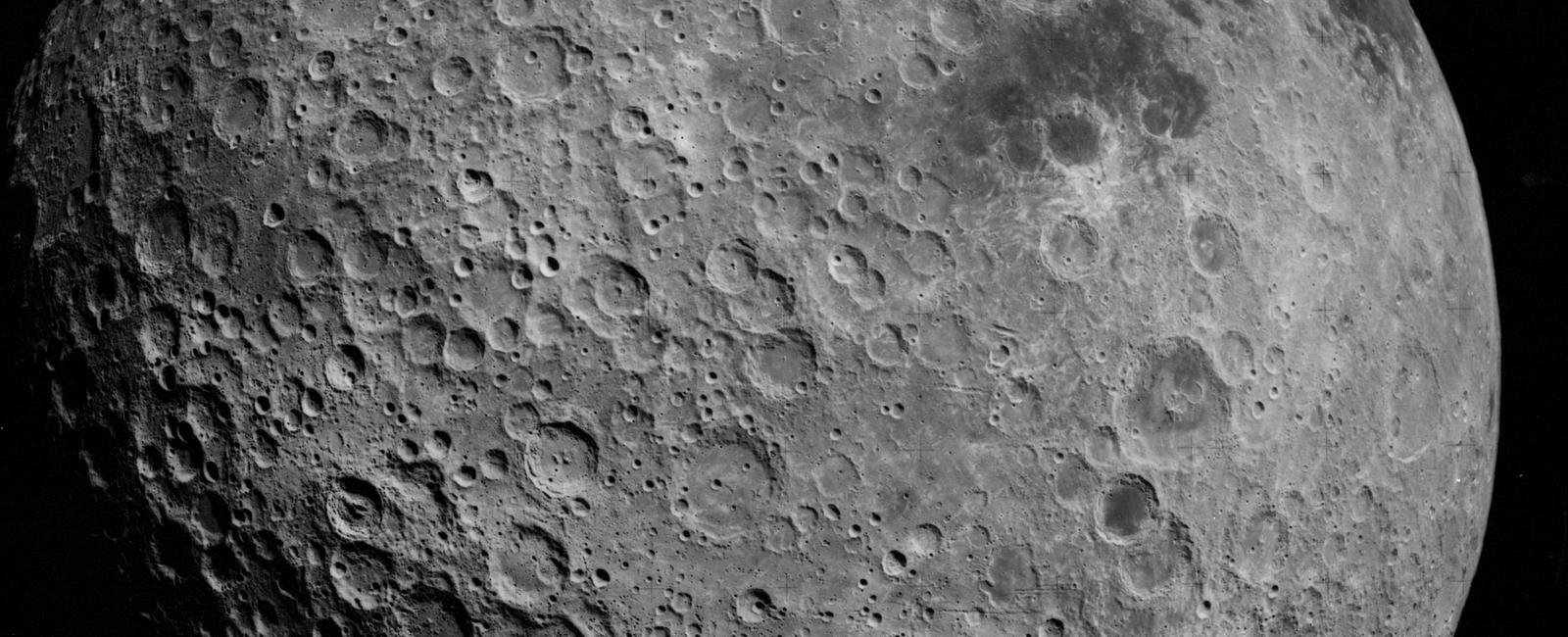
The far side of the moon looks very different to the near side and this is because it doesn t have ancient pools of solidified lava which is actually called maria

The Mysterious Dichotomy of the Moon's Far Side
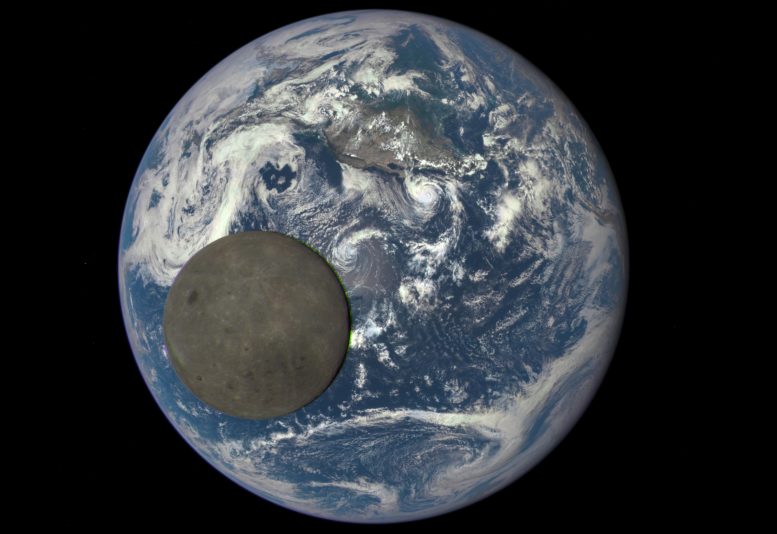

The Moon, Earth’s natural satellite, has always fascinated humanity with its enigmatic presence. However, did you know that the side of the Moon we see from Earth, known as the near side, looks strikingly different from the far side?
Contrary to popular belief, the far side of the Moon does not possess the vast ancient pools of solidified lava, called maria, which are prominently visible on the near side. This intriguing dissimilarity between the two sides has perplexed scientists for decades.
While the near side of the Moon displays dark, smooth areas called maria, which are visible to the naked eye from Earth, the far side is mostly covered with rugged terrains and mountainous regions. These disparities have only recently been explained through scientific observations and groundbreaking lunar missions.
