Fingers don t have muscles they have tendons that are controlled by the muscles of the forearm
Fingers don’t have muscles, they have tendons that are controlled by the muscles of the forearm.

When it comes to the human hand, its intricate design never fails to amaze. The human hand is capable of performing various intricate tasks with precision, including writing, typing, playing musical instruments, and many others. But have you ever wondered how our fingers are able to move and perform such intricate tasks?
Contrary to popular belief, fingers don’t actually have muscles. Instead, they have tendons that are controlled by the muscles located in the forearm. This unique arrangement allows us to move our fingers effortlessly and perform a wide range of activities.
The tendons, which are fibrous tissues, are responsible for connecting muscles to bones. In the case of the fingers, the tendons stretch from the muscles of the forearm all the way to the fingertips. These tendons run through the palm of the hand, guided by a network of sheaths, which aid in their smooth movement.
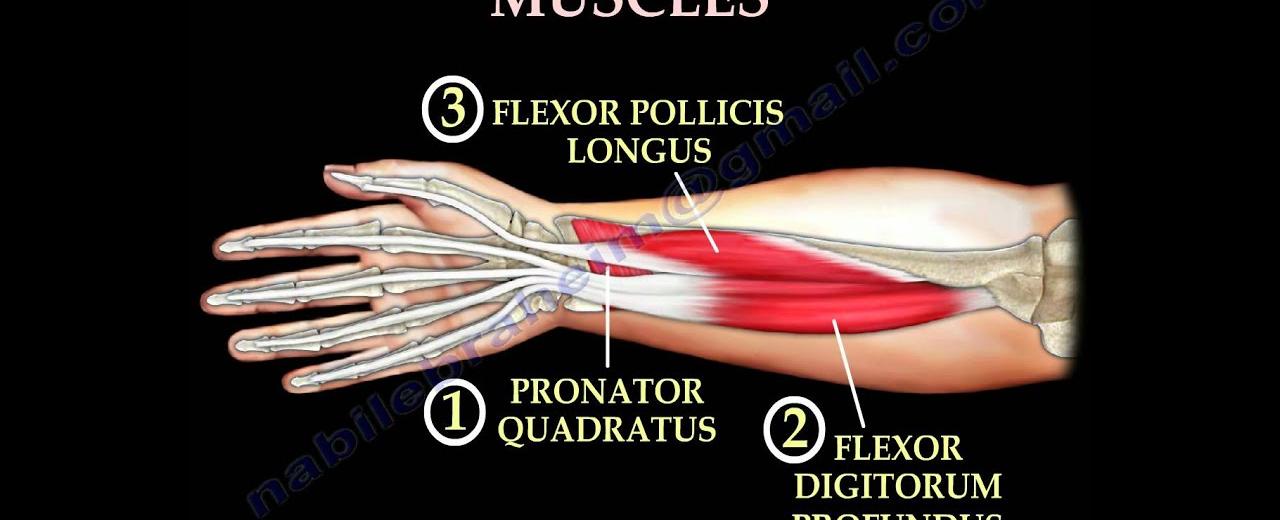
The muscles responsible for controlling the movement of the fingers are located in the forearm. There are two main groups of muscles in the forearm: the flexor muscles and the extensor muscles. The flexor muscles, as the name suggests, control the flexion or bending of the fingers, while the extensor muscles are responsible for their extension or straightening.

The flexor muscles are located on the palm side of the forearm and are connected to the tendons that control the bending of the fingers. When these muscles contract, they pull on the tendons, causing the fingers to curl.
On the other hand (pun intended), the extensor muscles are located on the backside of the forearm. These muscles control the extension of the fingers and are connected to the tendons that are responsible for straightening the fingers. When these muscles contract, they pull on the tendons, allowing the fingers to extend fully.
The coordination between these muscles and tendons is absolutely crucial for the dexterity of our hands. Without this well-balanced system, simple tasks such as typing on a keyboard or holding a pen would become extremely challenging or even impossible.
In conclusion, although fingers lack their own muscles, they are able to move and perform intricate tasks thanks to the tendons that are controlled by the muscles of the forearm. This fascinating arrangement showcases the incredible complexity and efficiency of the human body.
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

