Electric potential energy is measured in volts
Electric Potential Energy: Measured in Volts
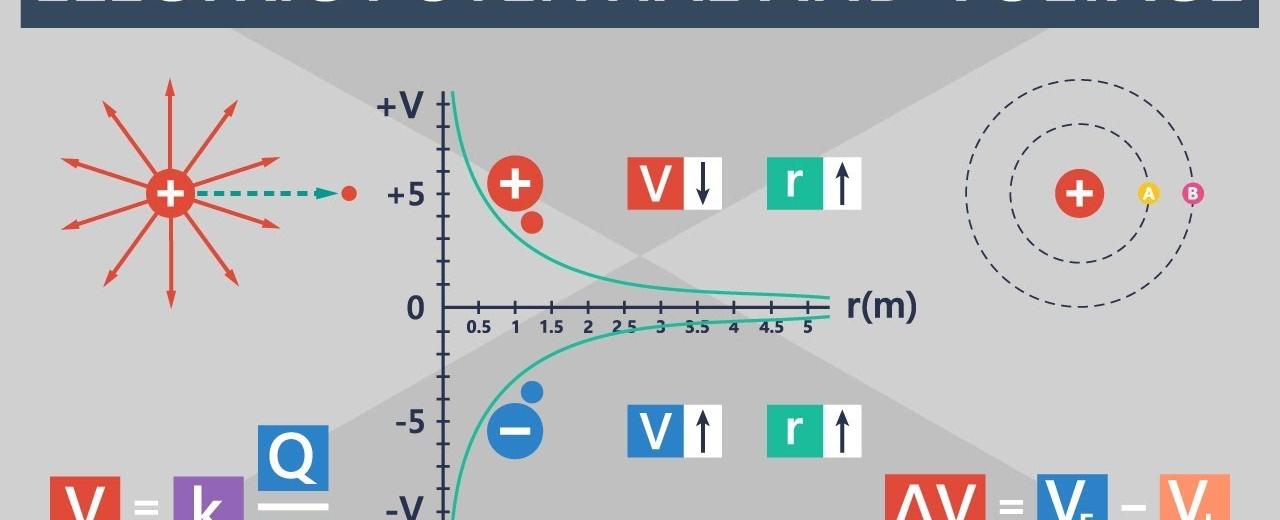
Electric potential energy is an essential concept in the field of physics and electrical engineering. It is a form of potential energy that results from the configuration and arrangement of charged particles within an electric field. Measured in volts, electric potential energy plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior and functioning of electrical systems.
Understanding Electric Potential Energy:
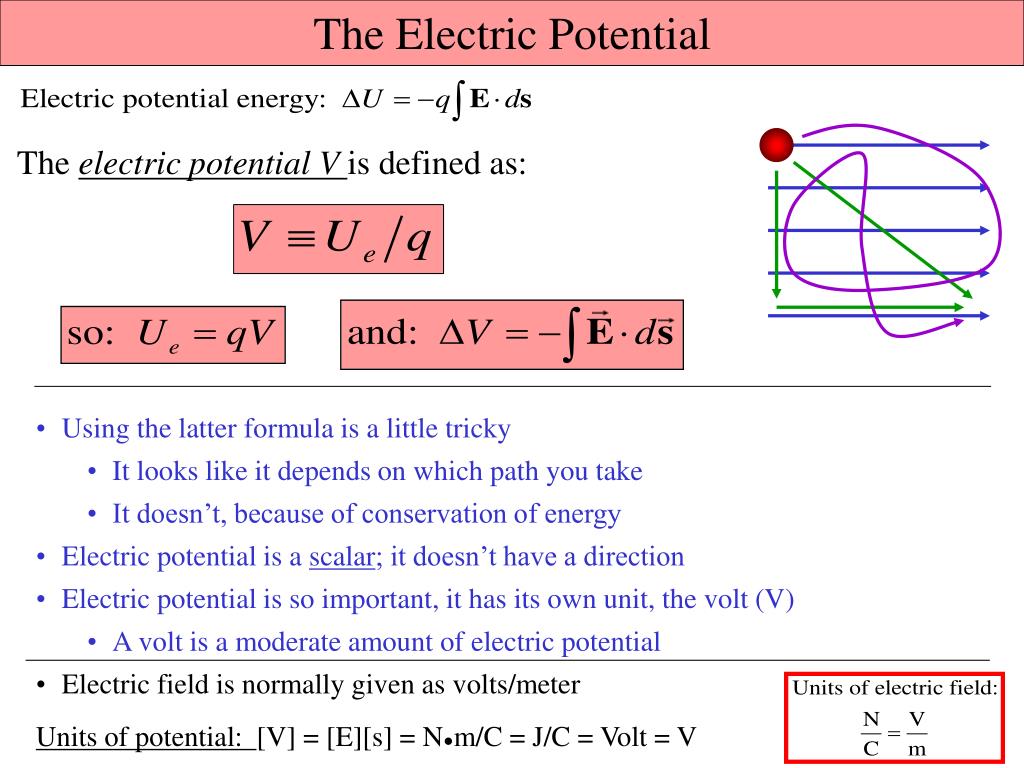
Electric potential energy refers to the capacity of an electric field to do work on a charged particle. It depends on the position of the charged particle within the electric field. The concept of electric potential energy arises from the fact that charged particles, such as electrons or protons, experience forces when placed in an electric field.
The electric potential energy of a charged particle is directly proportional to its charge and the electric potential difference, or voltage, experienced across the two points in the electric field. This potential difference, measured in volts (V), represents the amount of work required to move a unit charge from one point to another in an electric field.
The Role of Voltage:
Voltage, also known as electric potential difference, is a fundamental property used to quantify the strength of an electric field. It is represented by the symbol ‘V’ and measured in volts (V). Voltage is crucial in determining the electric potential energy of a charged particle. It represents the energy per unit charge available for a charge to do work.
In practical terms, voltage is often used to describe the difference in electric potential energy between two points in an electrical circuit. It determines the flow of electric current and is a crucial parameter in the design and analysis of electrical systems.
Relationship Between Electric Potential Energy and Voltage:
The relationship between electric potential energy and voltage can be understood using the analogy of a water reservoir. Just as the potential energy of water depends on its height above the ground, the electric potential energy of a charged particle depends on its position within the electric field.
The increase or decrease in voltage between two points in an electric field corresponds to a difference in electric potential energy. In other words, the voltage provides the driving force for the movement of charge, and the electric potential energy determines the work done by that charge.
Conclusion:
Electric potential energy, measured in volts, is a crucial concept in understanding the behavior of electric fields and electrical systems. It quantifies the capacity of an electric field to do work on charged particles. Voltage, representing the electric potential difference, plays a fundamental role in determining the potential energy of charged particles. By grasping this concept, one can gain a deeper understanding of the principles governing electricity and its various applications.

(Source: Introduction to Electric Potential Energy)
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

