Researchers found pregnancy shrinks the brain s gray matter that contains the cell bodies and synapses of nerve cells
Pregnancy Shrinks the Brain’s Gray Matter: Understanding the Changes in the Nervous System
During pregnancy, a woman’s body goes through various physical and hormonal changes to support the developing fetus. While most of these changes are well-known and expected, a lesser-known fact is that pregnancy can actually lead to a reduction in the brain’s gray matter.
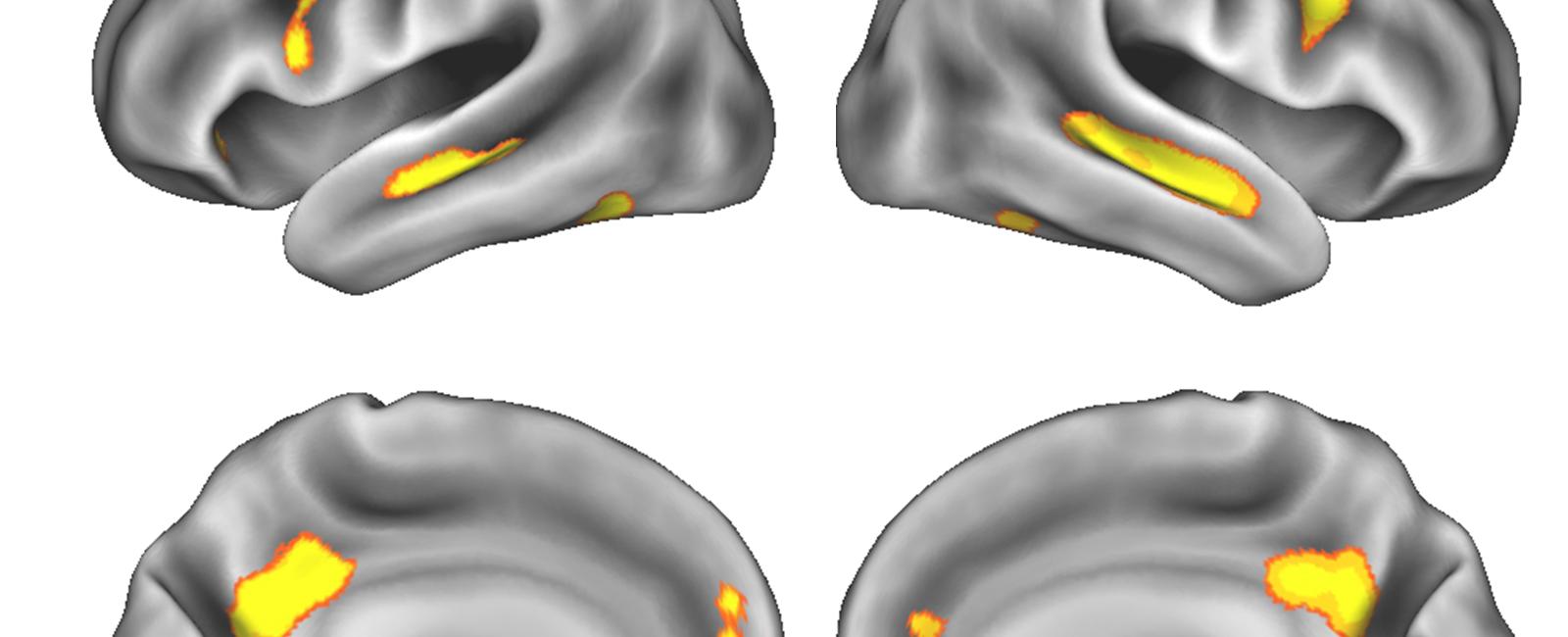
Gray matter, which constitutes the outer layer of the brain, contains the cell bodies and synapses of nerve cells. It plays a crucial role in processing information and controlling various bodily functions. A study conducted by researchers has shown that pregnancy causes a measurable decrease in gray matter volume, particularly in regions responsible for social cognition and adaptation to the environment.
