Each year 48 million people get sick from a foodborne illness 128 000 are hospitalized and 3 000 die
Each year 48 million people get sick from a foodborne illness, 128,000 are hospitalized, and 3,000 die.
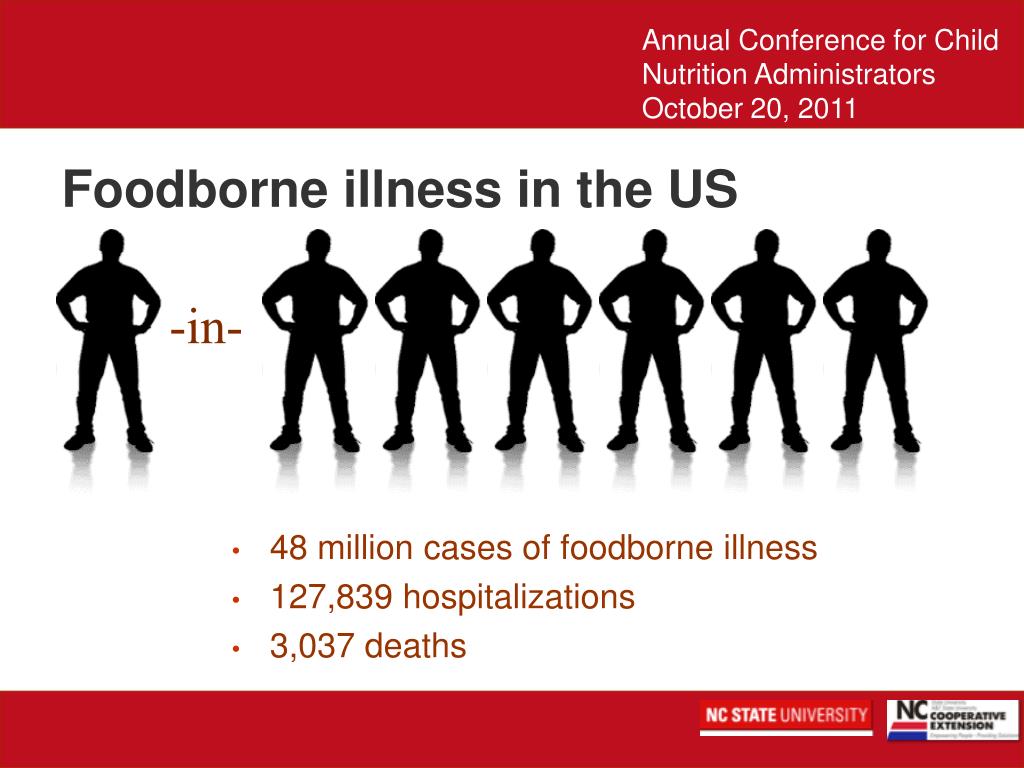
Food safety is a topic of increasing concern around the world. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), each year, a staggering 48 million people in the United States alone suffer from a foodborne illness. This alarming statistic demonstrates the need for greater awareness and measures to ensure food safety.
