Lungs are the only human organ that can float
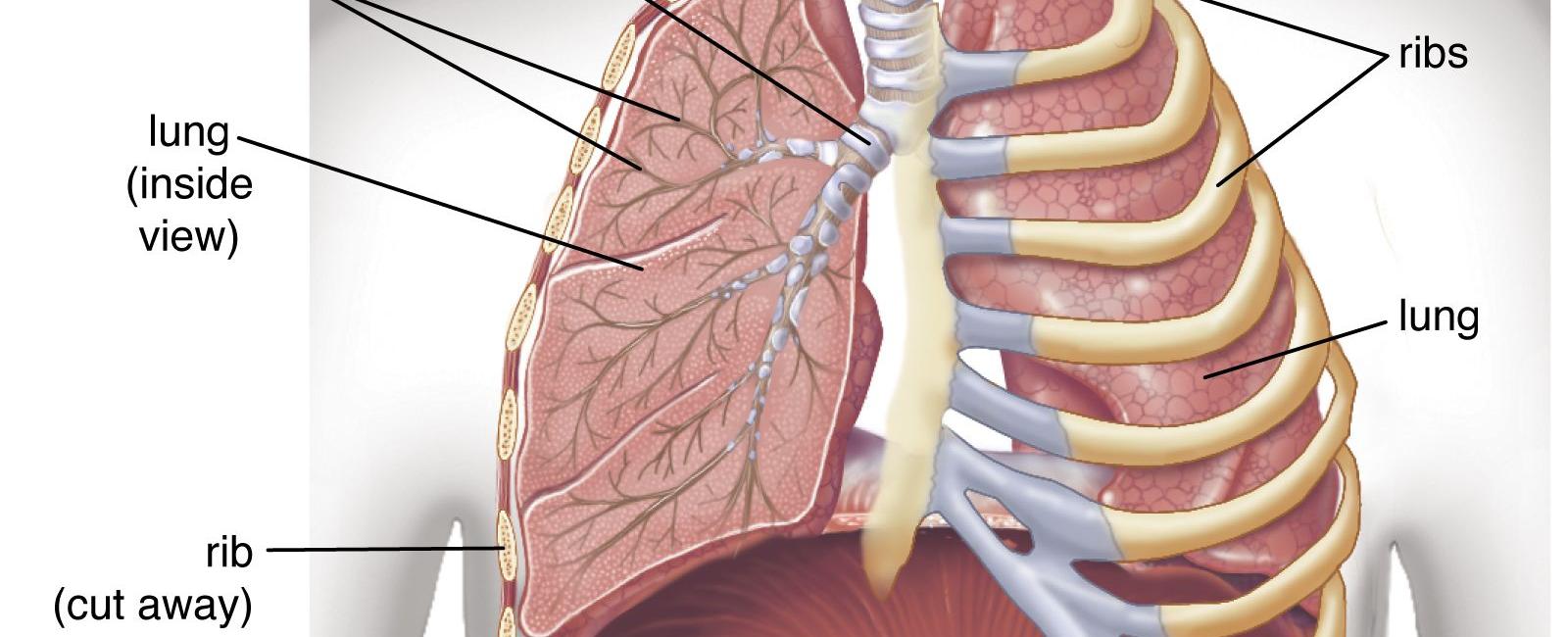
Lungs are the only human organ that can float.

Are you aware that lungs have the fascinating ability to float? It’s a unique characteristic that sets them apart from all the other organs in our body. In this article, we’ll delve into the intriguing world of lungs, uncovering the reasons behind their buoyancy.
Firstly, it’s important to understand the structure of our lungs. They are spongy and elastic organs, divided into lobes and composed of thousands of tiny air sacs called alveoli. These alveoli are primarily responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during respiration.
But what makes lungs float? The answer lies in their composition. Lungs are mostly made up of air and contain a small amount of liquid, which creates a lower density compared to other organs. This lower density allows them to float when placed in a liquid medium, such as water.
Moreover, the human body contains natural oils and fats that act as a protective layer around the lungs. These oils and fats contribute to the buoyancy of the lungs, enabling them to stay afloat. It’s like having built-in life jackets for our precious respiratory organs.
The ability of lungs to float has several implications. For example, during medical procedures such as lung transplant surgeries, the buoyancy of lungs plays a crucial role. It allows surgeons to accurately assess lung function and position while keeping the organ stable.
Apart from their floating capabilities, lungs fulfill vital functions in our body. They provide oxygen to our bloodstream and remove carbon dioxide, helping to maintain a healthy balance in our respiratory system. Without them, our survival would be impossible.
In conclusion, lungs are truly a marvel of nature. Their floating ability, unique among human organs, stems from their spongy and elastic composition, as well as the presence of oils and fats. The next time you marvel at the wonder of the human body, remember the extraordinary lungs that keep us breathing and floating. Sources: Bronchiectasis News Today.
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