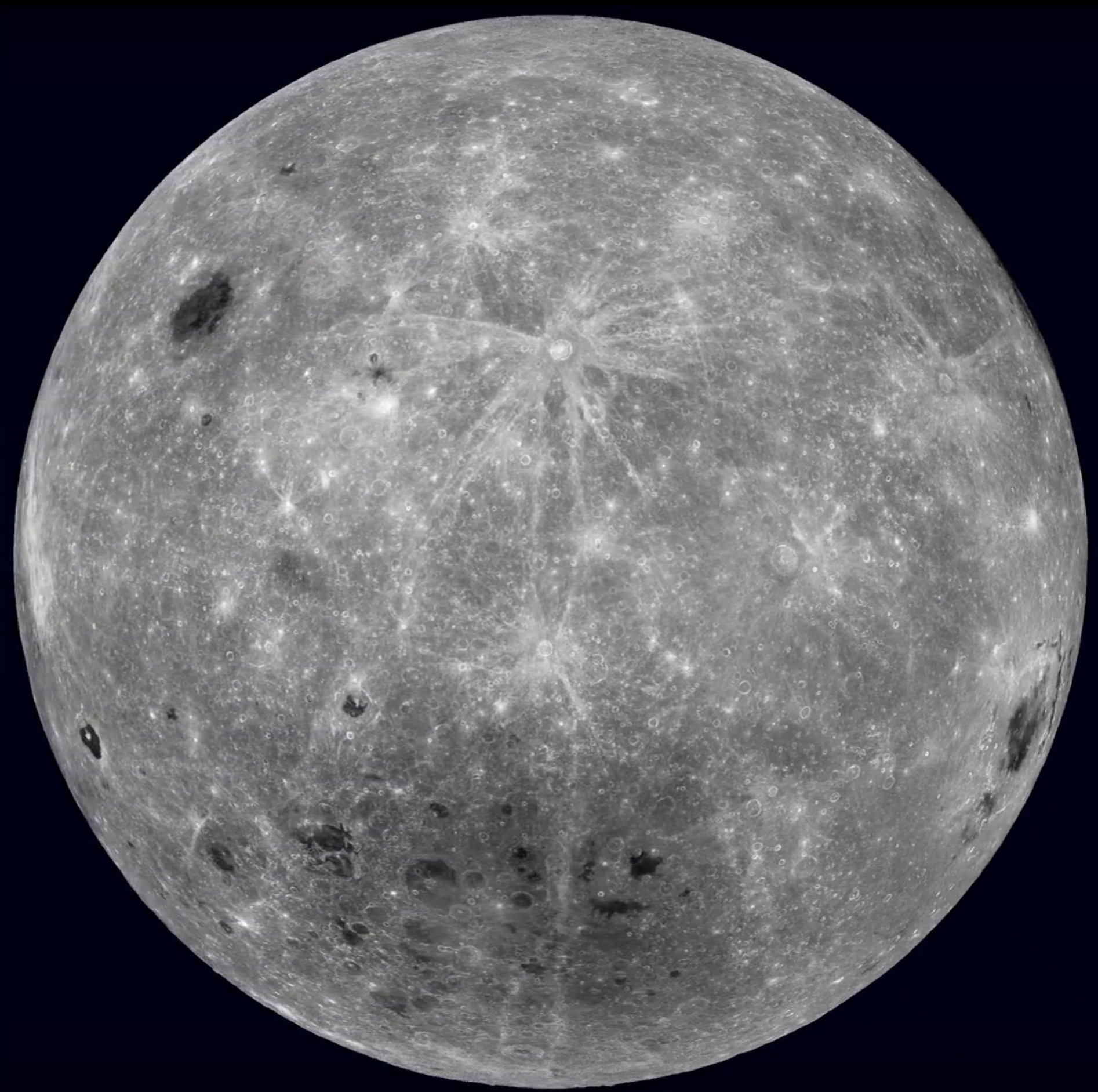
The maria on the near side are remnants of ancient volcanic activity that occurred billions of years ago. These lava flows originated from the Moon’s interior and flooded the basins, creating the characteristic dark patches we see today. However, on the far side, the maria are remarkably absent, leading to a stark contrast in appearance.
Several theories attempt to explain this fascinating dichotomy. One hypothesis suggests that the Moon’s crust on the far side is slightly thicker compared to the near side, preventing the magma from reaching the surface and forming maria. Another possibility is that the far side’s crust may have cooled more quickly, hindering the eruption and flow of lava.
Another contributing factor to the differences between the near and far sides involves the Moon’s formation and tidal forces. Early in its existence, the Moon was much closer to Earth, which caused gravitational forces to create tidal bulges. Over time, these bulges influenced the lunar crust, affecting the distribution of maria on the near side but not on the far side.
Understanding the dissimilarities between the Moon’s near and far sides is not only intriguing from an astronomical standpoint but also offers valuable insights into the Moon’s geological history. By studying the contrasting surface features, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the Moon’s volcanic activity and the processes that shaped its landscape.
While the existence of maria on the near side provides a stunning visual spectacle, the far side of the Moon offers its own beauty with its rugged and untouched terrains. Explorations of the far side through lunar missions, such as NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), have unveiled its mesmerizing landscapes and unveiled numerous secrets.
Continued exploration and research on the dichotomy of the Moon’s near and far sides promise to unravel further mysteries about our celestial neighbor. As scientists delve deeper into the intricacies of the Moon, humankind gains a greater appreciation for the wonders of our cosmic surroundings.
Source: SciTechDaily
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

