Mars has the solar system s biggest volcano
Mars has the solar system’s biggest volcano.
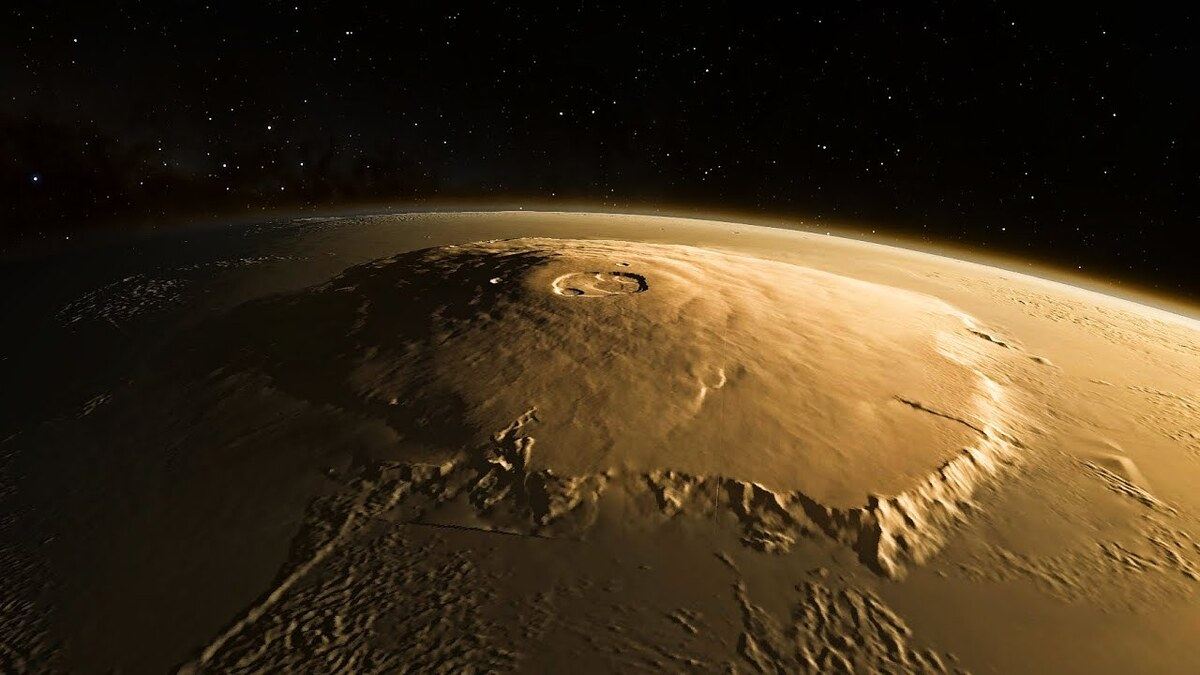


Mars, often referred to as the “Red Planet,” has long captured the fascination of scientists and astronomers alike. With its barren landscapes and intriguing features, Mars continues to unveil its secrets with ongoing research and exploration missions. One of the most remarkable wonders of Mars is its colossal volcano, known as Olympus Mons. With its stunning size and remarkable attributes, Olympus Mons stands as the largest volcano in the entire solar system.
Olympus Mons, a Latin name meaning “Mount Olympus,” is a shield volcano that extends its broad slopes over a staggering 370 miles (600 kilometers) in diameter. It reaches a height of approximately 13.6 miles (22 kilometers), making it nearly three times taller than Mount Everest, the highest peak on Earth. The sheer magnitude of Olympus Mons makes it a unique geological feature, dwarfing any other volcano on Mars or any other planet in the solar system.
This massive shield volcano is located in the Tharsis Montes region on Mars, positioned near the planet’s equator. The volcanic construction of Olympus Mons is distinct from that of Earth’s volcanoes, mainly due to the absence of tectonic plate boundaries on Mars. As a result, the volcano’s magma chamber remains stationary beneath the surface, allowing for the consistent and continuous eruption of lava. These eruptions produce thin, fluid lava flows that extend over great distances and create the flat, shield-like shape characteristic of shield volcanoes.
Olympus Mons holds another record in its favor; it also boasts the longest known volcanic lava flows in the solar system. These immense lava flows cover an area of around 99,000 square miles (256,000 square kilometers), approximately equivalent to the size of the state of Arizona. The colossal scale of Olympus Mons’ lava flows illustrates the immense volcanic activity that has taken place on the Red Planet over its geological history.
The geological formation of Olympus Mons can be attributed to the unique characteristics of Mars. Its lower gravity, roughly one-third of Earth’s gravity, allows for greater stress on the Martian crust, resulting in more prominent volcanic activity. Additionally, the absence of plate tectonics prevents the movement and recycling of crustal material, enabling the continual growth and expansion of the shield volcano over time.
As scientists continue to explore Mars, the study of Olympus Mons provides valuable insights into the geological makeup and volcanic processes of the Red Planet. Through detailed examinations of the volcano’s structure and composition, researchers hope to unravel the mysteries surrounding its formation and the potential implications for Mars’ geological and atmospheric history.
In conclusion, Olympus Mons stands as a testament to the intriguing geology of Mars. Its colossal size, impressive lava flows, and unique formation make it the largest volcano in the solar system. As ongoing missions unlock more knowledge about the Red Planet, the exploration of Olympus Mons promises to unravel further secrets about the fascinating world beyond our own.
Source: Wikipedia - Olympus Mons.
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

