The brain needs as much energy as a 10 watt light bulb and it doesn t matter if you are asleep or awake
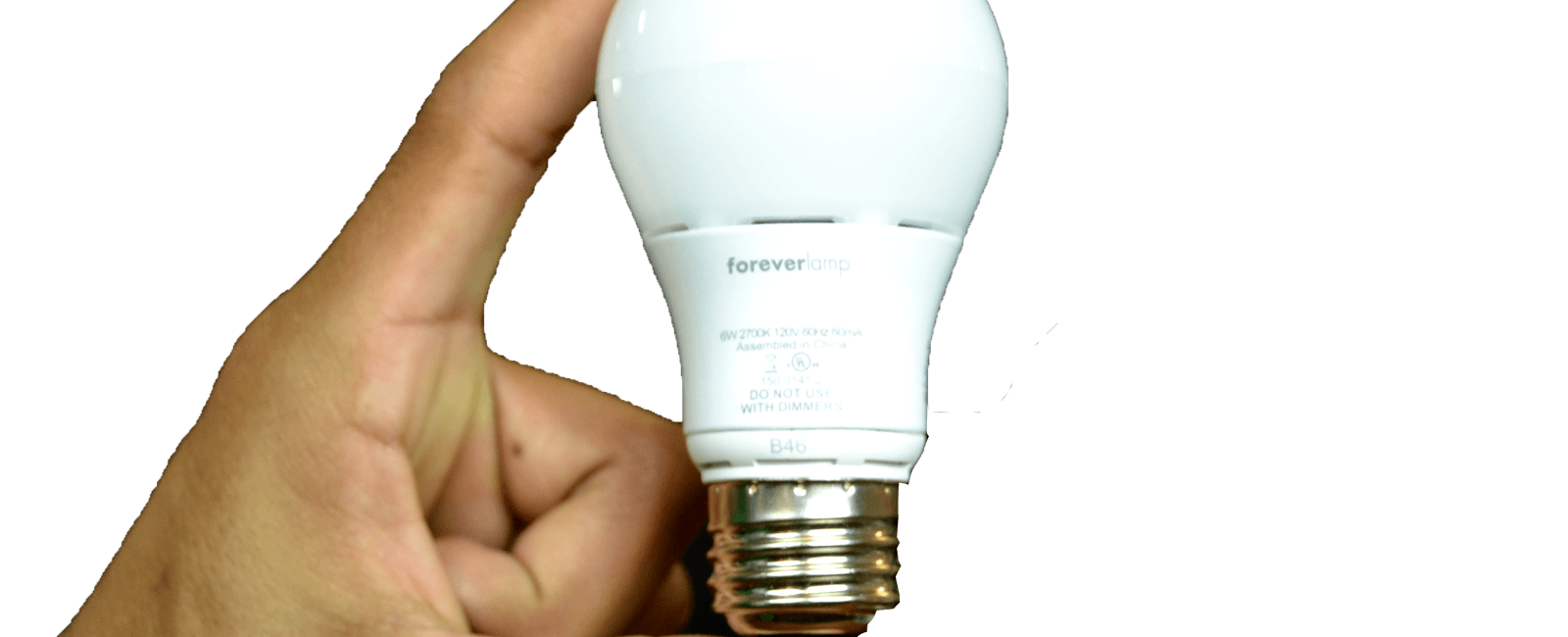

The Astonishing Fact: The Brain’s Energy Consumption equals a 10-watt Light Bulb
Did you know that our brain requires as much energy as a 10-watt light bulb, regardless of whether we are awake or fast asleep? This remarkable fact highlights the incredible power and efficiency of our brain, a complex organ that never rests.
The brain, despite weighing only about 2% of our body weight, consumes approximately 20% of the body’s total energy expenditure. This energy consumption is necessary to fuel the continuous activity within the brain, enabling it to perform its multitude of functions seamlessly.
To put the brain’s energy consumption into perspective, let’s take a closer look at a 10-watt light bulb. A 10-watt light bulb is not particularly bright and is often used in nightlights or devices that require minimal illumination. Surprisingly, despite being dim, it still requires a considerable amount of energy to produce light.
Just like a light bulb, the brain requires energy to function efficiently. Even when we’re asleep, our brain engages in numerous activities essential for our overall well-being. It regulates body temperature, controls breathing, and consolidates memories, among other crucial tasks. Additionally, it maintains the various bodily functions that keep us alive.
Another fascinating aspect of the brain’s energy consumption is its consistent requirement. Unlike many other organs in our body that experience fluctuations in energy demands, the brain’s energy needs remain relatively constant throughout the day and night. This stability allows our brain to function optimally, ensuring our cognitive abilities are always available when needed.
What powers the brain’s incredible energy demands? Glucose, a simple sugar, is the brain’s primary source of energy. It is derived from the food we consume, particularly carbohydrates. Once glucose enters the bloodstream, it is transported to the brain, where it is converted into energy through a process known as cellular respiration.
Considering the brain’s energy-intensive nature, it becomes evident why maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is vital for optimal brain function. Consuming foods rich in glucose, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help support the brain’s energy requirements and overall health.
Intriguingly, the constant energy consumption by the brain also results in the generation of a significant amount of heat. This heat production plays a role in the regulation of our body temperature, helping us maintain a stable internal environment.
As we continue to uncover the mysteries of the brain, facts like these leave us in awe of its astoundingly efficient design. The brain’s ability to perform complex tasks with minimal energy consumption is a testament to its superior engineering.
Next time you switch on a 10-watt light bulb, take a moment to appreciate the incredible energy efficiency of our brain. From the simplest tasks to the most intricate endeavors, our brain’s ceaseless energy consumption powers our every thought, action, and existence.
Sources:
Images:

Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

