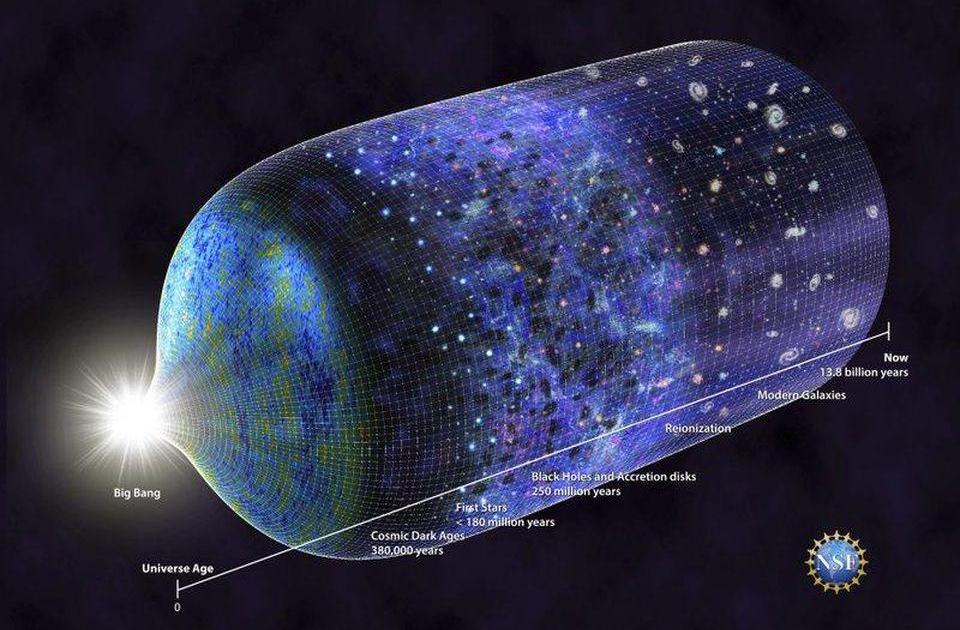
The first stars started shining about half a billion years after the big bang which happened about 13 8 billion years ago
The Birth of the Universe: The First Stars Illuminate the Cosmos
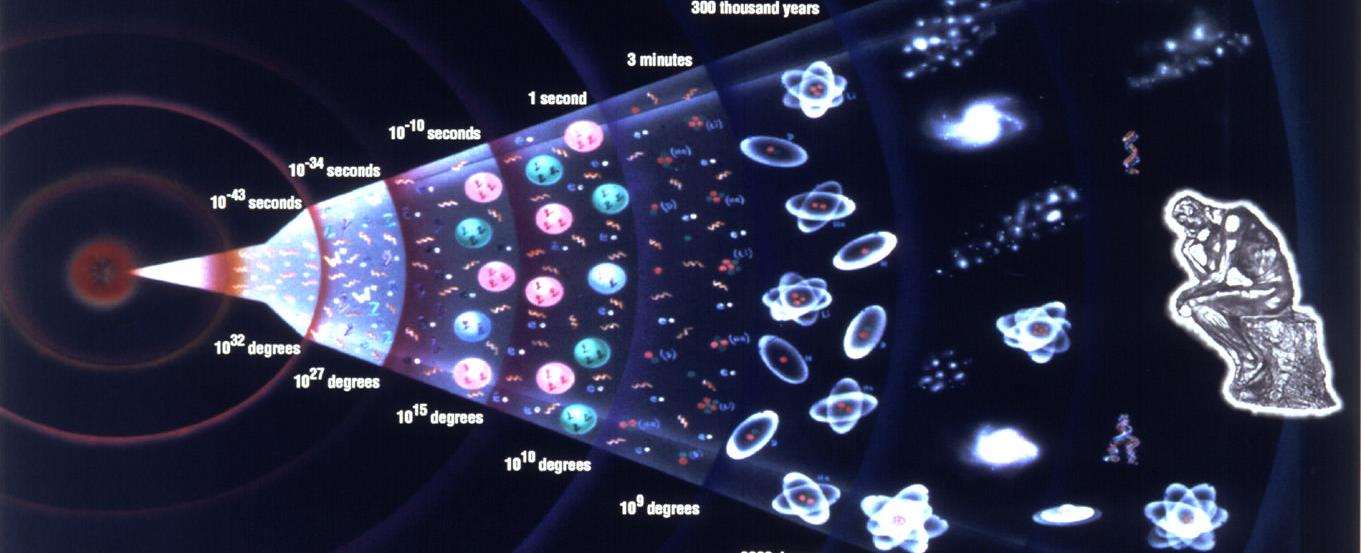
The universe, as we know it, came into existence with a colossal event known as the Big Bang. This cataclysmic explosion marked the beginning of time, space, and all energy in the cosmos. With an estimated age of 13.8 billion years, the universe has been a stage for numerous cosmic phenomena, including the awe-inspiring birth of stars.
