Synovial fluid which contains oxygen nitrogen and carbon dioxide acts as a lubricant for human joints
Synovial Fluid: The Lubricant for Human Joints
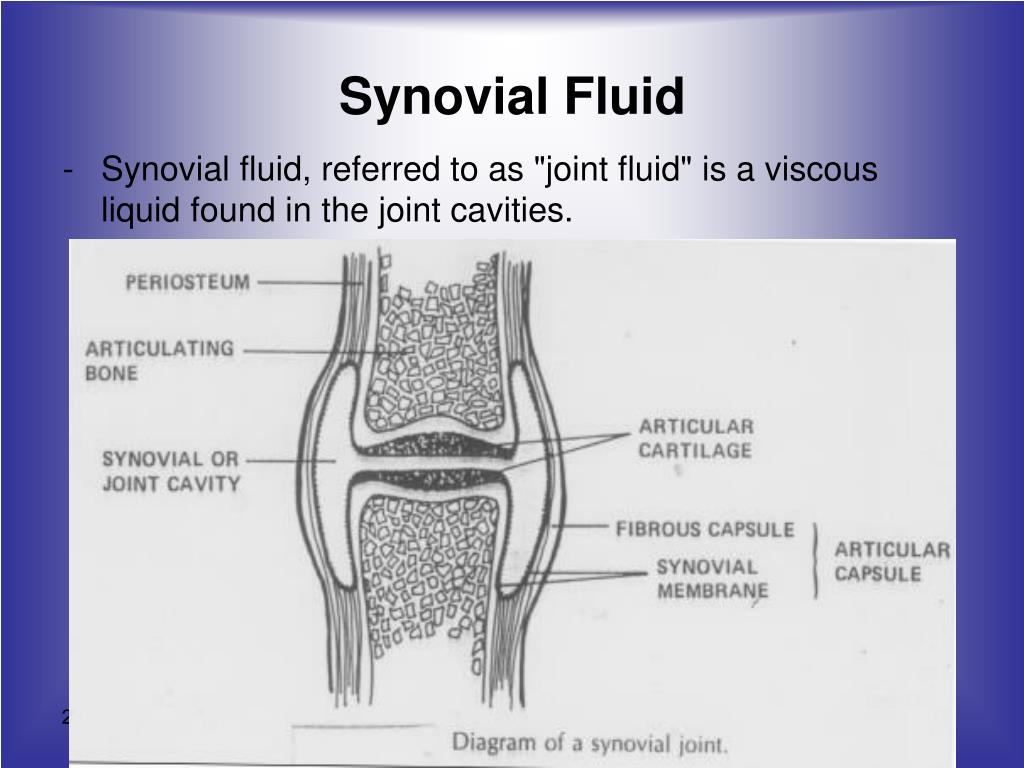
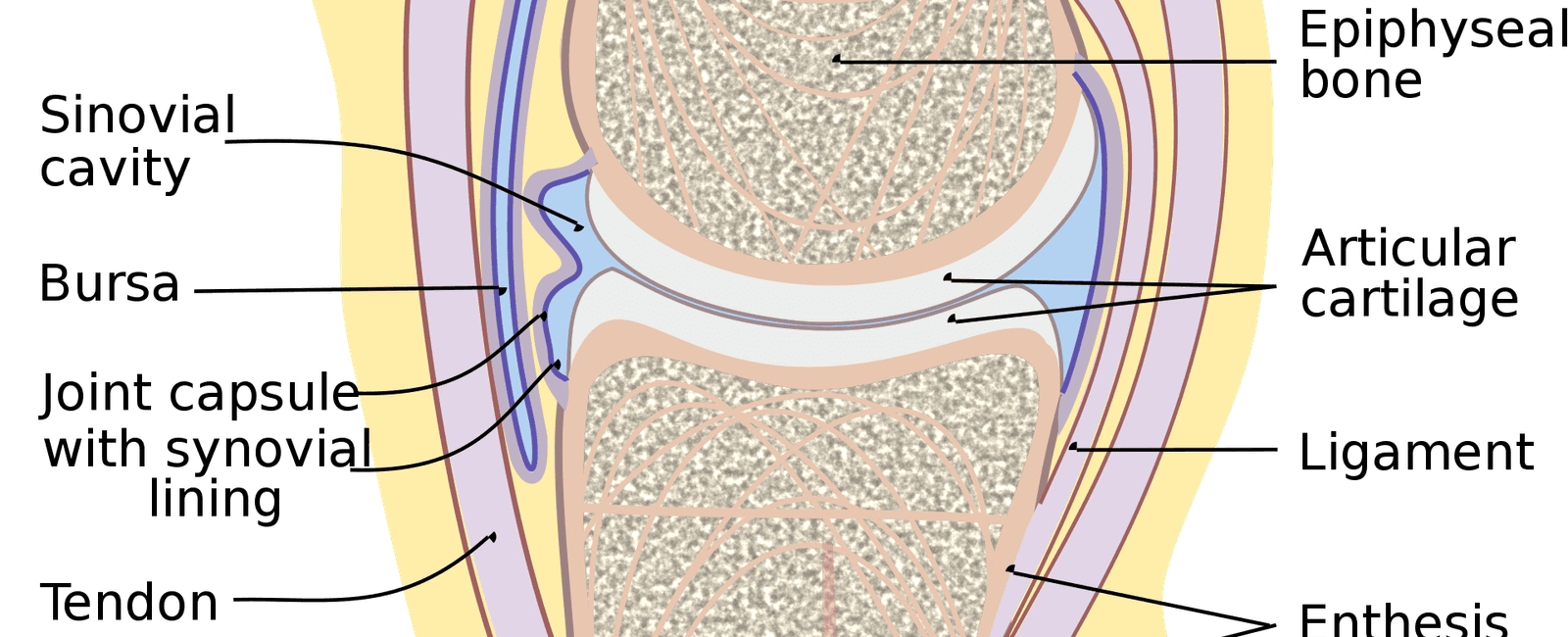
Synovial fluid is a viscous substance found within the synovial joints of the human body. This clear fluid acts as a vital lubricant, reducing friction between the bones, allowing for smooth and painless movement. Composed of a combination of oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide, synovial fluid serves multiple purposes, ensuring the optimal functioning of our joints.
The primary role of synovial fluid is to lubricate the surfaces of the joints. This attribute allows the bones within the joint to glide smoothly over each other, reducing friction and minimizing wear and tear. Without synovial fluid, joints would be susceptible to damage, leading to discomfort, stiffness, and restricted mobility.
Additionally, synovial fluid acts as a shock absorber, dissipating forces generated during movement. By providing cushioning, it minimizes the stress on the joints, preventing injuries and pain. This vital function is particularly crucial during weight-bearing activities such as walking, running, and jumping.

Not only does synovial fluid contribute to joint lubrication and shock absorption, but it also supplies essential nutrients to the articular cartilage. This protective layer covers the surfaces of the bones involved in the joint, acting as a buffer and preventing bone-on-bone contact. The nutrients delivered by the synovial fluid help maintain the health and integrity of the cartilage, ensuring its proper function and preventing degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis.
The composition of synovial fluid plays a significant role in its lubricating properties. Oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide, among other gases, are dissolved within the fluid, contributing to its viscosity and lubricating abilities. Additionally, the fluid contains hyaluronic acid and proteins, which further enhance its lubricating properties.
To maintain the health of synovial fluid, regular physical activity, including appropriate joint movement, is crucial. Physical exercise stimulates the production and circulation of synovial fluid, ensuring its optimal quantity and quality. Moreover, staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can support healthy synovial fluid production.
In conclusion, synovial fluid plays a vital role in maintaining the health and functioning of our joints. Its lubricating, shock-absorbing, and nutrient-supplying properties enable painless and smooth movement while protecting the cartilage from damage. Understanding the importance of synovial fluid emphasizes the significance of engaging in regular physical activity and adopting a healthy lifestyle to support the optimal function of our joints.
Sources:
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

