On average 90 per cent of people that have the disease lupus are female
On average, 90 per cent of people that have the disease Lupus are female.
Lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease, affects millions of people worldwide. One notable fact about this condition is that it predominantly affects females. On average, 90 per cent of individuals diagnosed with Lupus are women1^. This gender disparity raises intriguing questions about the underlying causes and potential genetic factors contributing to this phenomenon.
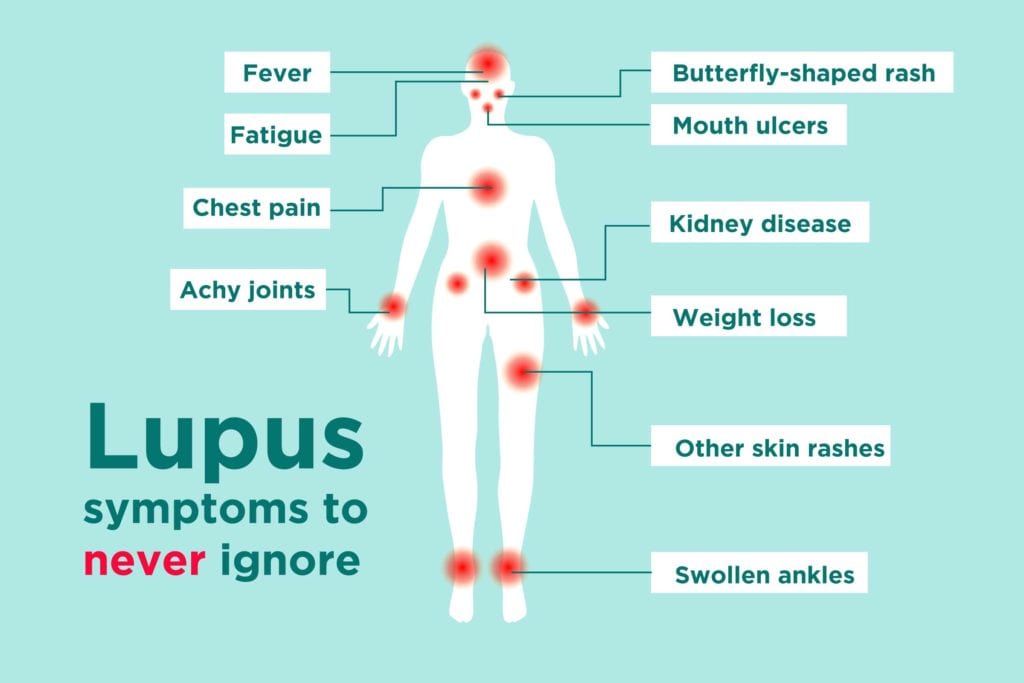
Lupus affects various parts of the body, leading to a range of symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and organ inflammation. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, resulting in chronic inflammation. While the exact cause of Lupus remains unknown, research suggests that it may be triggered by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.

The reason behind the significantly higher prevalence of Lupus among females is not entirely understood. Some studies indicate that hormonal differences, particularly estrogen and other female hormones, may play a role. Estrogen is known to modulate the immune response and may contribute to the increased susceptibility to autoimmune diseases in women. Additionally, certain genetic factors may also influence the likelihood of developing Lupus, with several genes linked to immune system function being more commonly found in females.
It is important to note that while Lupus predominantly affects women, it can still occur in men. However, the incidence rate among males is considerably lower. It is estimated that only around 10 per cent of Lupus cases occur in men1^. This stark difference underscores the need for further research to unravel the genetic and hormonal complexities behind this gender disparity.
The impact of Lupus extends beyond its physical symptoms. It often poses significant challenges for individuals living with the disease, affecting their quality of life and overall well-being. Raising awareness about Lupus, its symptoms, and the gender differences in its prevalence is crucial in promoting early detection and targeted support for those affected.
In conclusion, Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease that primarily affects women, with up to 90 per cent of cases occurring in females1^. While the reasons for this gender disparity are not fully understood, hormonal and genetic factors are believed to contribute to the increased prevalence of Lupus among women. Continued research and awareness are essential in improving diagnosis, treatment, and support for individuals living with this lifelong condition.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

