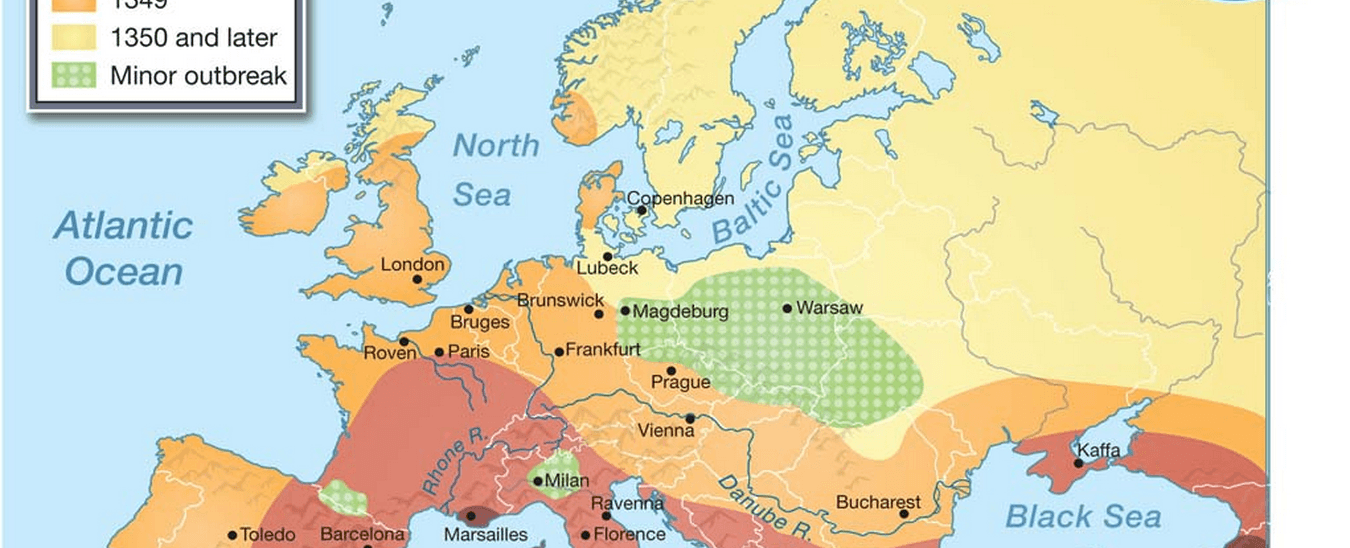
The black death reduced the population of europe by one third in the period from 1347 to 1351
The Black Death: A Devastating Plague in Europe from 1347 to 1351

The Black Death, also known as the Bubonic Plague, was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history. It caused widespread death and immense suffering across Europe from 1347 to 1351. This deadly disease, mainly transmitted by fleas carried by rats, had a profound impact on the population and society of Europe, reducing it by an estimated one-third.
During the 14th century, Europe experienced an unprecedented catastrophe as the Black Death swept through its towns, cities, and rural areas. This pandemic originated in Asia and arrived in Europe through trade routes, particularly the Silk Road. It quickly spread due to the increased mobility of people and goods during that period.
The Black Death had a substantial effect on the population of Europe, as it ravaged communities indiscriminately. The estimated death toll was approximately 25 million people, which accounted for around 30-50% of Europe’s population at that time. This massive loss of life left a lasting impact on both urban and rural areas, causing a severe decline in the number of people available to work the land and carry out essential tasks.

The demographic consequences of the Black Death were vast and far-reaching. With the sudden reduction in population, labor shortages became prevalent, and the need for workers increased substantially. This had an unintended consequence of empowering the surviving laborers, as their skills and expertise became highly sought after. This shift eventually led to significant social and economic changes across Europe.
Moreover, the Black Death also affected the social fabric of society. The fear and uncertainty caused by the pandemic led to an increase in religious fervor and the questioning of societal norms and values. This led to significant changes in religious practices, as people sought solace and answers to explain the devastating loss of life. It also influenced art, literature, and other forms of cultural expression, as the trauma of the Black Death left a lasting impression on European society.
In terms of economic repercussions, the diminished population resulted in a decline in overall consumption and pushed wages higher due to the scarcity of labor. The surviving laborers were in high demand, allowing them to negotiate for better working conditions and higher pay. This shift in the balance of power had a significant impact on the feudal system and marked the beginning of a gradual decline in serfdom and the rise of the middle class.
To this day, the Black Death remains a somber reminder of the fragility of human existence and the far-reaching effects of pandemics. Its impact on Europe was catastrophic, reducing the population by an estimated one-third in just a few years. The economic, social, and cultural consequences were profound, shaping the course of European history. Though humanity has made tremendous strides in healthcare and disease prevention since the 14th century, the memory of the Black Death serves as a testament to the resilience and adaptability of humankind in the face of adversity.
Source: History.com
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

