Meteoroids are objects in space ranging from dust grains to asteroids when meteroids enter a planet s atmosphere and burn like fireballs they re called meteors if the meteoroid stays intact and hits the planet s surface it s called a meteorite
Meteoroids, Meteors, and Meteorites: Exploring the Celestial Phenomena

Meteoroids, often seen as mysterious objects, exist in the vast expanse of space. Ranging from tiny dust grains to substantial asteroids, these celestial bodies capture our imagination as they travel through the cosmos. It is when these meteoroids enter a planet’s atmosphere that they ignite in a breathtaking spectacle, transforming into mesmerizing fireballs known as meteors. However, not all meteors meet a fiery demise. Some resilient meteoroids manage to endure the scorching entry and strike the surface of our planet, earning the name meteorite.
To understand meteoroids, meteors, and meteorites better, let’s delve into the intriguing journey these space travelers embark upon. Meteoroids begin their voyage in the depths of space, originating from various sources such as comets, asteroids, and even the Moon or Mars. They can be as minuscule as a grain of sand or as large as a towering asteroid. Traveling at incredibly high speeds, often exceeding 25,000 miles per hour, they wander aimlessly until they encounter a planet in their path.
When the meteoroids cross paths with a planet like Earth, they venture into its atmosphere. The intense air friction as they hurtle through the atmosphere causes the meteoroids to heat up and create a dazzling light display. These luminous streaks, commonly observed by humans, are known as meteors or shooting stars. The term “meteor” is derived from the Greek word “meteoron,” which means “high in the air.”

For many, witnessing a meteor shower is an awe-inspiring experience. Meteor showers occur when Earth’s orbit intersects with the debris left behind by comets or asteroids, resulting in an elevated number of meteors visible in the night sky. These meteor showers are named after the constellation from which they appear to originate, such as the famous Perseids or Leonids.
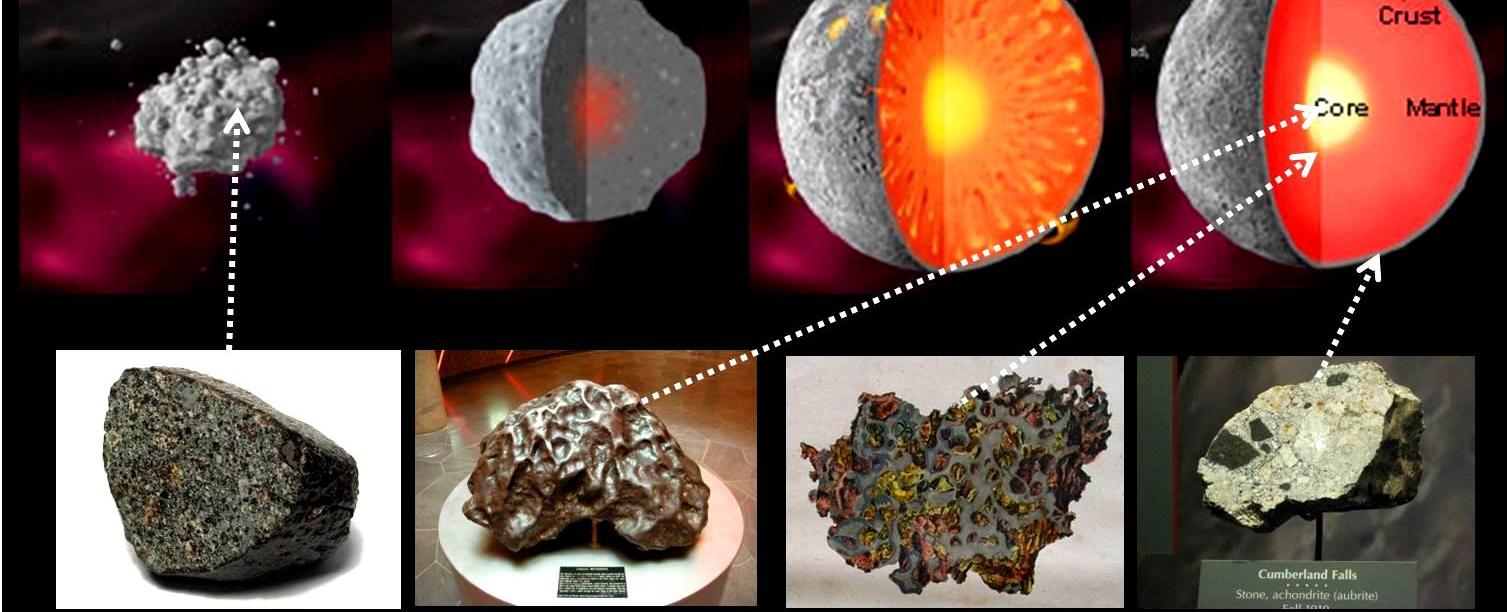
However, not all meteors burn up entirely during their fiery descent. More robust meteoroids manage to withstand the extreme heat and pressure, eventually reaching the planet’s surface. These survivors earn the esteemed title of meteorite. These fragments of other celestial bodies offer valuable insight into the composition and history of our solar system. Scientists eagerly analyze and study meteorites, as they often contain precious information about the formation and evolution of planets, including our own.
Meteorites come in three main types, each with unique characteristics: iron, stony-iron, and stony meteorites. Iron meteorites primarily consist of iron and nickel, often revealing a metallic appearance. Stony-iron meteorites, as the name implies, are a combination of rocky and metallic materials. Lastly, stony meteorites predominantly comprise rocky materials and can be further categorized into different subtypes based on their composition and structure.
The study of meteorites, known as meteoritics, helps scientists unravel the mysteries of our solar system and contributes to our understanding of the origins of life on Earth. By examining these extraterrestrial visitors, researchers gain valuable insights into the geological processes shaping our planet and others in the universe.
As we gaze up at the night sky, let us remember that the mesmerizing lights of meteors are fleeting reminders of the vastness and wonder of the cosmos. The next time you spot a shooting star, take a moment to appreciate the incredible journey of a meteoroid, the fiery transformation into a meteor, and the rare survival as a meteorite—a relic from beyond our world.
Source: NASA
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