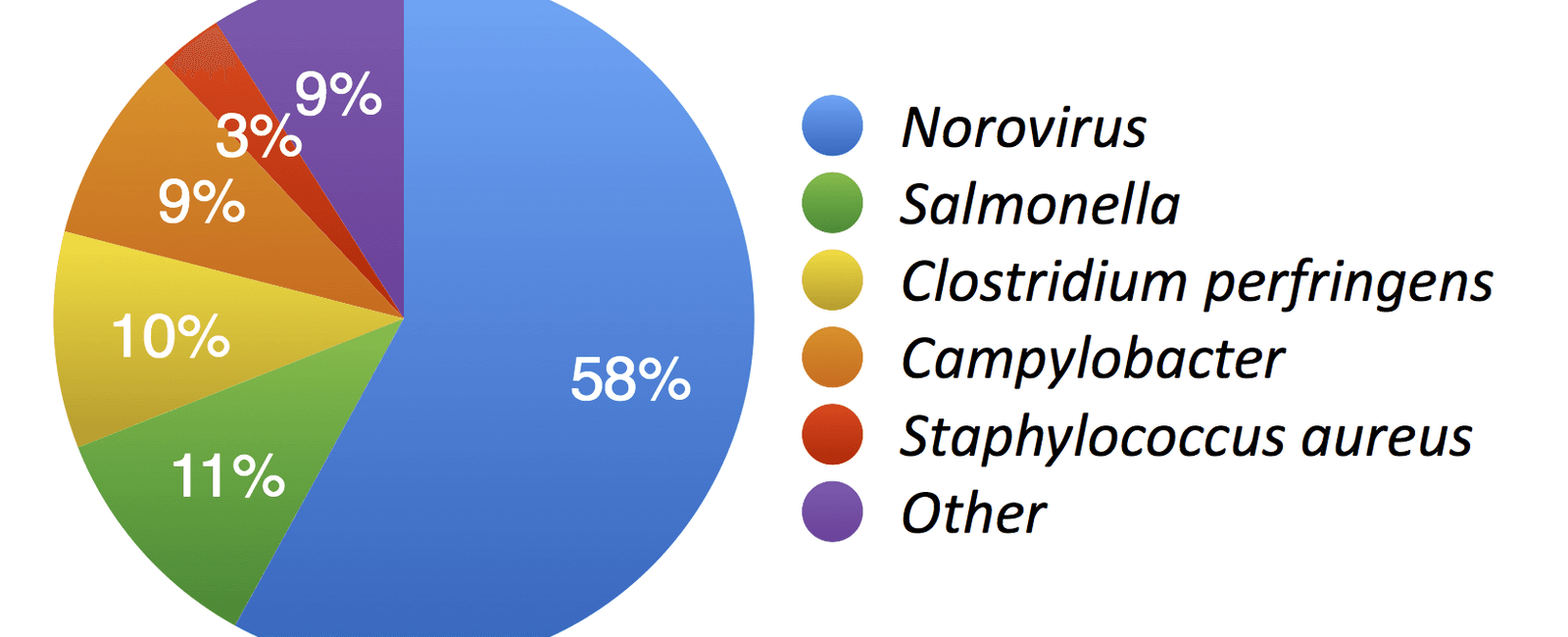
Foodborne illnesses are caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages. The CDC identifies several key pathogens responsible for these illnesses, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites. These harmful microorganisms can contaminate food at any stage—from production and processing to cooking and preparation.

Bacterial pathogens, such as Salmonella and E. coli, are among the most common culprits behind foodborne illnesses. These bacteria can be found in raw or undercooked meat, unpasteurized milk, and fresh produce contaminated with animal feces. Viral pathogens, like norovirus, can spread easily in contaminated water or food and are responsible for many cases of acute gastroenteritis. Parasites, such as Toxoplasma gondii and Cryptosporidium, are often associated with undercooked or contaminated meat, water, and produce.
Foodborne illnesses can range from mild to severe, and in some cases, they can be life-threatening. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and fatigue. While most cases resolve on their own within a few days, some individuals, particularly those with weakened immune systems, may require hospitalization. Tragically, approximately 3,000 people die each year in the United States due to foodborne illnesses.
To prevent foodborne illnesses, it is crucial to follow safe food handling practices. This includes thorough handwashing, proper sanitation of utensils and surfaces, separating raw and cooked foods, cooking foods to the appropriate temperature, and storing them at safe temperatures. Additionally, it is essential to consume pasteurized dairy products, wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, and avoid consuming raw or undercooked meat and eggs.
In conclusion, foodborne illnesses pose a significant public health problem, affecting millions of people each year. By understanding the causes of these illnesses and implementing stringent food safety measures, we can reduce the risk of contamination and protect the health and well-being of individuals and communities. To learn more about foodborne illnesses and how to prevent them, visit the CDC’s website on foodborne germs.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