The First Glows in the Dark Void
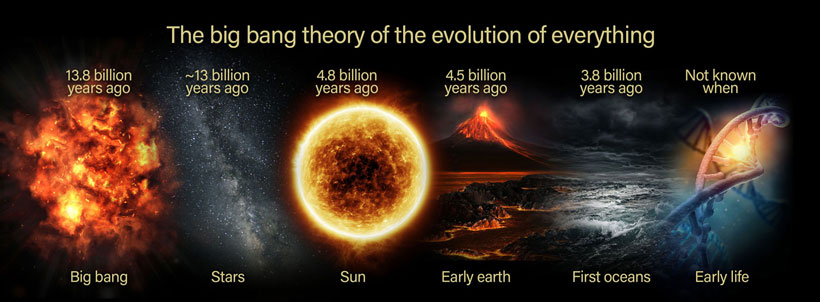
About half a billion years after the Big Bang, a momentous event took place. The first stars ignited, bathed the cosmos in their ethereal light, and forever changed the course of the universe. These celestial beacons were born amidst the primordial gas and dust that permeated the ancient universe.
The birth of the first stars occurred when gravity gathered dense pockets of matter within the universe. Over time, these regions of intense compression accumulated enough mass and pressure to ignite nuclear fusion, allowing the stars to shine brightly. As they came alive, their radiance illuminated the darkness and set the stage for further cosmic evolution.
Illuminating the Universe’s Cosmic Web
The emergence of the first stars played a vital role in the cosmic web formation, a vast network of galaxies, clusters, and filaments spanning the universe. As these stars formed, they enriched the surrounding space with heavy elements, such as carbon, oxygen, and iron. These elements, created through nuclear fusion within the stars themselves, were then scattered into the interstellar medium when the stars eventually reached the end of their life cycles.
The enriched interstellar gas, fortified with the remnants of the first stars, provided the building blocks for subsequent generations of stars. These subsequent stars were born in denser and more diverse environments, influencing the formation of galaxies, stellar clusters, and ultimately, the mesmerizing tapestry of cosmic structures that exist today.
Tracing the Footprints of History
Studying the first stars enables scientists to seek answers to fundamental questions about the universe’s beginnings. By observing their light, scientists can decipher the chemical composition of these ancient stellar objects, offering insights into the conditions prevailing during the universe’s infancy.
To gain a clearer understanding of the first stars, astronomers employ an array of telescopes, each with its unique capabilities. Ground-based observatories, like the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), peer into the distant reaches of space, capturing radio emissions that reveal the spectral signatures left by these primordial stars.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Origins
The illumination of the first stars represented a crucial milestone in cosmic history. Their existence paved the way for the formation of galaxies, planets, and eventually life itself. Studying these ancient stellar objects not only unveils the origins of our universe but also sheds light on our own place within it.
As scientists continue their quest to unravel the mysteries of our cosmic origins, the first stars stand as beacons, guiding our understanding of the universe’s beginnings. Each discovery further enriches our knowledge of the immense tapestry of existence and fuels our curiosity to explore the vastness that lies beyond.
Source: Big Think.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

