One day on neptune is the equivalent of 16 hours on earth
One Day on Neptune: 16 Earth Hours
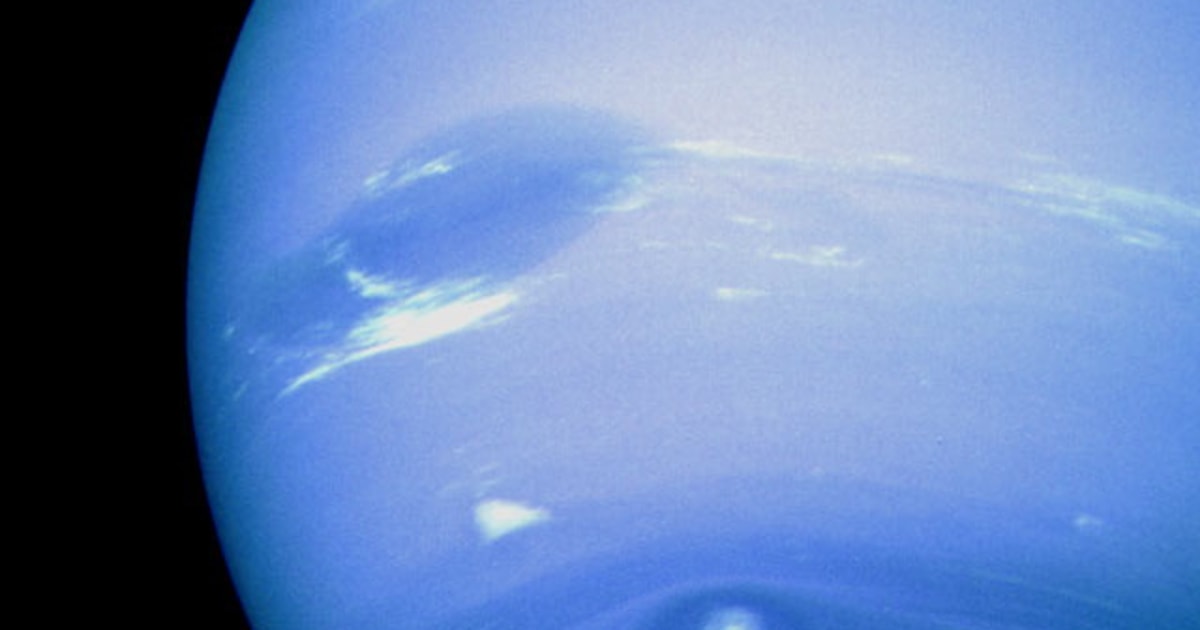 Image Source: NBC News
Image Source: NBC News
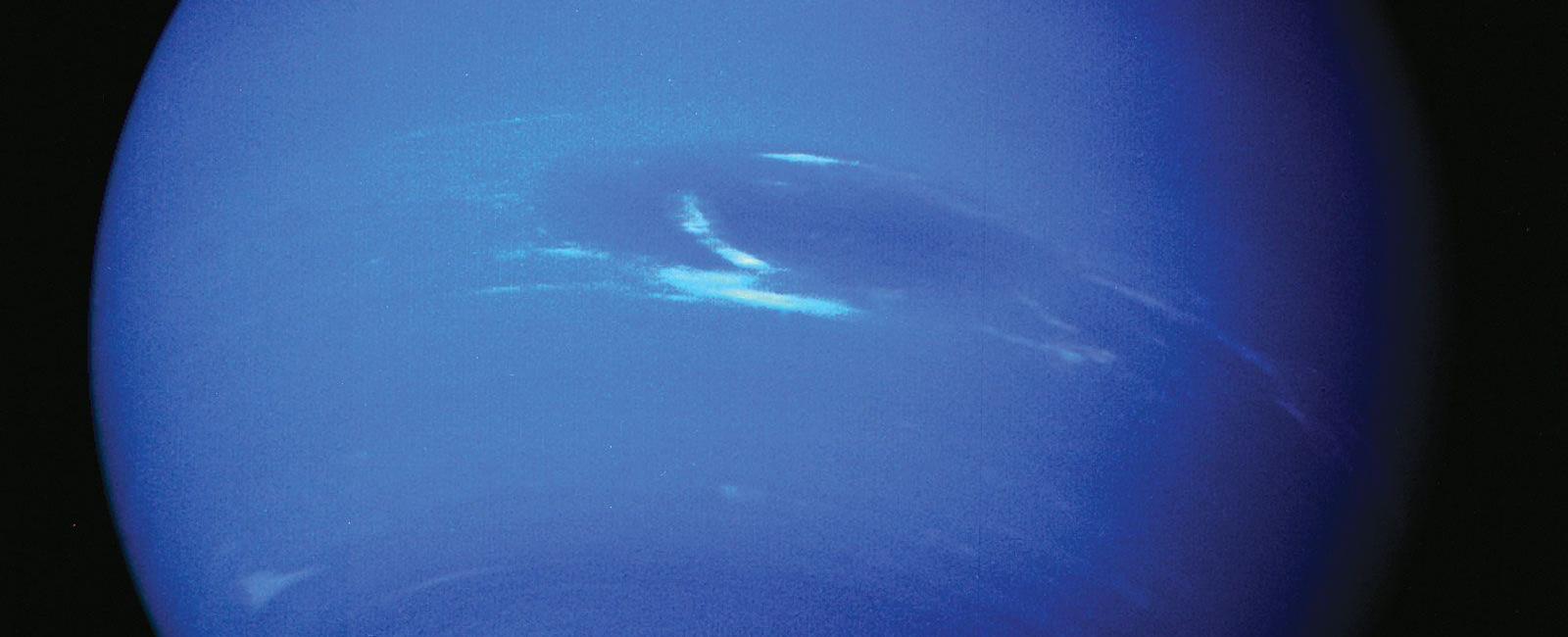
Neptune, the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun, is home to some intriguing phenomena and fascinating discoveries. Among these is the fact that one day on Neptune is equivalent to 16 hours on Earth. This disparity in the length of a day on Neptune compared to that on Earth has sparked curiosity and led scientists to delve deeper into understanding the dynamics of this captivating distant planet.
Neptune, named after the Roman god of the sea, is often referred to as an ice giant, characterized by its icy composition and vast oceans of liquid diamond. Its mysterious atmosphere is predominantly composed of hydrogen, helium, and traces of methane, giving it a distinct bluish hue.
The length of a day on Neptune is significantly shorter than that on Earth. While Earth takes approximately 24 hours to complete a full rotation on its axis, Neptune spins much more swiftly, accomplishing a full rotation in just about 16 hours. This discrepancy in day length arises from various factors unique to Neptune’s composition and structure.
Neptune, like other gas giants, is predominantly composed of gas and lacks a solid surface. Consequently, the rotation speed of a planet can vary depending on the distribution of mass within it. Unlike Earth, Neptune experiences an extreme case of differential rotation. This phenomenon occurs when different parts of a planet rotate at varying speeds. Such differential rotation leads to variations in the length of the day across different latitudes on Neptune.
