Eight countries are within the arctic region russia canada the united states greenland norway iceland sweden and finland they form the intergovernmental arctic council
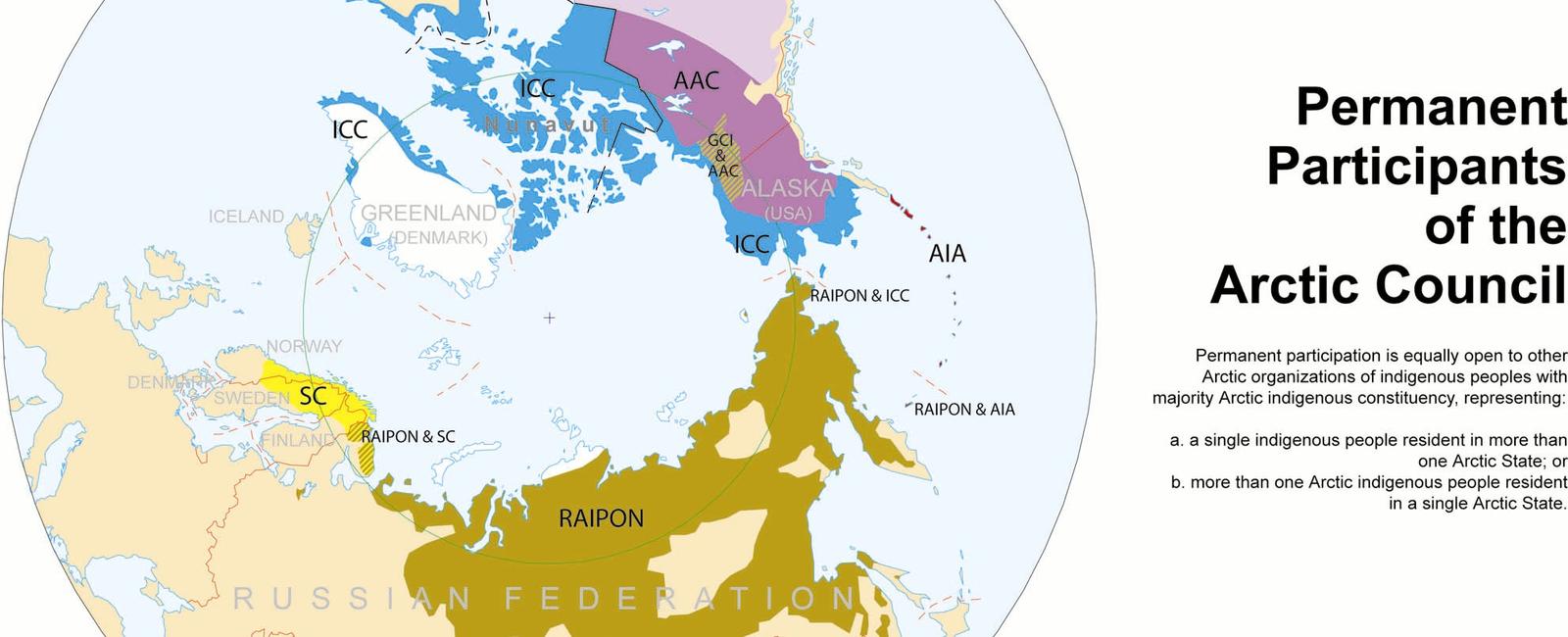
Eight countries are within the Arctic region: Russia, Canada, the United States, Greenland, Norway, Iceland, Sweden, and Finland. They form the intergovernmental Arctic Council.