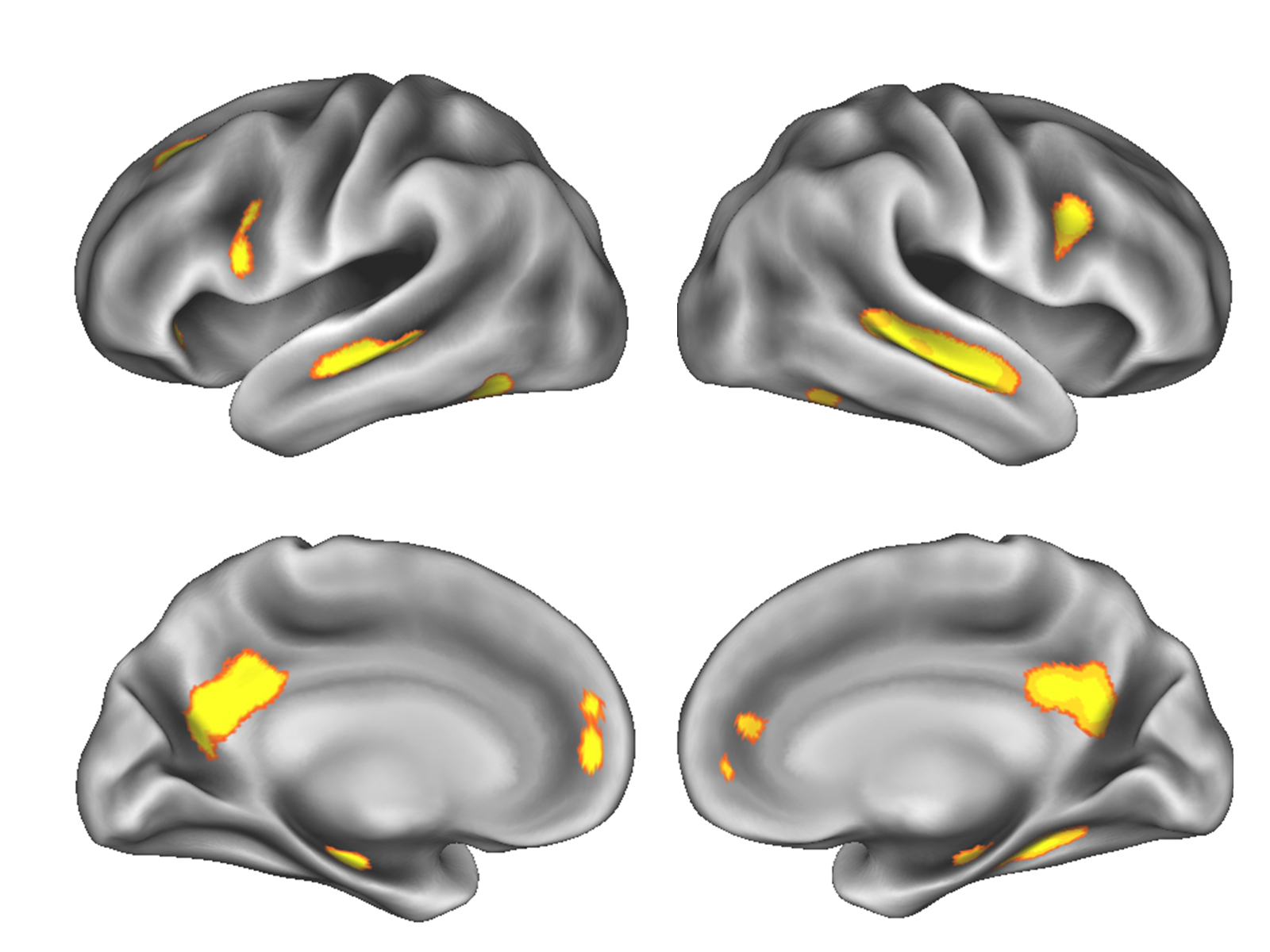
The study involved scanning the brains of women before and after pregnancy using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The findings revealed a significant reduction in gray matter volume, particularly in the prefrontal and temporal cortex. These areas play a critical role in higher cognitive functions such as memory, decision-making, and emotional regulation.
Although the exact reason behind this phenomenon is not yet fully understood, researchers hypothesize that it is likely due to a combination of hormonal changes and the brain’s natural adaptation to motherhood. During pregnancy, hormonal levels fluctuate significantly, including increased levels of estrogen and progesterone, which play important roles in fetal development. These hormonal changes are believed to remodel the brain’s structure and neural connections.
Additionally, the brain undergoes certain adaptations to prepare the mother for the demands of caring for a newborn. These changes ensure heightened sensitivity towards the baby’s cues, increased emotional attachment, and improved caregiving abilities. The reduction in gray matter volume observed in the study may represent a neural reorganization to optimize these maternal responses.
Despite the decrease in gray matter volume during pregnancy, it is important to note that this change is temporary. Researchers have found that within the first year after childbirth, the brain begins to regain its pre-pregnancy size. This suggests that the brain is highly plastic and capable of adapting to new circumstances, even during such a significant life event as pregnancy.
Understanding the changes that occur in the brain during pregnancy provides valuable insights into the complexities of the female body and its remarkable ability to adapt and support the development of new life. Further research in this area may shed light on the intricate mechanisms underlying the brain’s plasticity and the long-term effects of pregnancy on cognitive function and mental health.
Sources:
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

