The human tongue is made up of groups of muscles and is always working as even when humans sleep the tongue pushes saliva down the throat
The Fascinating Strength and Never-Ending Work of the Human Tongue
The human body is a miraculous network of organs, tissues, and muscles, each with its own unique purpose and functionality. One such extraordinary organ is the tongue, which often goes unnoticed despite its significant contributions to everyday life. This article delves into the captivating world of the human tongue, exploring its muscular structure and its ceaseless activity, even during sleep.
The Tongue: An Intricate Network of Muscles
When you visualize the tongue, you may picture a soft, pink, muscular structure residing in your mouth. While that image is accurate, there is much more beneath the surface. The human tongue is a complex organ made up of multiple groups of muscles, working harmoniously to accomplish various tasks throughout the day. Unlike many other muscles in the body, these tongue muscles are not attached to bones; instead, they are anchored to the base of the skull and intertwined with connective tissues.
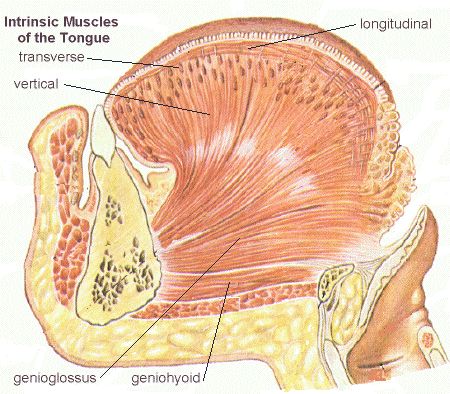
The primary muscle groups that make up the tongue are intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. The intrinsic muscles are responsible for altering the tongue’s shape, allowing it to move in various directions and perform intricate actions like rolling, folding, and contracting. On the other hand, the extrinsic muscles, comprising four pairs, are responsible for controlling the tongue’s position and movement within the mouth.
The Tireless Work of the Tongue
One of the most astonishing aspects of the human tongue is its ceaseless activity. Even when we’re sound asleep, our tongues continue to work relentlessly. The tongue plays an essential role in the production of saliva, an often underappreciated bodily fluid that facilitates digestion and maintains oral health. It achieves this by pushing saliva down the throat, ensuring the continuous lubrication of the esophagus and helping to break down food particles during the digestive process.
This perpetual motion of the tongue during sleep can be attributed to the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions, including saliva production. The autonomic nervous system operates independently of our conscious control, allowing our tongues to work effortlessly throughout the night.
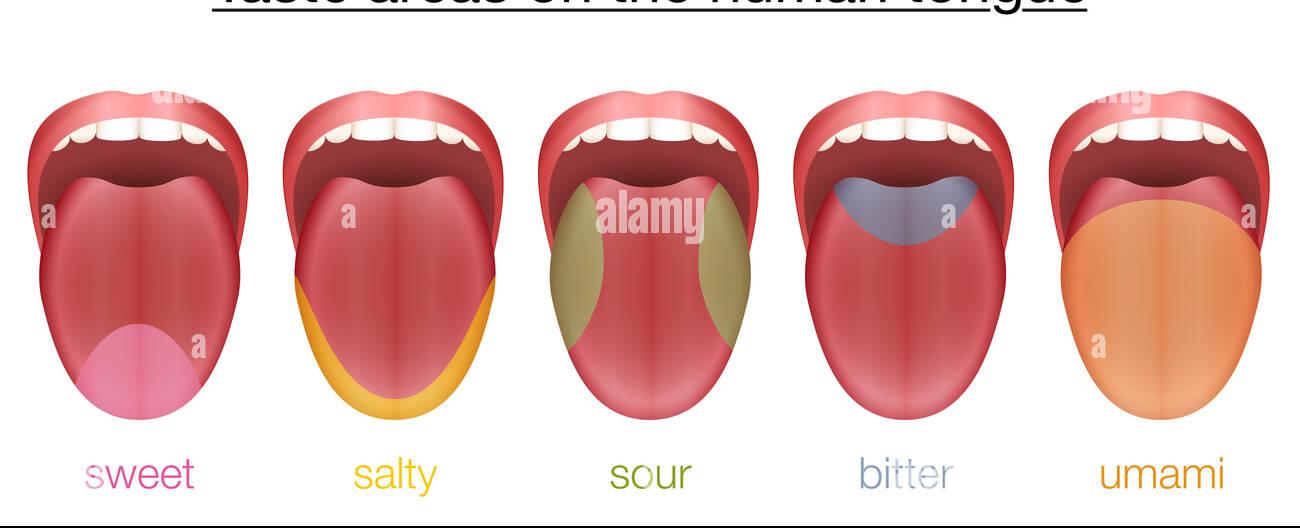
In addition to its function during sleep, the tongue is constantly in motion during wakefulness. It assists in various activities such as talking, chewing, and swallowing. Moreover, the tongue aids in the perception of taste, as its taste buds detect and transmit different flavors to the brain, enriching our sensory experiences.
Conclusion
The human tongue is an extraordinary muscle, constantly at work, even when we are unaware of its tireless efforts. Its intricate muscular structure and the autonomic nervous system’s control enable the tongue to perform vital tasks, such as the secretion of saliva and the perception of taste. As we marvel at the complexity and perpetual motion of the tongue, let us not forget to appreciate its incredible capabilities and the essential role it plays in our everyday lives.
Sources:
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