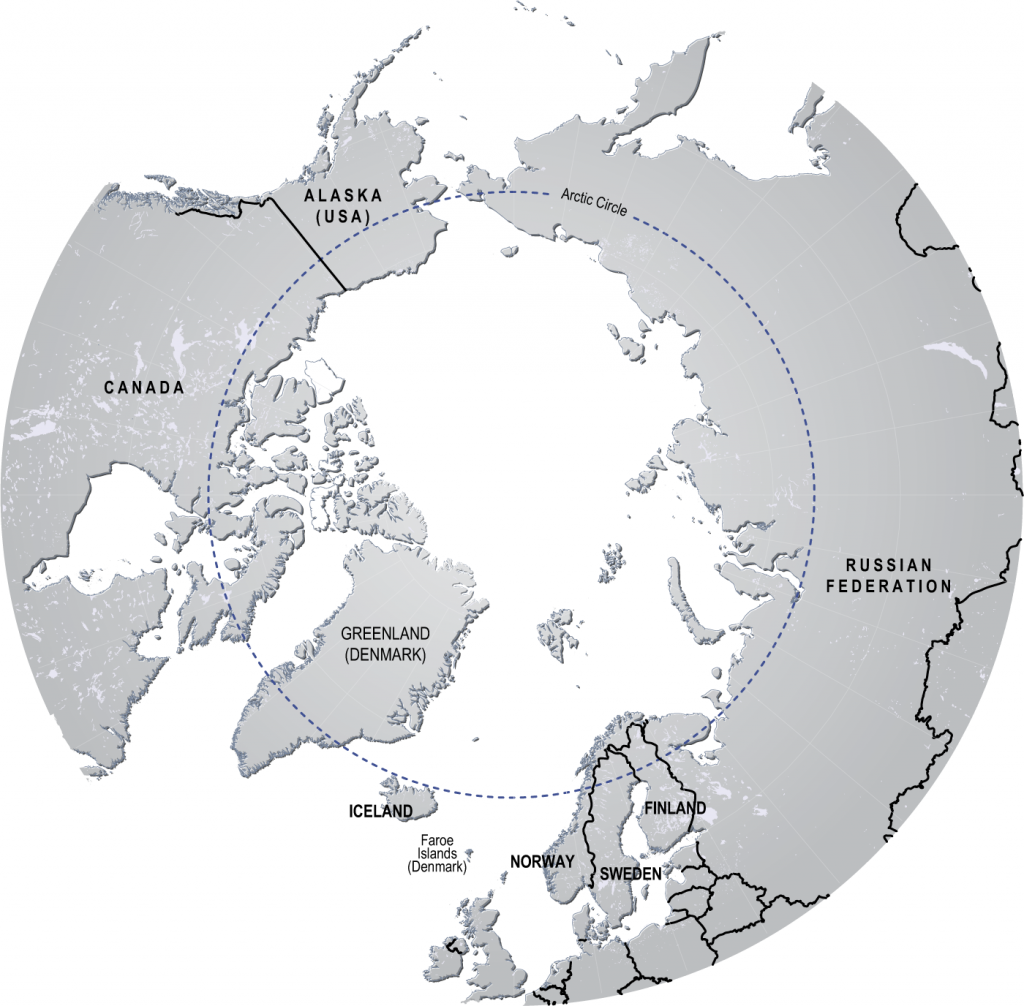
The Arctic region, also known as the “Great North,” encompasses the northernmost parts of our planet. It holds immense ecological significance, with its unique ecosystems and abundant natural resources. Eight countries, including Russia, Canada, the United States, Greenland, Norway, Iceland, Sweden, and Finland, have territorial claims within this pristine region.

These eight countries form the intergovernmental Arctic Council, an organization established to promote cooperation among them in addressing the challenges faced by the Arctic region. The council acts as a platform for member states to collaborate on issues such as environmental protection, sustainable development, and scientific research.
Russia, as the largest country in the world, occupies a significant portion of the Arctic region. It is known for its extensive exploration and exploitation of natural resources, particularly oil and gas.
Canada, another major Arctic country, boasts extensive coastlines along the Arctic Ocean. It is home to numerous indigenous communities that have a deep connection with the region’s ecosystems and resources.
The United States stretches its influence into the Arctic through the state of Alaska. Alaska’s vast landscapes, including glaciers and unique wildlife, contribute to the region’s overall diversity.
Greenland, an autonomous territory of Denmark, is the world’s largest island and is predominantly covered by ice. Its strategic location places it within the Arctic Circle, and it holds immense potential for mineral resources and tourism.
Norway is known for its strong focus on environmental protection and sustainable development in the Arctic. The country actively promotes research related to climate change and the effects on its Arctic ecosystems.
Iceland, despite not having land in the Arctic Circle, still has significant influence in the region due to its proximity and participation in Arctic affairs. It is renowned for its renewable energy sources and geothermal technologies.
Sweden and Finland complete the list of member states of the Arctic Council. While they do not have coastlines directly bordering the Arctic Ocean, they still possess territories within the Arctic Circle, contributing to the council’s collective efforts.
Through the Arctic Council, these eight countries collaborate to protect the environment, promote sustainable practices, and ensure the well-being of the indigenous communities living in the Arctic region. The council’s work includes research initiatives, policy-making, and monitoring the impact of climate change in the area.
In conclusion, the Arctic Council plays a vital role in ensuring the sustainable development and preservation of the Arctic region. Despite the challenges posed by climate change and competing interests, these countries come together to safeguard the unique ecosystems and resources found within the vast Arctic landscape.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

