Humans use a total of 72 different muscles in speech
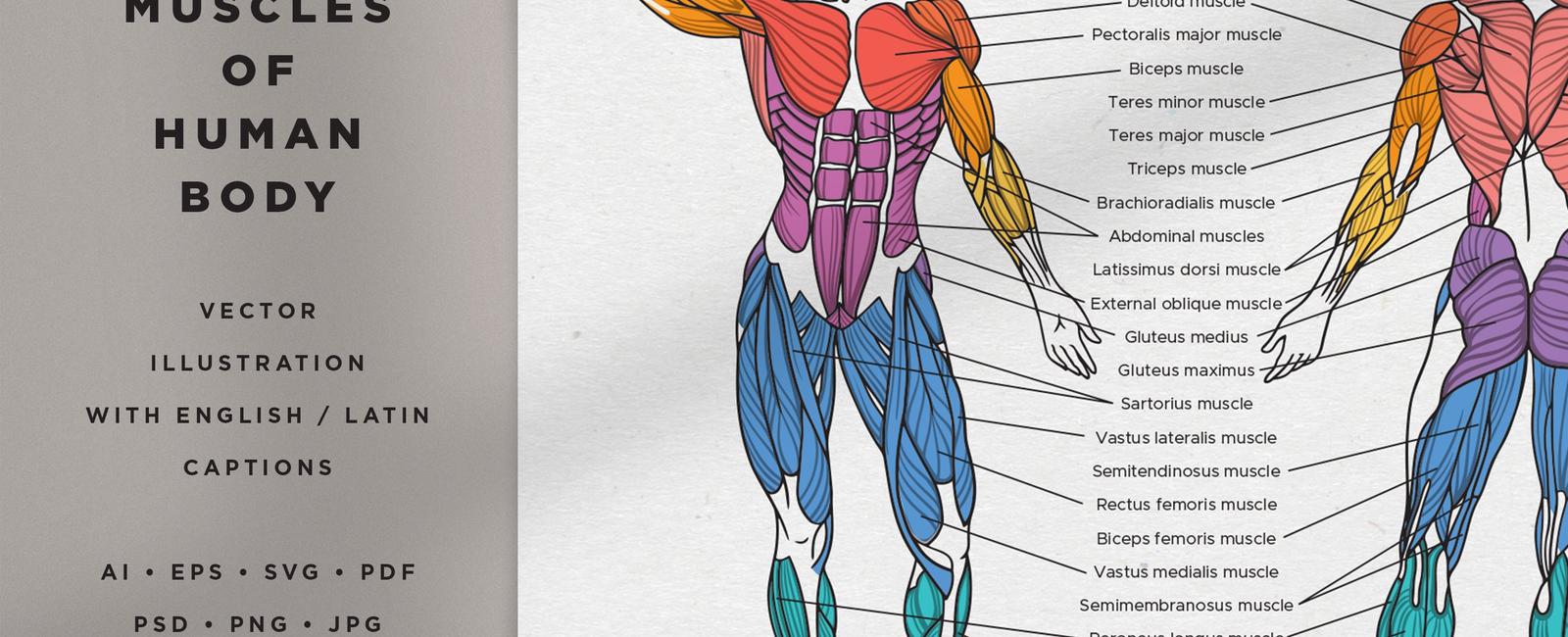
Humans use a total of 72 different muscles in speech.
When we speak, we rarely think about the intricate process that enables us to produce sounds and communicate with others. Behind the scenes, our bodies engage a complex network of muscles that work in harmony to generate speech. In fact, humans utilize a remarkable total of 72 muscles when we speak.
The muscles involved in speech production can be grouped into different categories. These categories include respiratory muscles, laryngeal muscles, articulatory muscles, and resonatory muscles. Each category performs specific functions, contributing to the production of a wide range of sounds and expressions.
Respiratory Muscles: Our respiratory system plays a crucial role in speech production. The primary respiratory muscles involved in speech are the diaphragm, intercostal muscles, and abdominal muscles. These muscles control the airflow and provide the necessary pressure for speech sounds to be created.
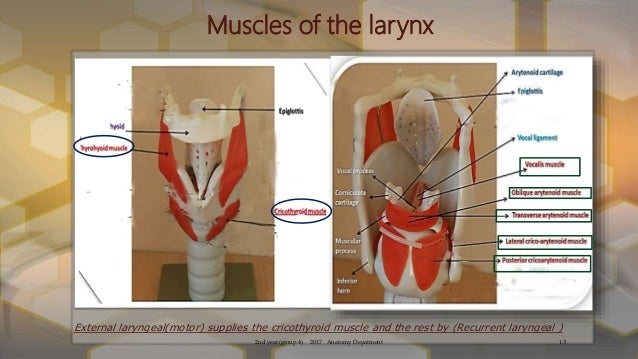
Laryngeal Muscles: The larynx, commonly known as the voice box, houses several muscles responsible for voice production. The vocal cords, or vocal folds, are stretched across the larynx and vibrate as air passes through, creating sound. Muscles in the larynx adjust the tension and position of the vocal cords to produce different pitches and tones.
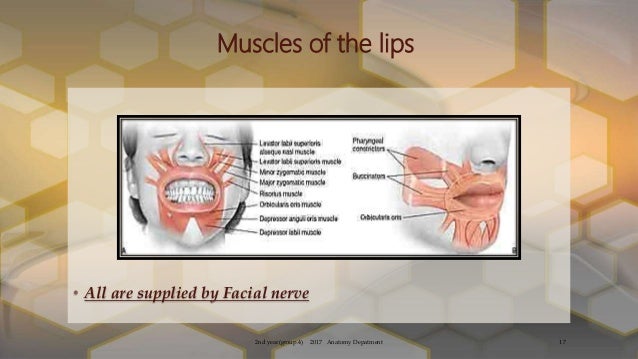
Articulatory Muscles: The articulatory muscles shape and mold the sounds produced by our vocal cords into recognizable speech. These muscles control our lips, tongue, jaw, and velum (the soft part at the back of the roof of the mouth). By manipulating the position and movement of these articulators, various consonant and vowel sounds are formed.
Resonatory Muscles: Resonance refers to the quality and timbre of our voice. The resonatory muscles, including the pharyngeal muscles and soft palate, modify the sound produced by the vocal cords by altering the size and shape of the vocal tract. They help us produce different speech sounds that give our voice its unique characteristics.
The coordination of these 72 muscles enables us to express our thoughts, emotions, and ideas through speech. It is fascinating to think about the intricate and seamless nature of this process, which occurs effortlessly for most individuals.
Understanding the complexity of the muscles involved in speech production sheds light on the importance of proper oral health and muscular coordination. Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking professional help when necessary can help support speech development and overall communication skills.
From a scientific perspective, researchers continue to study the nuances of these muscles to gain a deeper understanding of speech production and potential therapies for speech disorders. This knowledge has profound implications for individuals with speech difficulties, as interventions can be developed to target specific muscle groups and enhance speech capabilities.
In conclusion, the human body is equipped with a remarkable network of 72 muscles that collaborate in perfect synchrony to enable speech. The respiratory, laryngeal, articulatory, and resonatory muscles all play vital roles in speech production. Acknowledging and appreciating the complexity of these muscles can foster a greater understanding of speech and communication as a whole.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

