Regular exercise helps boost the immune system
Regular exercise is not only beneficial for maintaining physical fitness but also plays a crucial role in boosting the immune system. Numerous studies have shown that engaging in regular exercise can strengthen our body’s defense mechanisms, helping us fight off infections and diseases. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which exercise positively impacts the immune system and why it should be an integral part of our daily routine.
Exercise and Immune System: A Powerful Combination
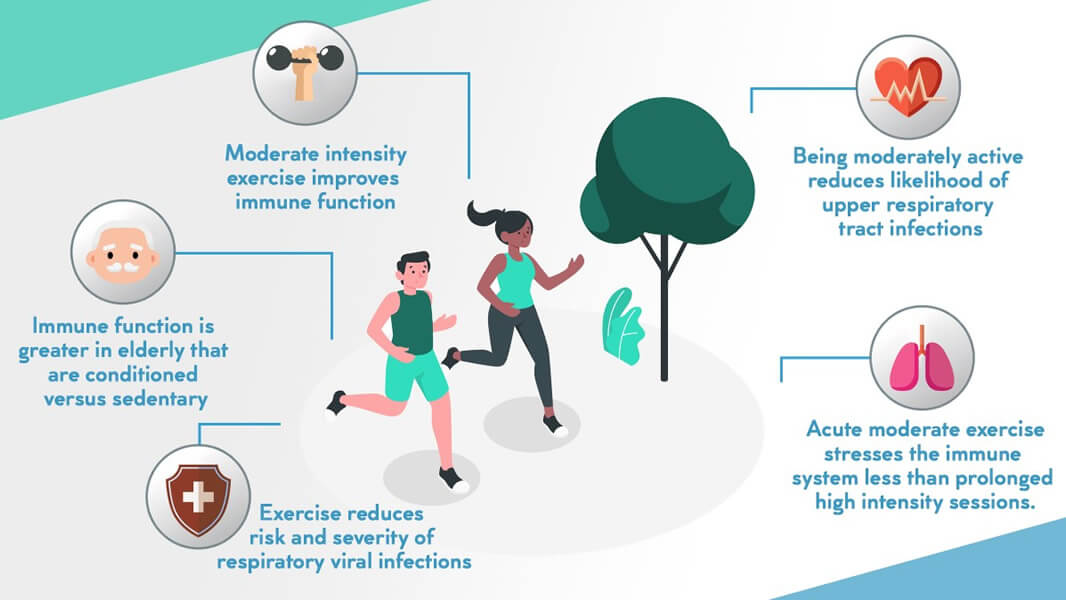
Exercise has been found to have a profound effect on the immune system, enhancing its functionality and overall effectiveness. When we engage in physical activity, a series of complex physiological changes occur within our body. These changes trigger a cascade of events that contribute to a reinforced immune response.
One of the primary ways exercise boosts the immune system is by promoting better blood circulation. As we workout, the heart pumps blood more efficiently, allowing immune cells to travel more effectively throughout the body. This increased blood flow ensures that immune cells reach various tissues and organs in need of protection, reducing the risk of infection.
Regular exercise also has a positive impact on the respiratory system, another crucial component of the immune system. It improves lung capacity and strengthens respiratory muscles, enabling better oxygen uptake. This improved oxygenation not only enhances overall physical performance but also helps immune cells function optimally, ensuring a robust defense against harmful pathogens.
Strengthened Immune Response through Exercise
Exercise has been shown to enhance the immune system’s response to pathogens and other foreign invaders. It stimulates the production and circulation of various types of immune cells, including white blood cells, neutrophils, and natural killer cells. These cells play essential roles in identifying, attacking, and eliminating harmful substances from the body.
Moreover, engaging in physical activity increases the production and release of antibodies and cytokines. Antibodies help neutralize and destroy harmful antigens, while cytokines act as messengers between immune cells, coordinating their response to infections. By boosting antibody and cytokine production, exercise optimizes the immune system’s ability to recognize and combat threats effectively.
Reducing Inflammation and Stress
Chronic inflammation and increased stress levels can negatively impact the immune system, making us more susceptible to illnesses. However, regular exercise has been shown to mitigate these factors, ultimately strengthening the immune system.
Physical activity helps balance the production of cortisol, a stress hormone that, in excessive amounts, can impair immune function. By reducing cortisol levels, exercise aids in maintaining a healthy immune response. Additionally, exercise activates the release of endorphins, widely known as “feel-good” hormones, which help reduce stress and promote a positive mental state.
Furthermore, studies have demonstrated that exercise can reduce chronic inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation can weaken the immune system and contribute to the development of various diseases. By decreasing inflammation, exercise supports the immune system’s ability to function optimally.
Incorporating Exercise into Your Routine
Now that we understand the numerous benefits of exercise on the immune system, it is essential to incorporate physical activity into our daily lives. It is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic exercise every week.
Moderate aerobic exercise includes activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, while vigorous aerobic exercise might involve running, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), or playing a sport. Strength training exercises that target all major muscle groups should also be incorporated two or more days a week.
Remember to start slowly if you are new to exercising and gradually increase the intensity and duration over time. Listen to your body, and if you have any concerns or medical conditions, consult with a healthcare professional before starting an exercise regimen.
Conclusion
Regular exercise is a powerful tool in optimizing the immune system’s functioning, enabling our bodies to better defend against infections and diseases. By incorporating exercise into our daily routine, we can strengthen our immune response, reduce inflammation, and manage stress effectively. Start building healthy habits today and embrace physical activity as a means to support your immune system and overall well-being.

Source: MedlinePlus
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff