Since tree rings provide a snapshot of the earth s climate history scientists can use them to tell its age and changes in the climate including volcanic eruptions droughts and other natural disasters
Tree Rings: A Window into Earth’s Climate History

From the majestic forests that cover our planet to the small trees lining our streets, every tree tells a unique story. But did you know that within those stories lies a wealth of information about Earth’s climate history? Tree rings, like pages in a book, provide scientists with invaluable insights into the age and changes in our climate.
But how do tree rings provide such a snapshot of our past? Let’s dig deeper.
The Science Behind Tree Rings
The study of tree rings, known as dendrochronology, dates back to the early 20th century. Each year, as a tree grows, it forms a new layer of cells right beneath its bark. In favorable conditions, this layer is thick, indicating a year of growth. In harsher conditions, the layer is thinner, signifying a year of limited growth. By counting these rings, scientists can determine a tree’s age and study the patterns they form.
A Climate Time Machine
Tree rings are like time capsules, carrying information about Earth’s climate from centuries past. By examining the width and color of each ring, scientists can gather invaluable data about the environmental conditions in which the tree grew.
Connecting the Dots: Climate and Tree Rings
Tree rings act as intricate witnesses to the Earth’s climate patterns, recording important events such as volcanic eruptions, droughts, and other natural disasters. By analyzing the patterns across multiple trees, scientists can piece together a detailed picture of our planet’s climate history.
Volcanic eruptions, for example, release large amounts of ash and gases into the atmosphere, affecting the growth patterns of trees. These events leave a clear mark on the tree rings, providing clues to the timing and magnitude of past eruptions.
Similarly, droughts and other extreme weather events influence the thickness of individual rings. A period of prolonged drought will result in narrower rings, indicating a challenging environment for tree growth.
The Link to Climate Change
As the Earth’s climate changes, tree rings become even more critical in understanding and predicting its future. By studying tree rings from past centuries, scientists can observe the impact of natural factors on our climate and place current changes in a historical context.
A Tool for Conservation and Sustainability
Aside from unraveling the secrets of our climate history, tree rings offer valuable insights for conservation and sustainable land management. By identifying past periods of environmental stress, scientists can develop strategies to mitigate the impact of future events and preserve our planet’s biodiversity.
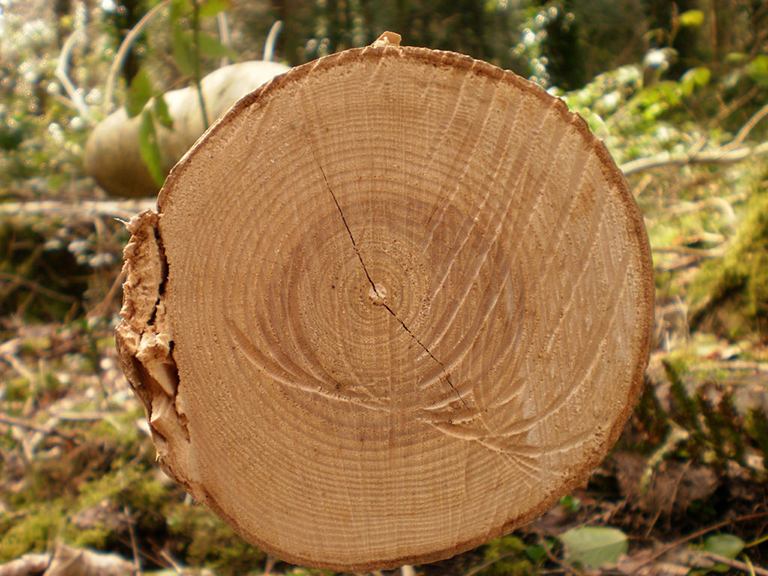

In conclusion, tree rings provide a fascinating window into Earth’s climate history. From recording the effects of volcanic eruptions to revealing the severity of droughts, these unique rings offer scientists a timeline of our planet’s past environmental conditions. By harnessing the power of tree rings, we can better understand our climate, take action to address climate change, and work towards a more sustainable future.
Source: Climate NASA
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

