2003 study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that Neanderthal hyoid bones differed significantly from those of modern humans. This disparity suggests that Neanderthals may have lacked the ability to produce certain sounds, highlighting the pivotal role of the hyoid bone in the evolution of speech.
Hyoid Bone: A Mysterious Bone
Despite its rich historical and biological significance, the hyoid bone remains relatively unfamiliar to many. Its unattached nature sets it apart from the rest of our skeletal framework, making it a bone of intrigue for researchers and medical professionals alike.
As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of the human body, the unique qualities of the hyoid bone pique their curiosity and draw attention to its various functions and implications.
In conclusion, the hyoid bone, nestled discreetly in your throat, holds a special place in the human body. Its unattached nature makes it distinct from all other bones, while its role in swallowing, speaking, and its historic significance adds to its intrigue. Understanding the importance of this bone brings us closer to comprehending the intricacies of our remarkable bodies.
Sources:
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

