Humans are related to fungi
Humans are Related to Fungi


Did you know that humans are related to fungi? It may sound surprising, but it’s true! While fungi may seem like an entirely different form of life, they actually share a common ancestry with humans. This fascinating connection between our species has been a subject of scientific research and study.
Fungi, including mushrooms, yeasts, and molds, are classified in their own kingdom, separate from animals, plants, and bacteria. They have their own unique characteristics and play essential roles in various ecosystems. However, recent studies have unveiled the similarities between humans and fungi, highlighting the genetic and evolutionary connections we share.
One of the remarkable similarities between humans and fungi is the presence of chitin in our bodies. Chitin is a tough structural polysaccharide that is also found in the cell walls of fungi. In humans, chitin is found in the outer shells of insects and crustaceans, as well as in the lining of our respiratory tracts. This common trait suggests a shared evolutionary history between our two species.
Furthermore, humans and fungi both possess similar immune systems. Our immune systems are designed to defend our bodies against harmful pathogens and infections. Fungi, on the other hand, have evolved unique defense mechanisms to protect themselves from competing organisms. The similarities in our immune systems highlight the evolutionary links between humans and fungi and the ways we have adapted to survive in our respective environments.
Research has also revealed that humans and fungi share certain genes that have similar functions. For example, the HOX genes, which are involved in the development of body plans and structures, are found in both humans and fungi. This discovery suggests that these genes have been conserved throughout evolution and play vital roles in the development of complex organisms.
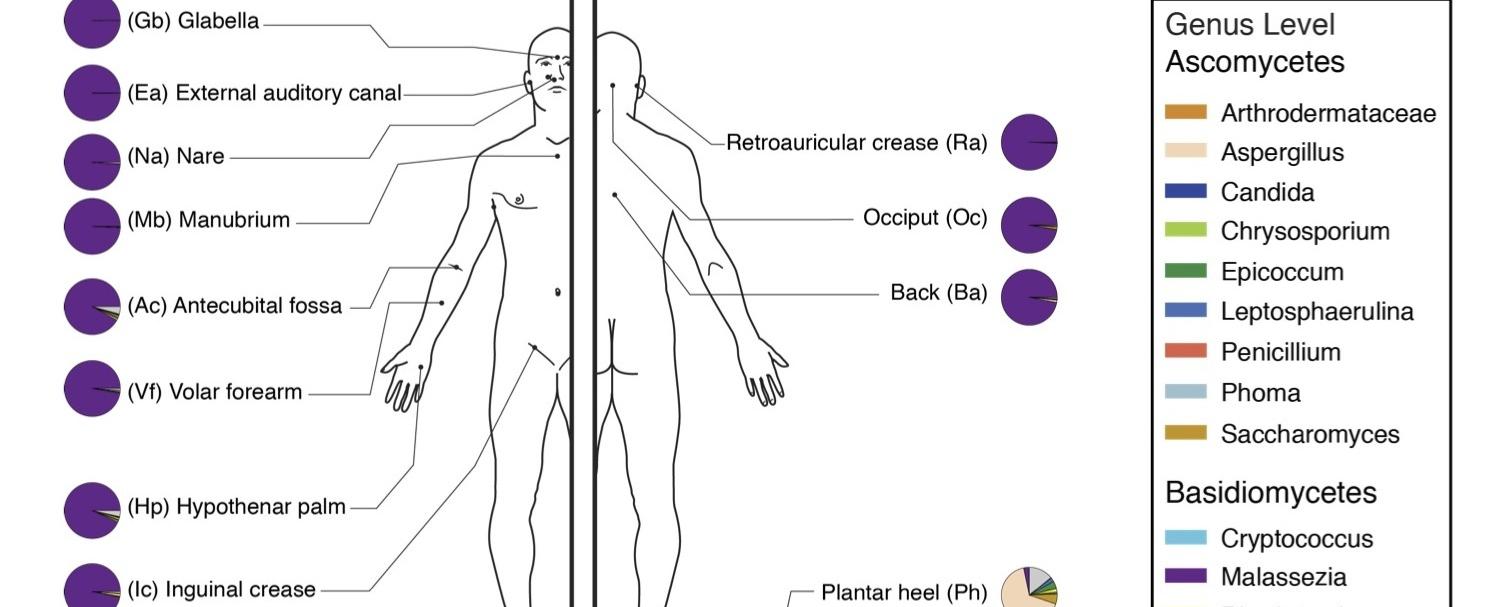
In addition to genetic similarities, there is evidence of a close relationship between humans and fungi at the microbiological level. Our bodies host a diverse community of microorganisms known as the human microbiome. This microbiome, which includes bacteria, viruses, and fungi, plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. Fungi are present in various parts of our bodies, such as the skin, mouth, and gut, where they may have beneficial or harmful effects depending on the species.
The complex interactions between humans and fungi go beyond our shared genetic and microbiological connections. Throughout history, humans have relied on fungi for various purposes. We have used mushrooms and yeasts in our diets, fermented foods and beverages, and even in the production of antibiotics. Fungi have also been used in industrial processes and biotechnology, contributing to numerous scientific advancements.
In conclusion, humans are indeed related to fungi, despite their apparent differences. Our shared genetic traits, immune system similarities, and microbiological connections provide insights into our evolutionary history and the complex interactions between our species. Understanding our relationship with fungi can lead to further scientific discoveries and advancements in various fields. So the next time you come across a mushroom or enjoy a slice of bread, remember the hidden connection between humans and fungi.
Source:
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

