Crustaceans living in the deepest parts of the world s oceans contain toxic chemicals that were banned decades ago

Crustaceans in the Deepest Oceans Carry Toxic Chemicals Banned Decades Ago
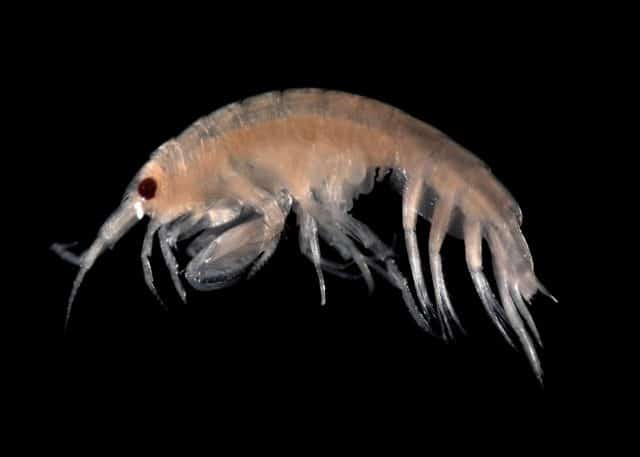

Did you know that the mysterious and unexplored depths of the world’s oceans house a hidden danger? Recent scientific research has revealed that crustaceans living in the deepest parts of the ocean contain toxic chemicals, which were banned decades ago. This alarming discovery raises questions about the long-term impacts of human activities and the potential consequences for marine life.
Crustaceans, which include species such as crabs, lobsters, and shrimp, play a crucial role in the marine ecosystem. They form an essential part of the food chain, providing sustenance for larger predators. However, due to their position in the food chain, they are also vulnerable to accumulating harmful substances.
In the 1960s and 1970s, numerous toxic chemicals, including polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), were widely used in industrial manufacturing, agriculture, and pest control. Unfortunately, these chemicals have persisted in the environment, and their toxic properties have led to their global ban.
However, despite being banned for several decades, these toxic chemicals have managed to infiltrate even the most remote parts of the world’s oceans. The deep-sea trenches, located thousands of meters below the surface, were thought to be safe from human pollution. Nevertheless, recent scientific expeditions have found evidence of toxic contamination in deep-sea crustaceans.
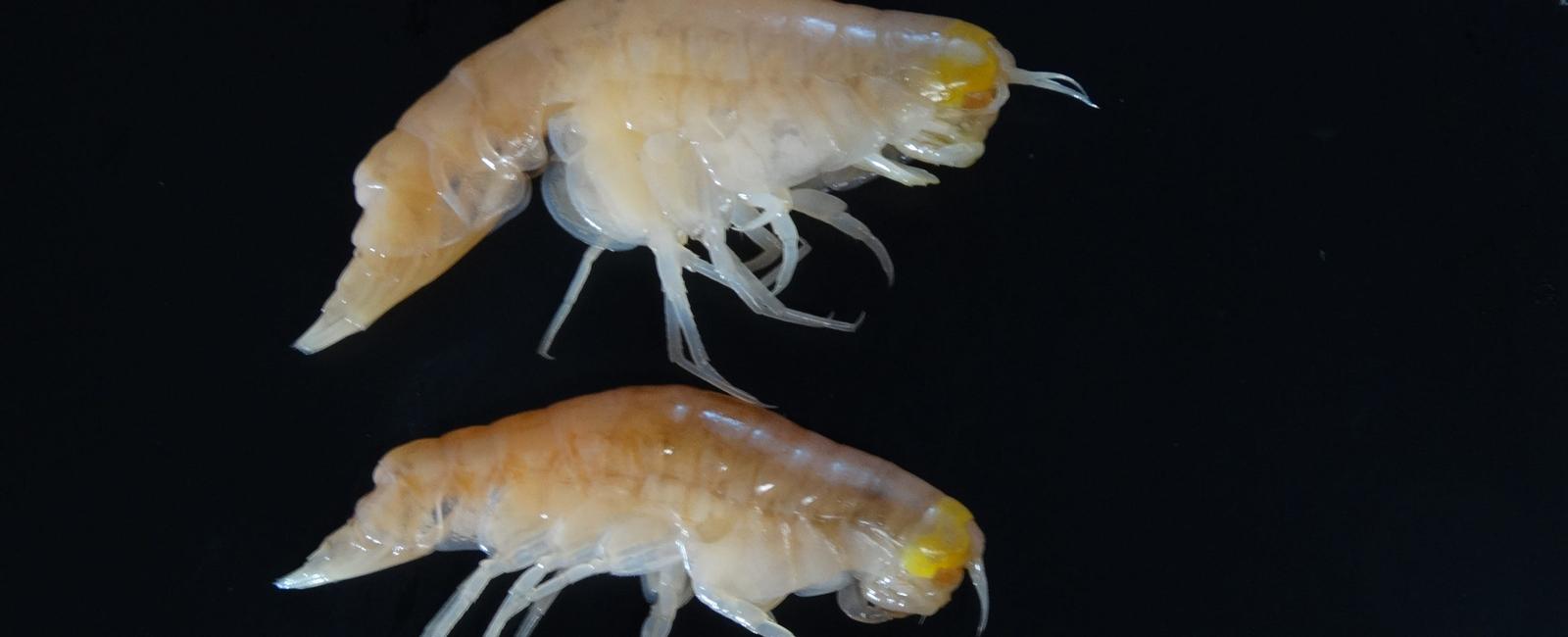
Scientists have been collecting samples of amphipods, a type of small shrimp-like crustacean, from the Mariana Trench in the western Pacific Ocean. Surprisingly, these samples, retrieved from depths exceeding 10,000 meters, contained worrying levels of toxic chemicals. PCBs were detected in all the samples, with concentrations up to 50 times higher than those found in shallower waters.
The accumulation of these toxic chemicals in the deepest parts of the ocean is concerning due to the potential implications for the entire marine ecosystem. Crustaceans are a vital food source for many species, including deep-sea fish and whales. As these predators consume contaminated crustaceans, they risk accumulating these toxic chemicals in their own bodies. This process, known as bioaccumulation, can have severe consequences for the health and survival of these species.
Furthermore, the presence of toxic chemicals in deep-sea crustaceans could also impact human health. Given the significant consumption of seafood worldwide, it is essential to understand the extent of contamination and its potential effects on human populations.
To address this issue, further research is urgently needed to explore the full extent of toxic contamination in deep-sea crustaceans and its implications for the marine ecosystem. Understanding the mechanisms of bioaccumulation and the fate of these toxic chemicals in the depths of the ocean is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate their impact.
In conclusion, the presence of toxic chemicals in crustaceans living in the deepest parts of the world’s oceans is a deeply concerning issue. The persistence of banned chemicals in these remote and inaccessible areas raises questions about the long-lasting impacts of human activities on the marine environment. Urgent action is required to better comprehend the extent of contamination and take measures to protect both the aquatic ecosystem and human health.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

