Jupiter is surrounded by waves of radiation
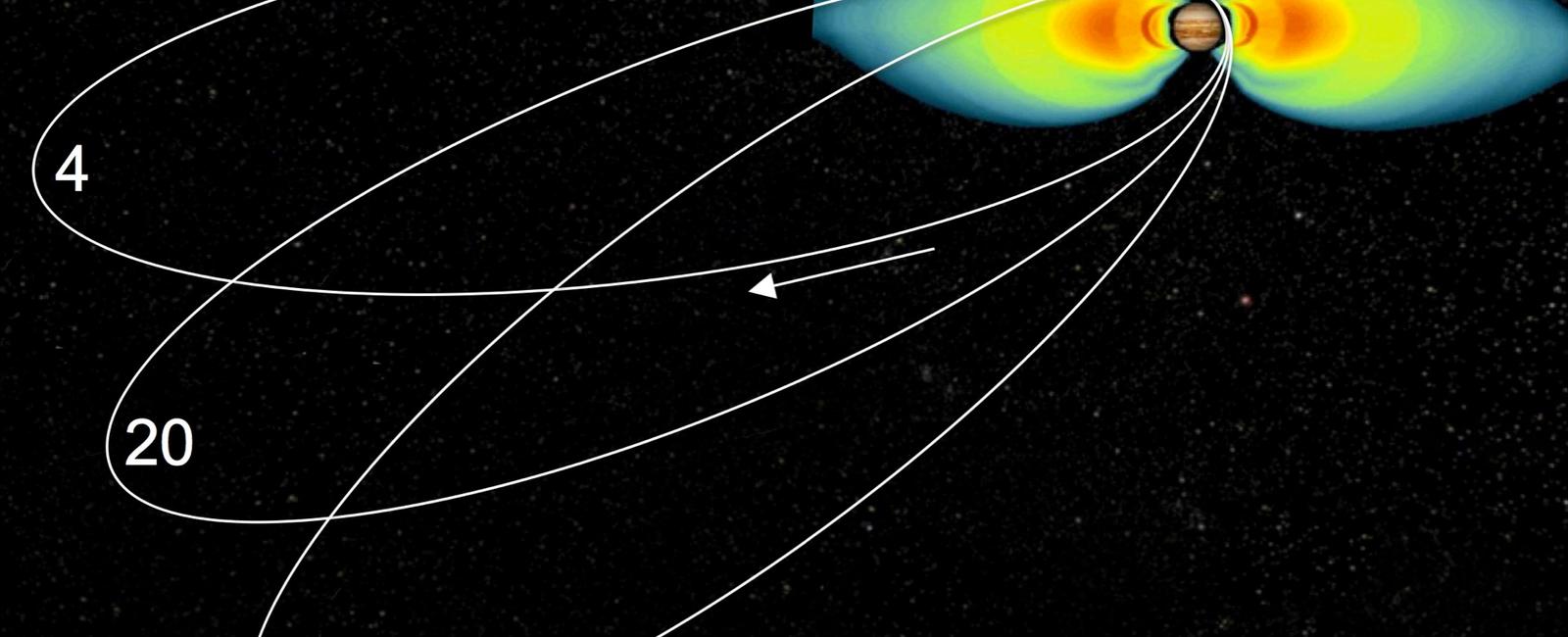
Jupiter is surrounded by waves of radiation.

Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, has always fascinated scientists and astronomers alike. One of the most intriguing aspects of this gas giant is the fact that it is surrounded by waves of radiation. These radiation waves, also known as the Van Allen belts, are a crucial element in understanding the planet’s unique characteristics and its role in the solar system.
The Van Allen belts are zones of charged particles that surround Jupiter, stretching for thousands of kilometers. Named after the scientist James Van Allen, who discovered them in 1955, these belts are similar to Earth’s Van Allen belts but significantly more intense. They consist of high-energy protons and electrons trapped by the planet’s magnetic field, creating a vibrant and dynamic environment around Jupiter.

Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field, the strongest of any planet in our solar system, plays a crucial role in generating and maintaining these radiation belts. This magnetic field is created by the planet’s immense metallic hydrogen core, and it extends far beyond the visible boundaries of Jupiter itself. As charged particles from the solar wind interact with this magnetic field, they become trapped in these belts, creating the waves of radiation that surround the planet.
These radiation waves are not only a unique astronomical phenomenon but also have significant implications for space exploration. Astronomers and scientists studying Jupiter and its moon Europa pay close attention to these belts, as they can have a profound impact on any spacecraft or probe passing through them. The charged particles in the radiation belts can damage sensitive electronics and interfere with communication systems. Understanding and navigating these belts is crucial for the success of any mission to Jupiter and its moons.
In addition to spacecraft considerations, the radiation belts around Jupiter provide valuable insights into the planet’s internal structure and its influence on the surrounding space environment. By studying the characteristics of these belts, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of Jupiter’s magnetic field, its composition, and the processes occurring within its atmosphere. This knowledge is valuable in deciphering the formation and evolution of not only Jupiter but also other gas giants in our universe.
With ongoing advancements in technology and space exploration, scientists are continuously uncovering new aspects of Jupiter’s radiation belts. The Juno spacecraft, launched in 2011, has been instrumental in capturing detailed images and measurements of these belts, further enhancing our knowledge of Jupiter’s magnetosphere. As our understanding improves, we can expect even more remarkable discoveries about this awe-inspiring planet and its waves of radiation.
In conclusion, Jupiter’s unique feature of being surrounded by waves of radiation, known as the Van Allen belts, fascinates astronomers and scientists worldwide. These belts, consisting of charged particles trapped by Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field, provide valuable insights into the planet’s characteristics and play a significant role in space exploration. By delving deeper into Jupiter’s radiation belts, scientists are unlocking the mysteries of this gas giant and expanding our knowledge of the vast universe we inhabit.
Source: The Nine Planets
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

