The giant red star betelgeuse has a diameter larger than that of the earth s orbit around the sun
The Giant Red Star Betelgeuse: Larger Than Earth’s Orbit around the Sun
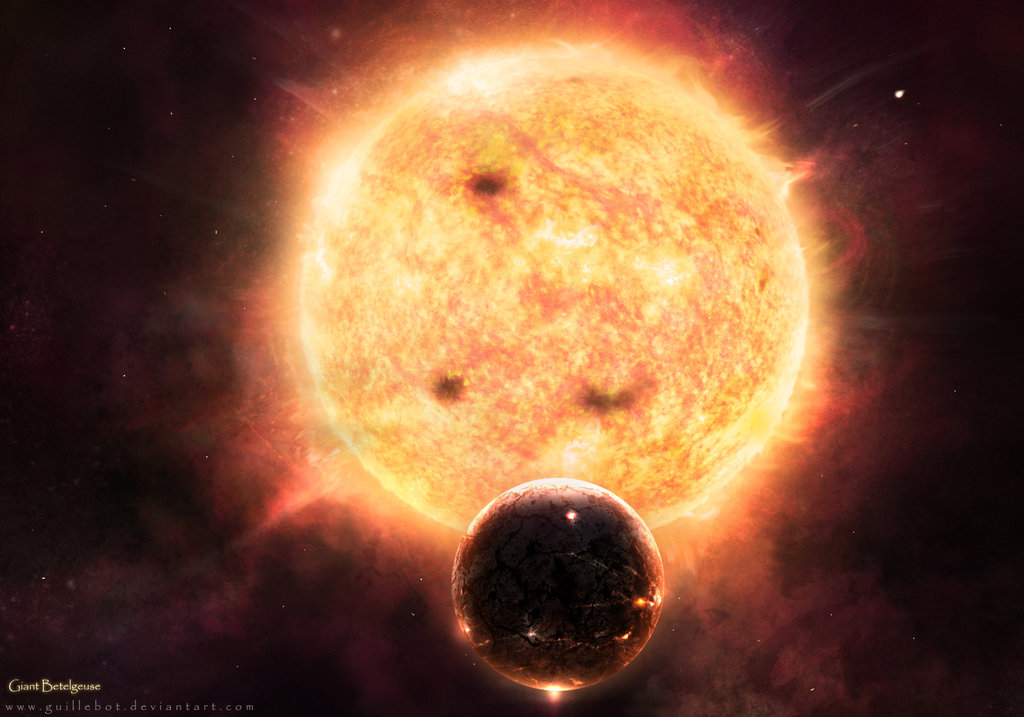
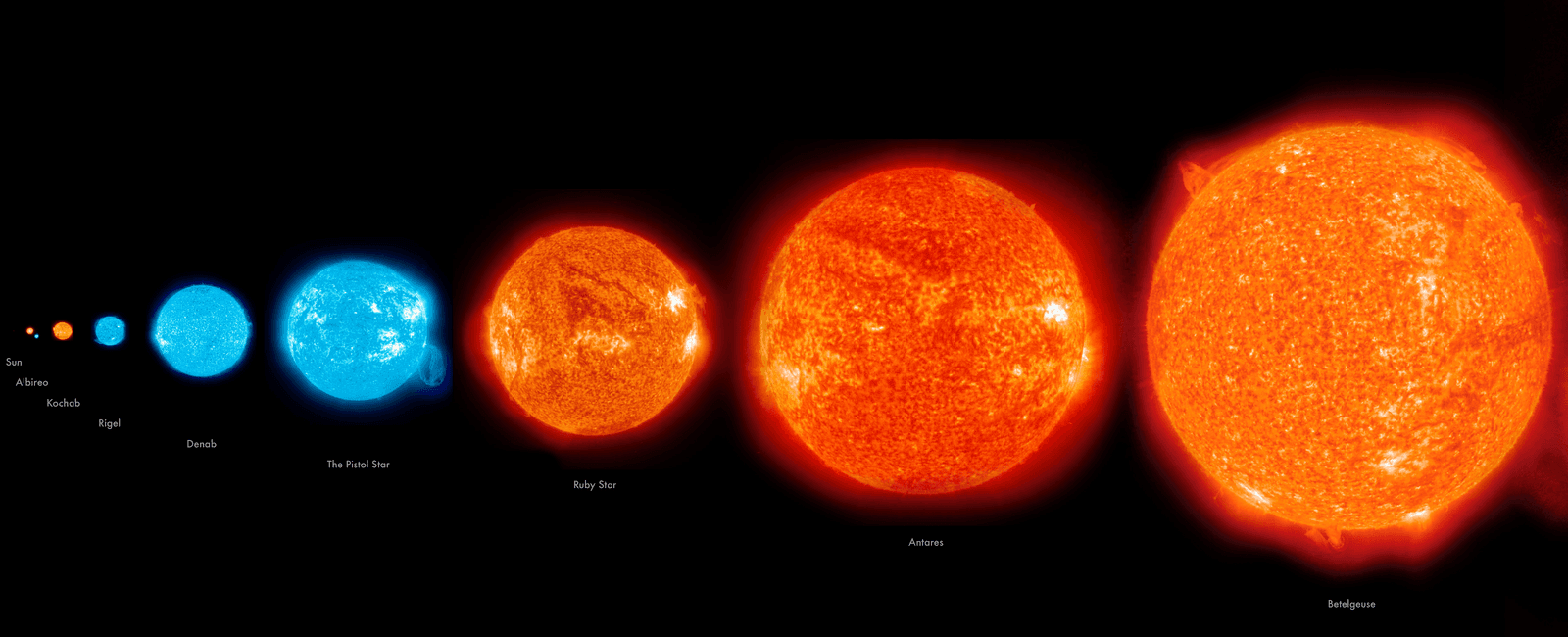
Betelgeuse, the famous giant red star located in the constellation of Orion, holds a remarkable distinction - its diameter is larger than that of Earth’s orbit around the Sun. With an immense size that surpasses our solar system’s dimensions, Betelgeuse captivates astronomers and stargazers alike, showcasing the wonders of the universe.

Betelgeuse’s colossal proportions are truly mind-boggling. To comprehend the enormity of this celestial body, it’s essential to consider the vastness of Earth’s orbit. Our planet travels around the Sun in an elliptical path, with an average distance of approximately 93 million miles (150 million kilometers). This great distance takes roughly 365.25 days to complete a full revolution, defining a single year.
Now, envision this orbit magnified to its extremes, dwarfing the Earth-Sun distance we are accustomed to. Betelgeuse’s diameter, estimated to be around 900 times larger than our Sun, stretches approximately 1.19 billion miles (1.92 billion kilometers). To put it into perspective, if we were to replace our Sun with Betelgeuse, its surface would extend at least beyond the orbit of Mars.
Betelgeuse belongs to the category of red supergiant stars, which are among the most massive stars in the universe. However, its tremendous dimensions are not fixed. As with other stars, Betelgeuse is constantly undergoing changes and transformations. Scientists have observed variations in its size, brightness, and even shape, making it an object of intense study and fascination.
In recent years, Betelgeuse made headlines due to its mysterious “Great Dimming” event. Around late 2019 and early 2020, the star underwent a noticeable decrease in brightness, causing speculation about potential imminent supernova explosions. This unexpected dimming triggered an even greater interest in Betelgeuse and led to extensive research.
Various theories emerged to explain the cause of this temporary dimming. Some scientists proposed the presence of large-scale dust clouds, which partially obstructed the star’s light. Others suggested the formation of cooler spots on Betelgeuse’s surface, affecting its luminosity. While the exact reason still remains a subject of investigation, the “Great Dimming” added to Betelgeuse’s reputation as an extraordinary celestial entity.
Studying stars like Betelgeuse not only expands our understanding of the universe but also provides valuable insights into stellar evolution and the lifecycle of massive stars. Observing these titans of the cosmos allows scientists to unravel the secrets hidden within their colossal structures, stellar winds, and explosive deaths.
In conclusion, Betelgeuse’s diameter surpasses the vast expanse of Earth’s orbit around the Sun, emphasizing its grandeur and captivating astronomers around the world. This red supergiant star, with its intriguing behavior and breathtaking dimensions, serves as a reminder of the limitless wonders that exist beyond our own small corner of the universe.
Source: Wikipedia
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