The exact cause of this differential rotation on Neptune is still being studied, and scientists hypothesize that it may be influenced by various factors, such as wind patterns in the planet’s atmosphere, vertical mixing of gases, and the presence of internal heat sources. These factors contribute to the complex dynamics of Neptune’s atmosphere and result in the remarkable variation in day length.
 Image Source: Pinterest
Image Source: Pinterest
Neptune’s shorter day has several implications for the planet’s climate and weather patterns. The rapid rotation generates strong atmospheric winds, reaching speeds of up to 1,500 miles per hour (2,400 kilometers per hour). These powerful winds are responsible for the distinct cloud formations and storms observed on Neptune, such as the infamous Great Dark Spot, a giant storm system akin to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.
Understanding the day length on Neptune helps scientists gain valuable insights into the planet’s internal structure, atmospheric dynamics, and the processes that shape its unique characteristics. The data obtained through observations and space missions provide crucial information for comparative planetology, enabling researchers to draw parallels between Neptune and other celestial bodies in our solar system and beyond.
In summary, Neptune’s eccentric nature extends beyond its magnificent color and captivating storms. With a day duration of just 16 hours, Neptune offers a realm of possibilities for scientists to study the mechanisms behind its complex atmospheric dynamics. Unraveling the mysteries of this distant planet paves the way for a deeper comprehension of our universe and the diversity it holds.
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

